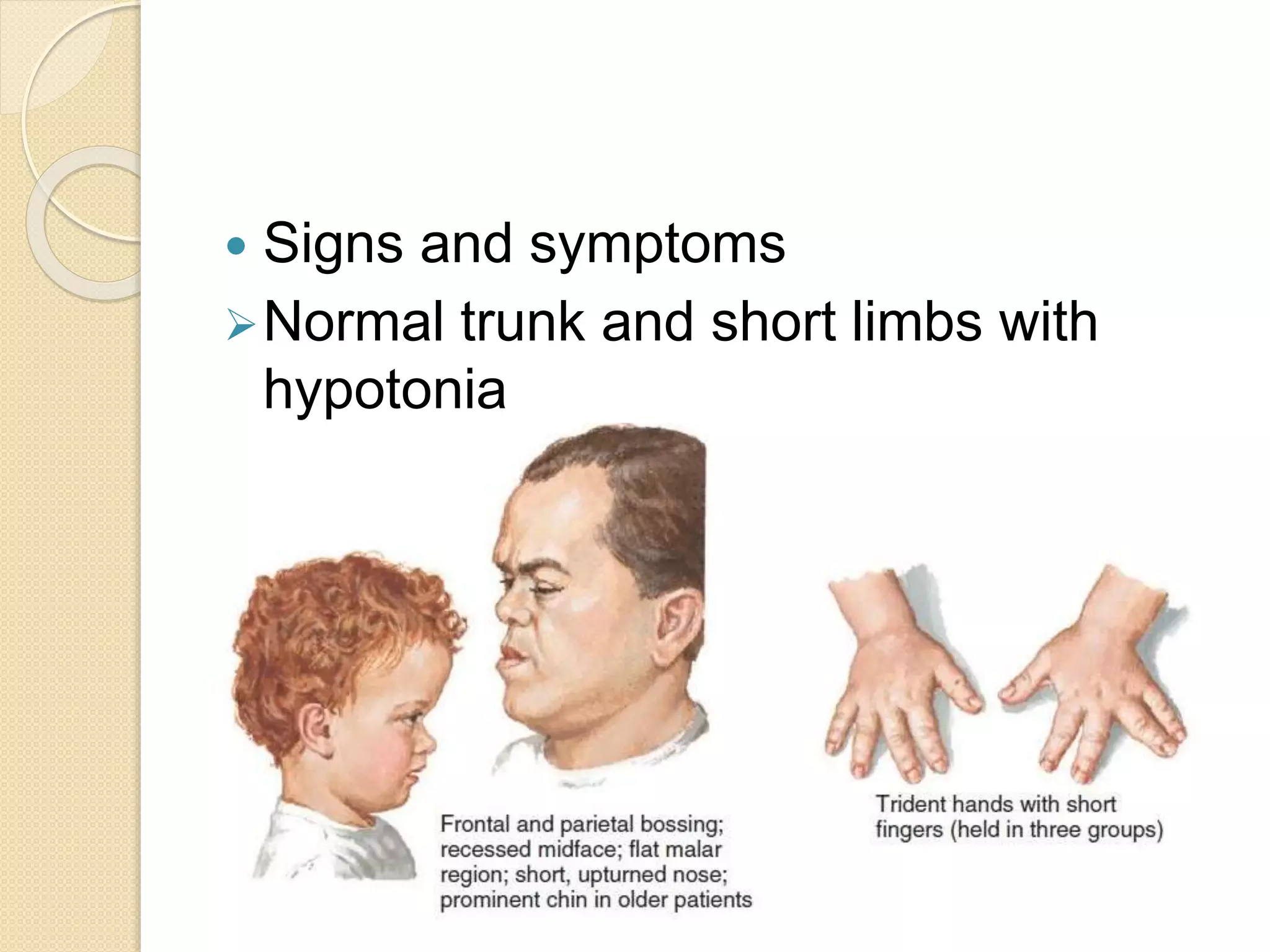
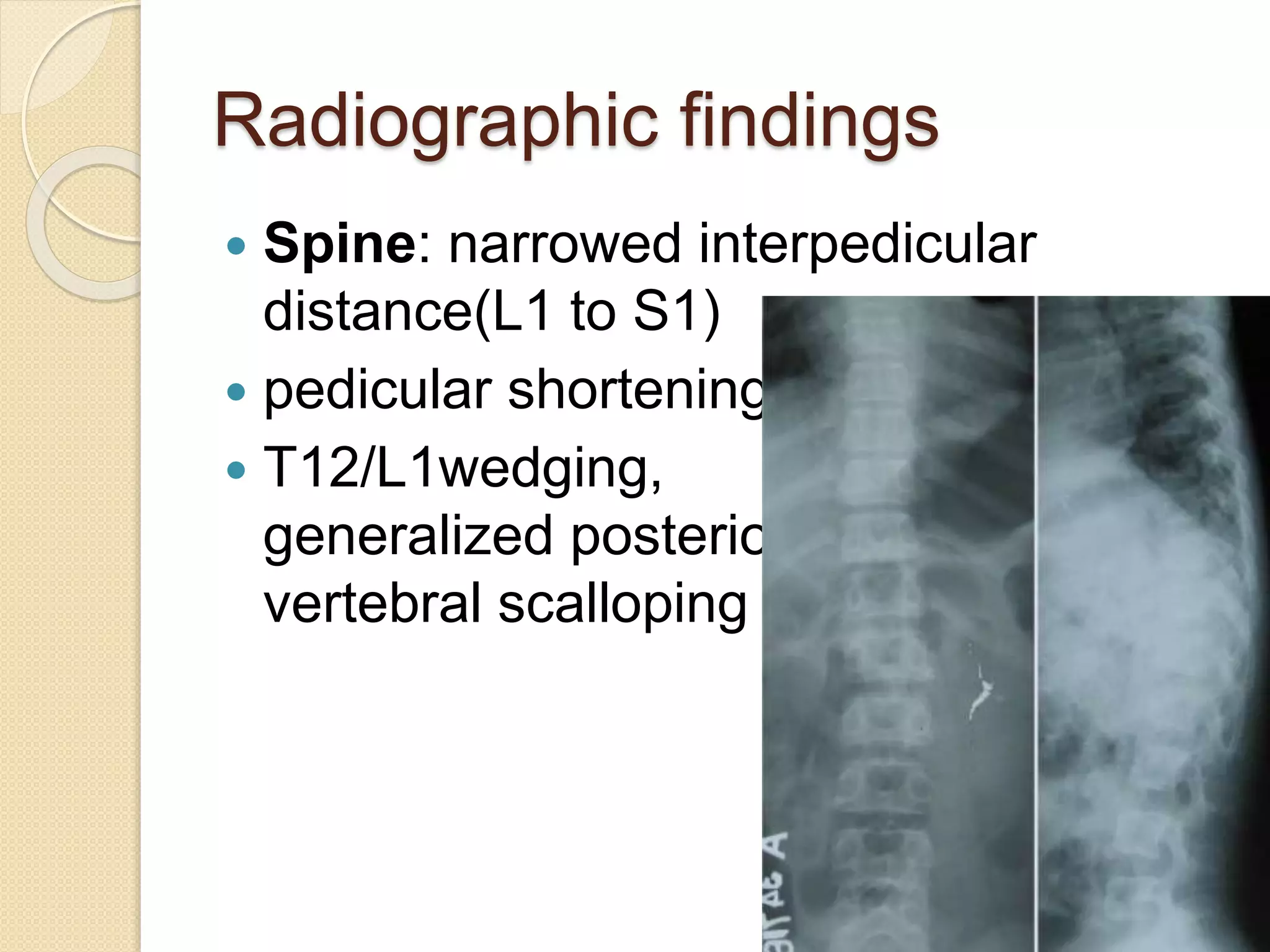
