Embed presentation
Download to read offline

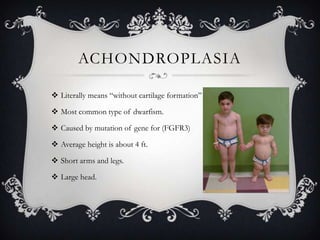






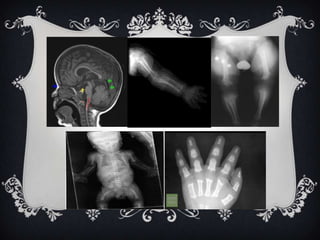

Achondroplasia is the most common type of dwarfism, caused by a mutation in the FGFR3 gene. It is characterized by an average height of 4 feet, with short arms and legs and a large head. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern and causes disproportionate skeletal growth with bowed legs and short stature.








