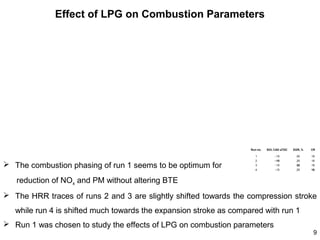
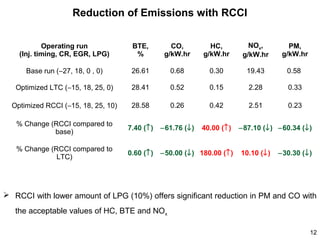
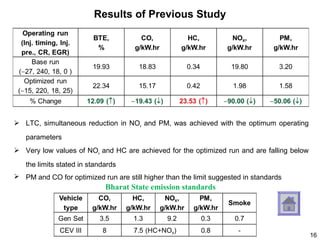
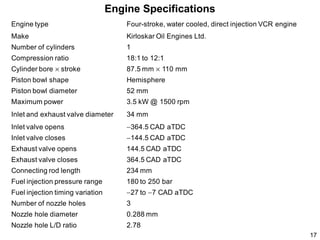
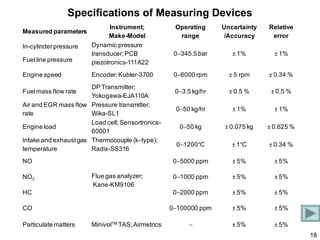
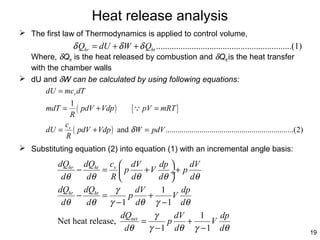
This document summarizes an experimental study on achieving Reactivity Controlled Compression Ignition (RCCI) in a diesel engine using liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to simultaneously reduce emissions and fuel consumption. Key findings include:
- Introducing LPG (10-40%) into the intake reduced particulate matter (PM) and nitric oxides (NOx) while increasing hydrocarbons (HC) and reducing brake thermal efficiency (BTE).
- Optimal RCCI was achieved with 10% LPG, significantly reducing PM and carbon monoxide (CO) within emission limits while maintaining acceptable HC, NOx, and BTE.
- RCCI combustion was characterized