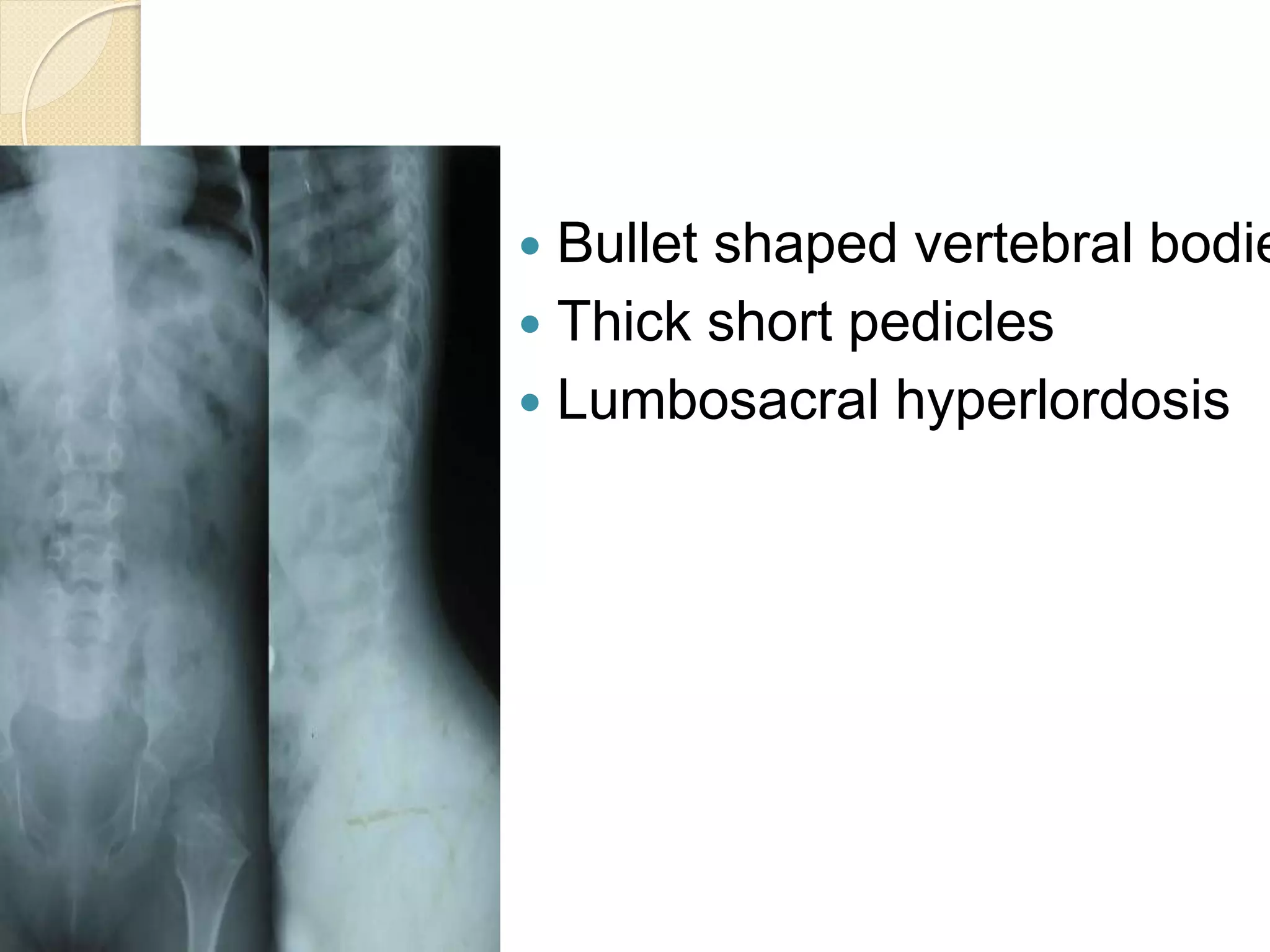
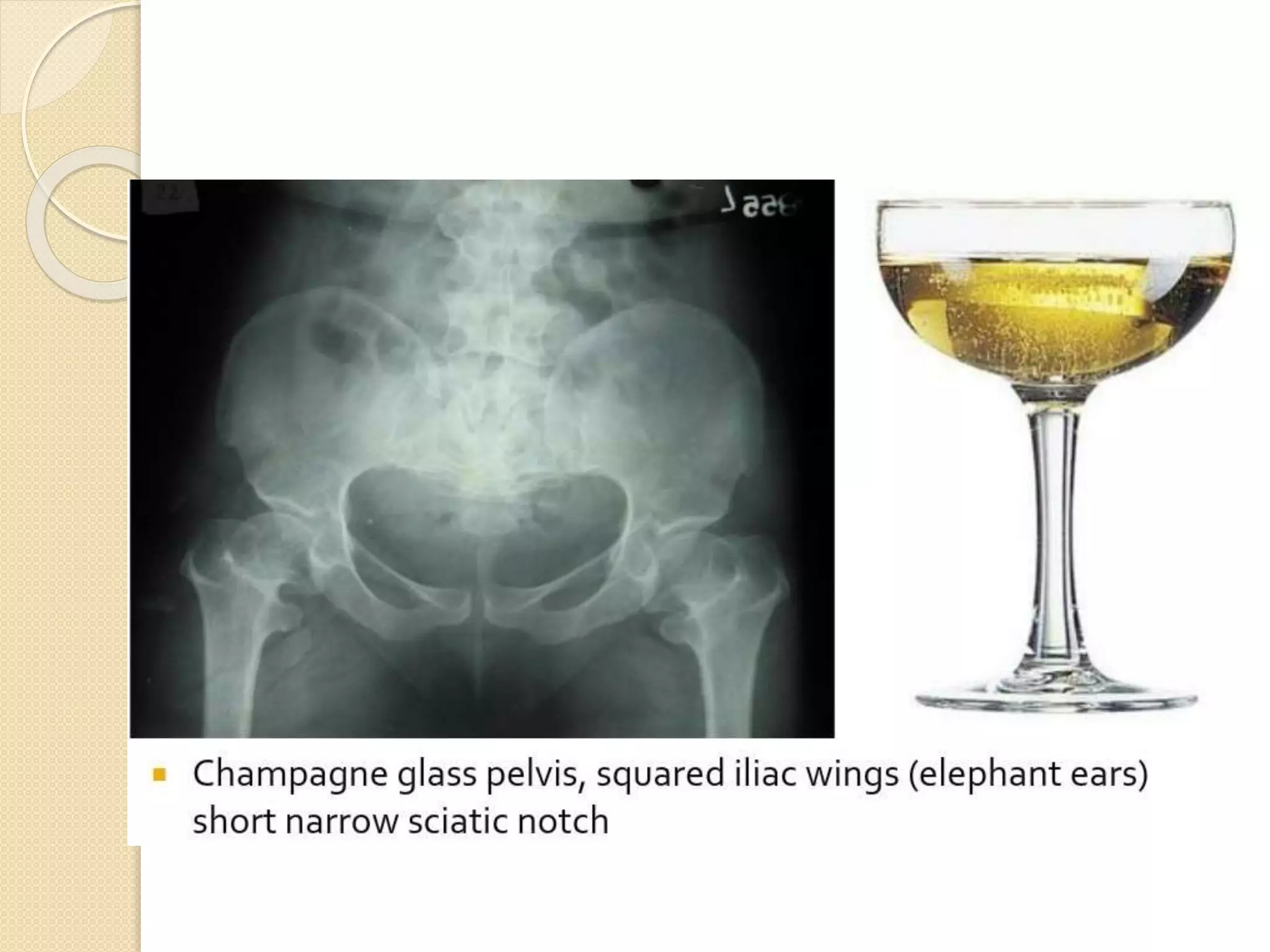
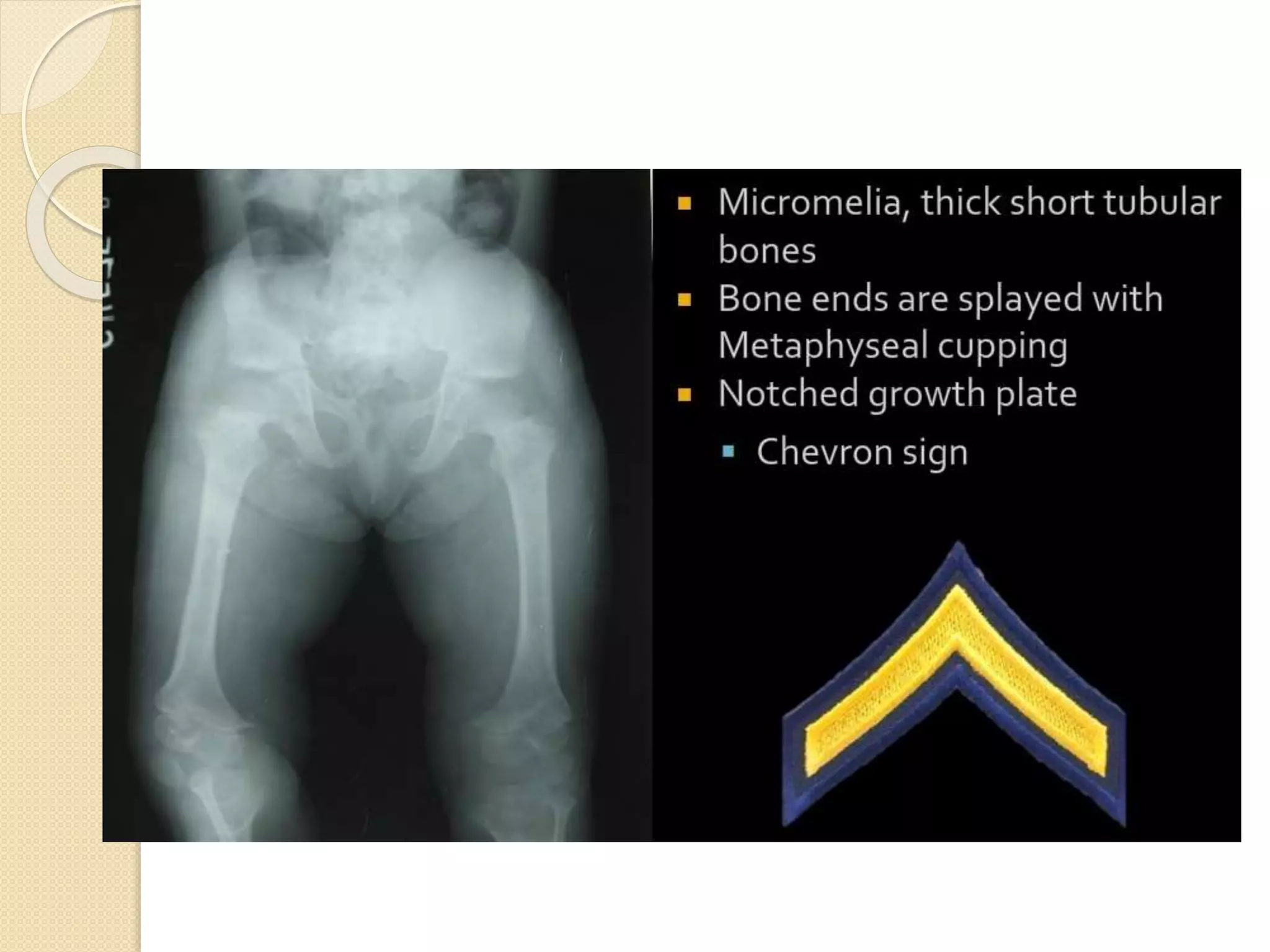
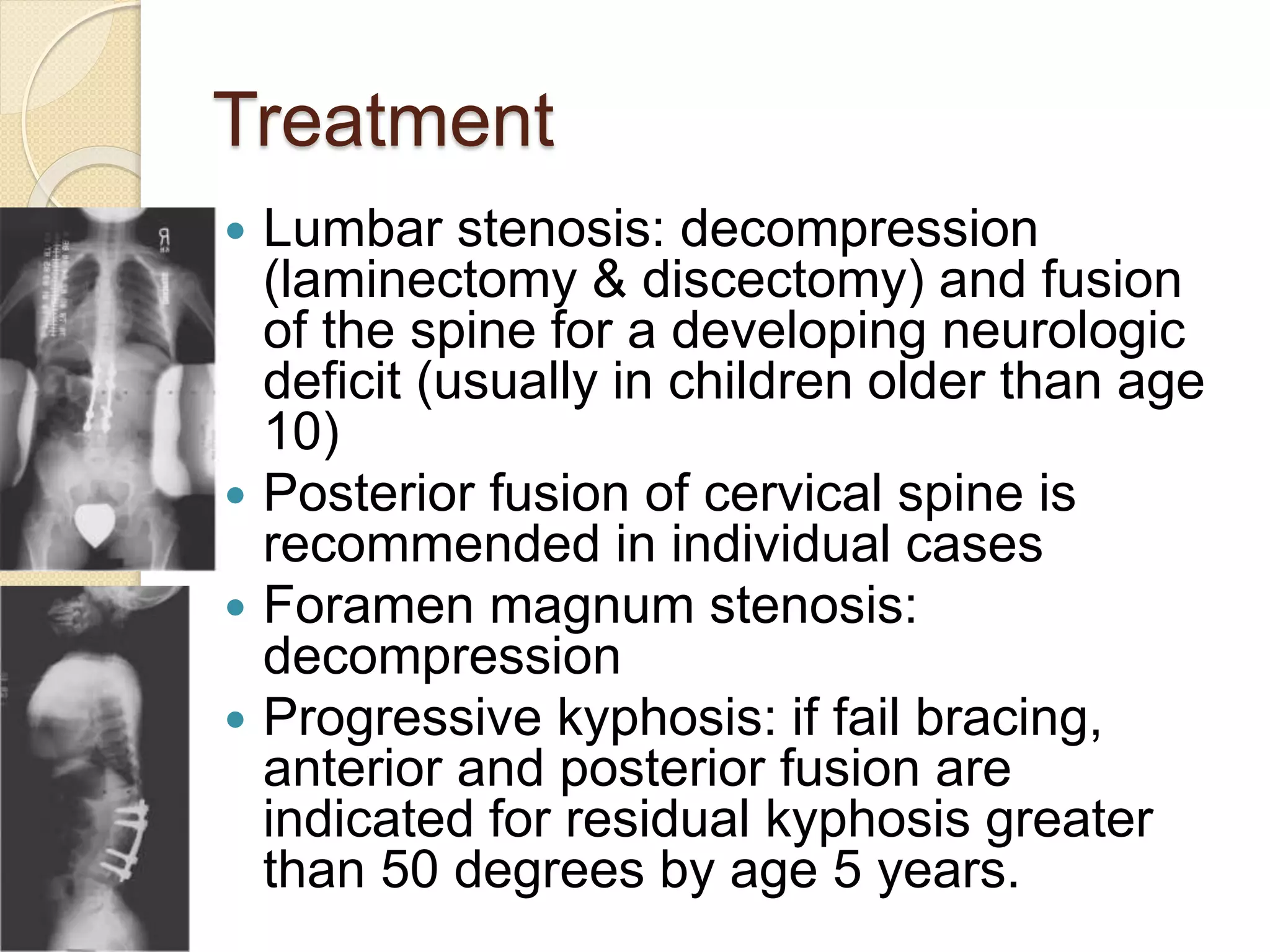
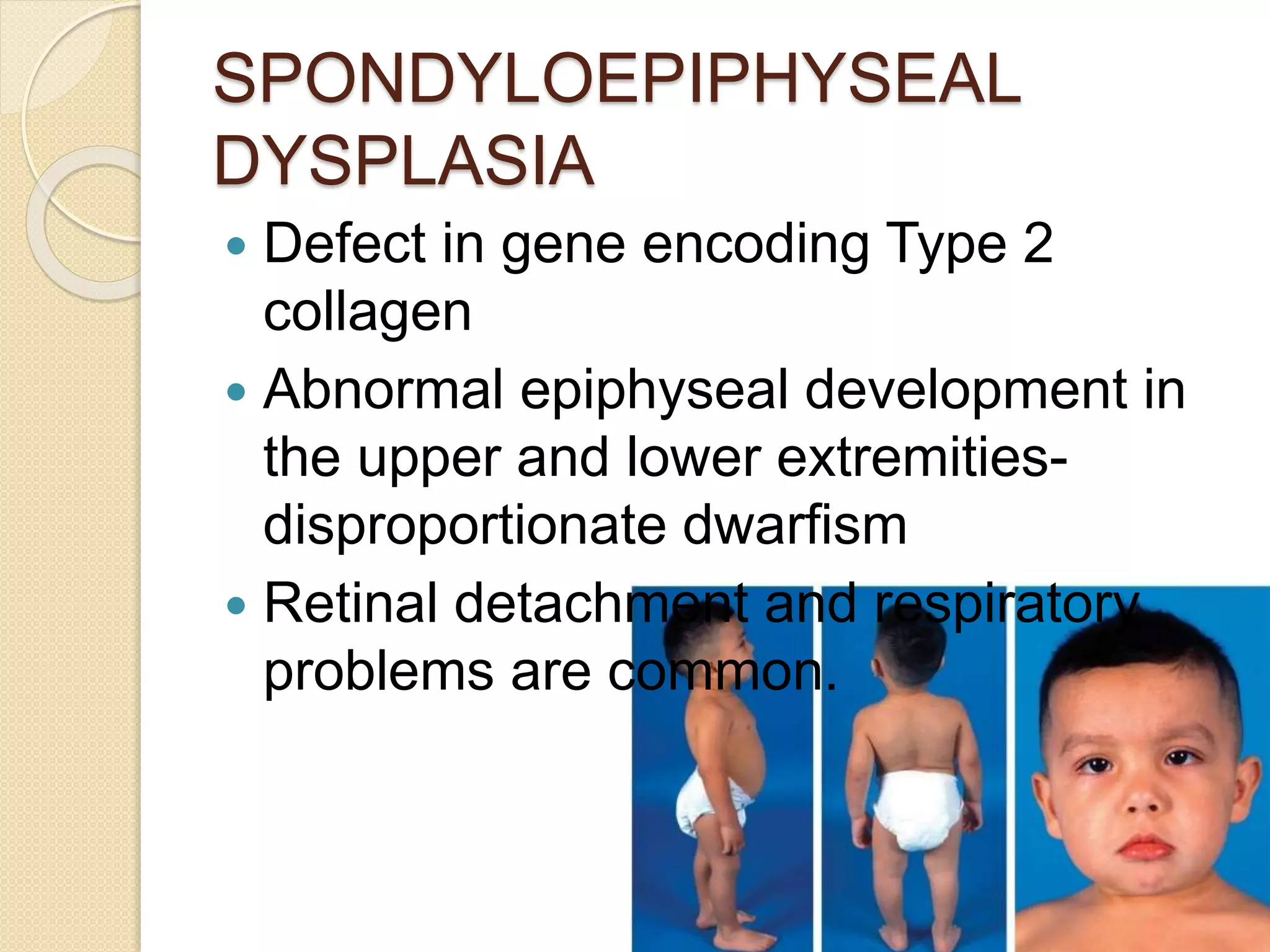
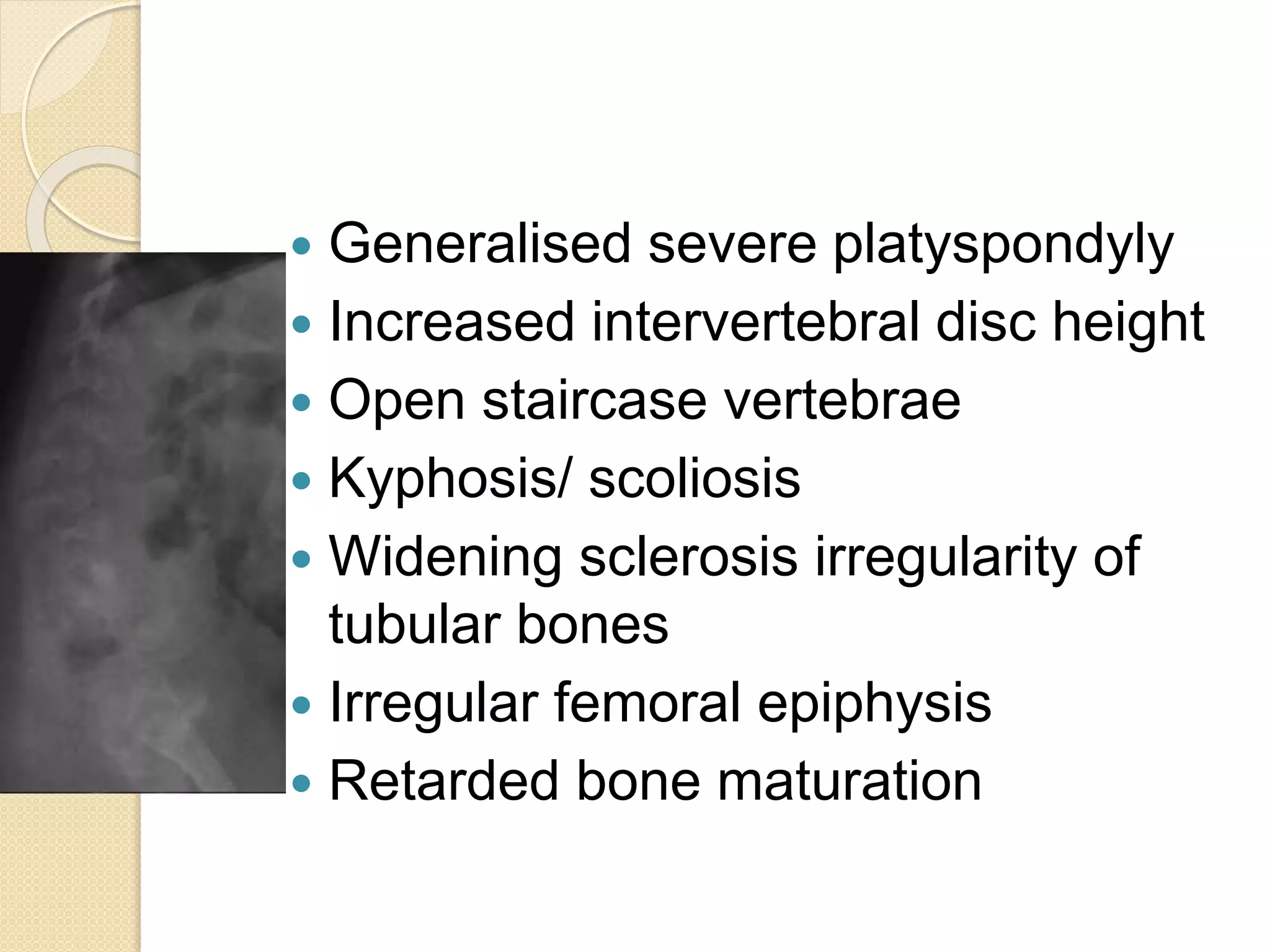
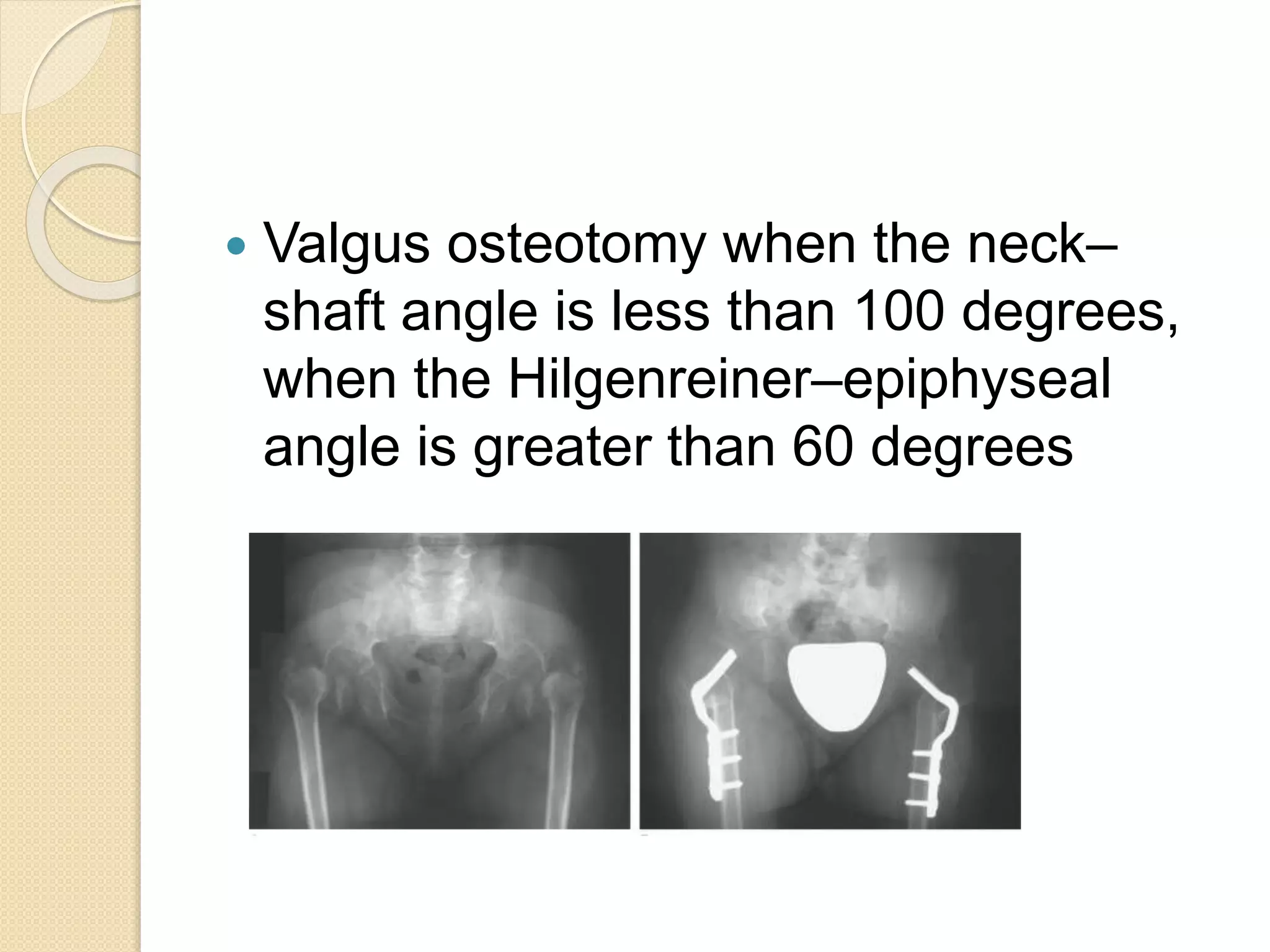
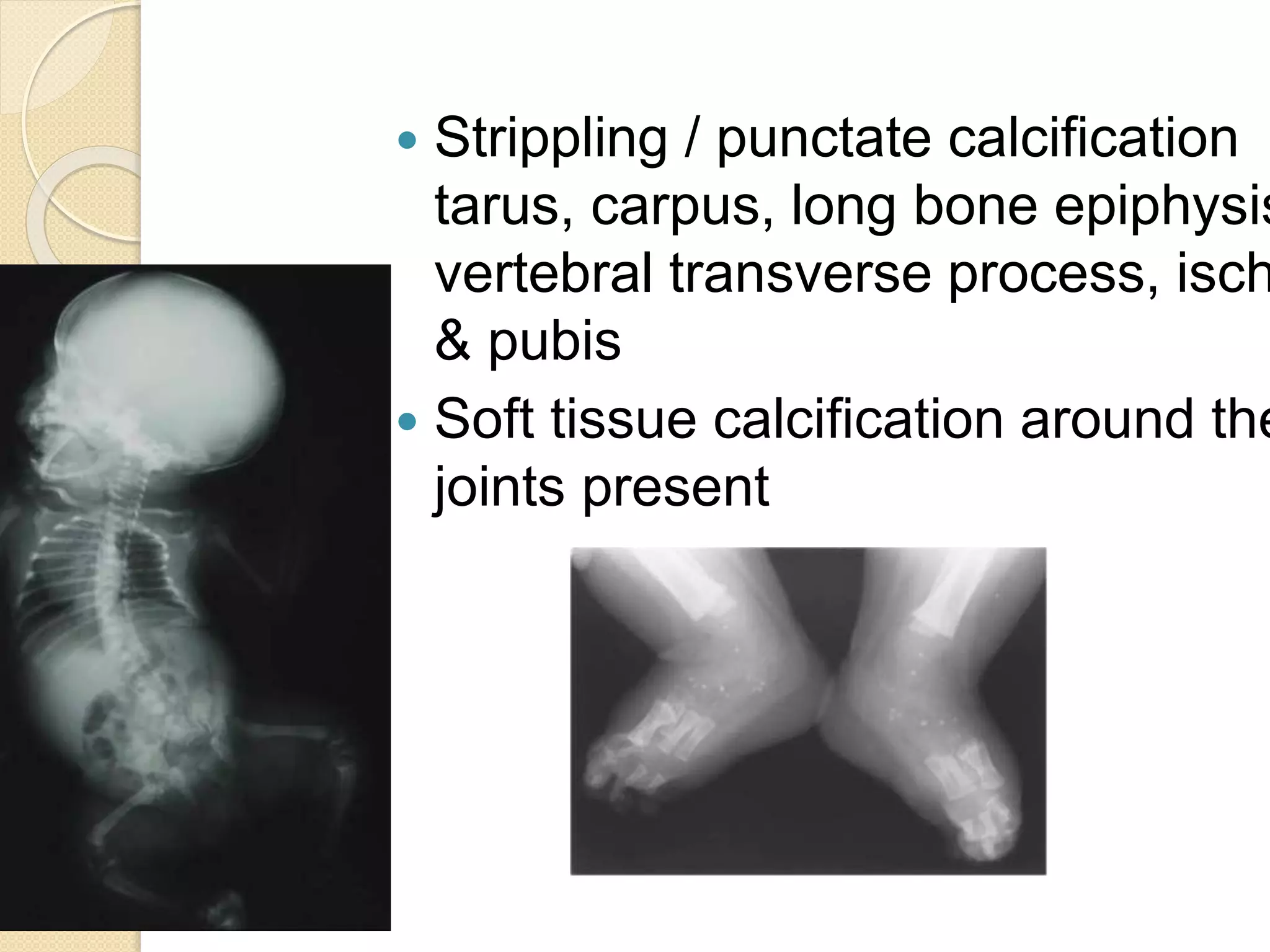
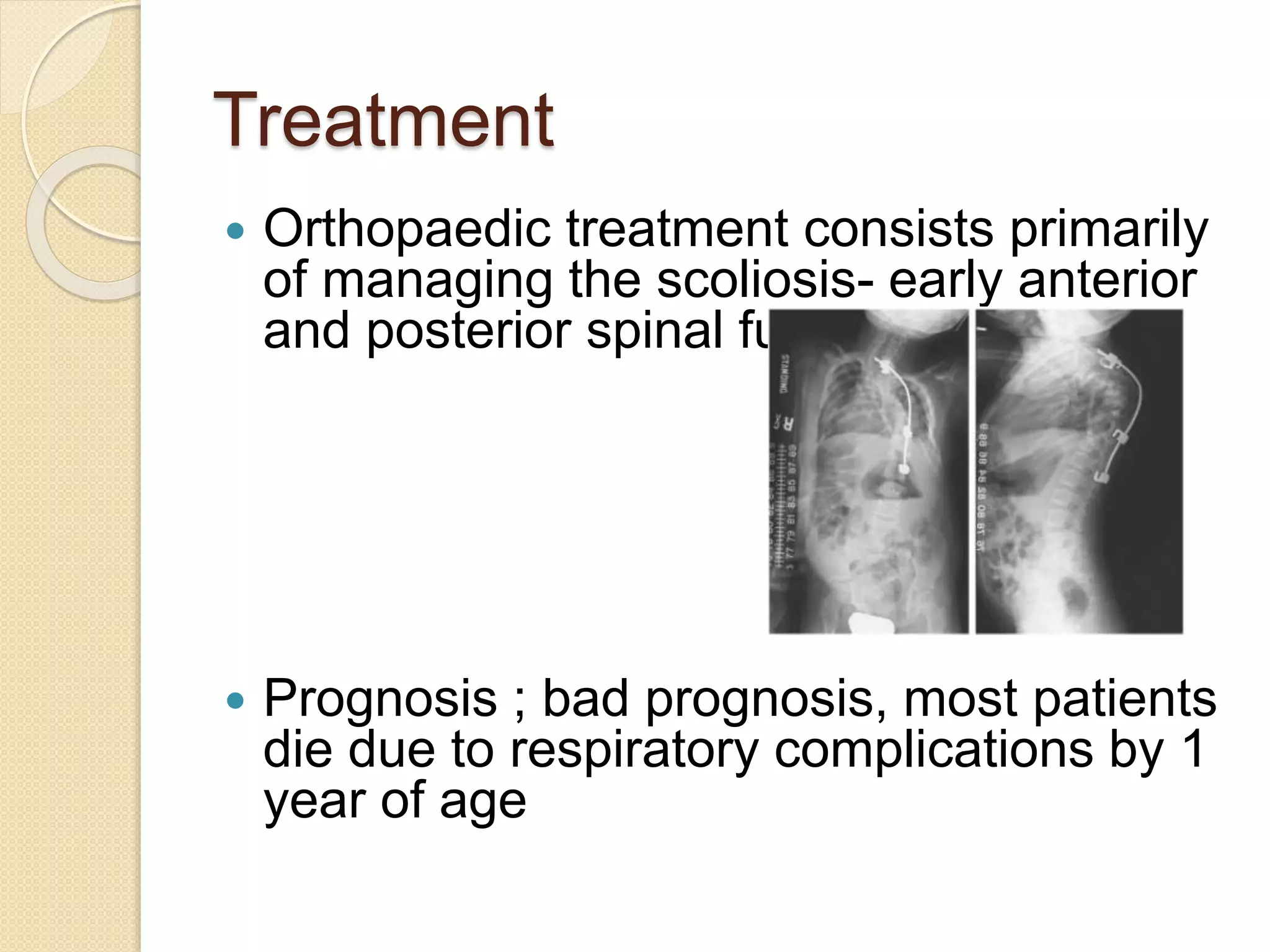
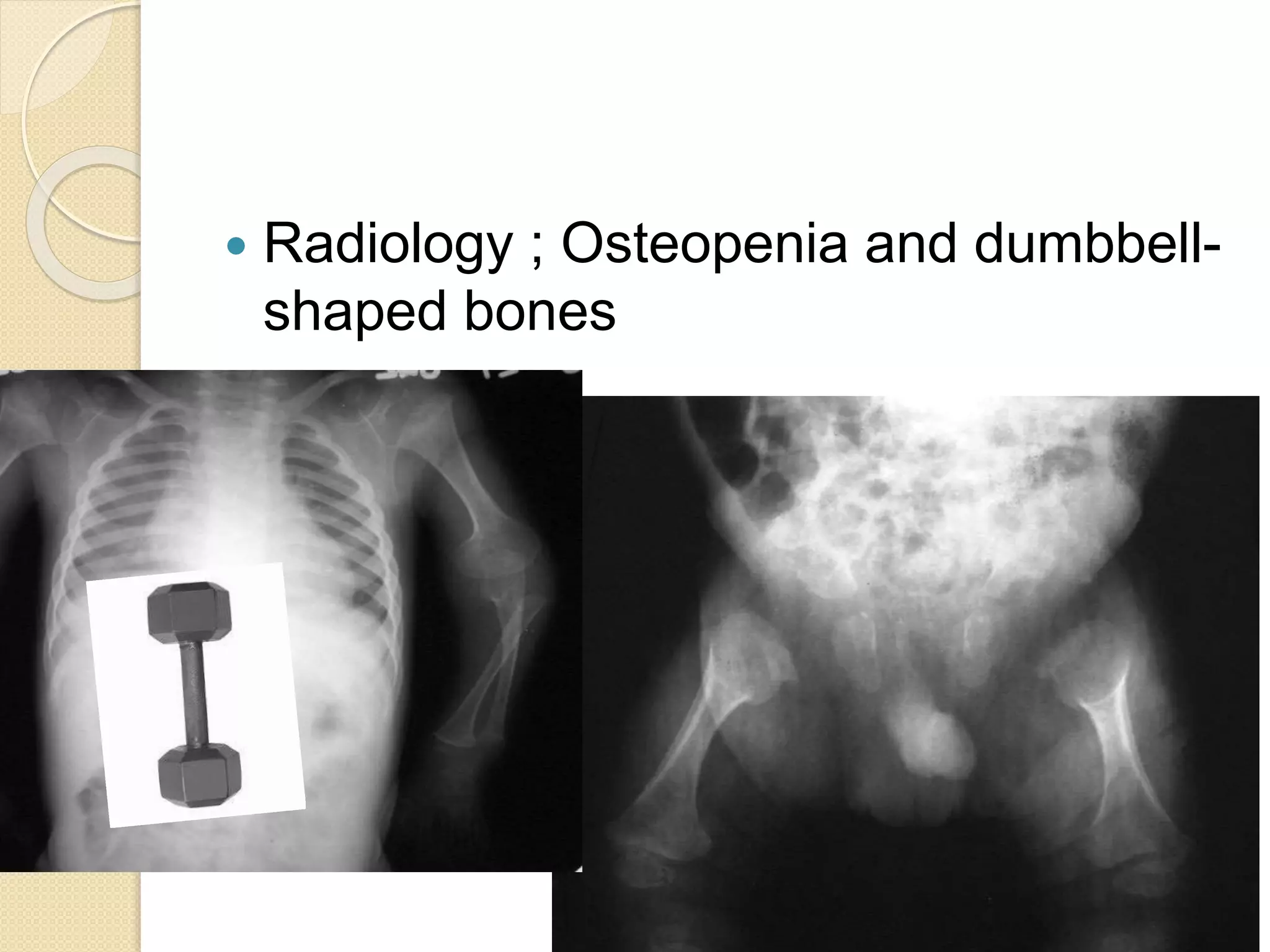
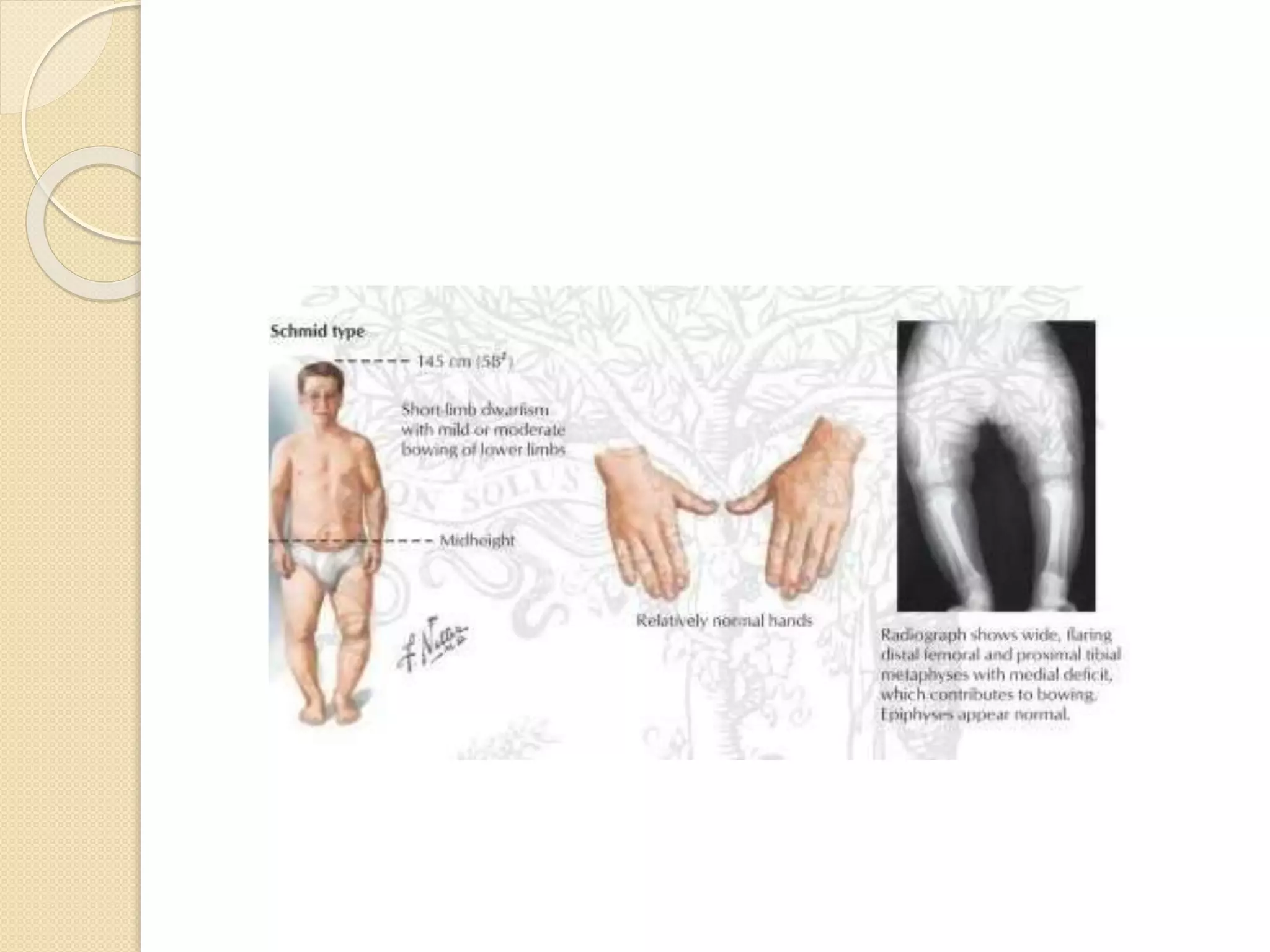
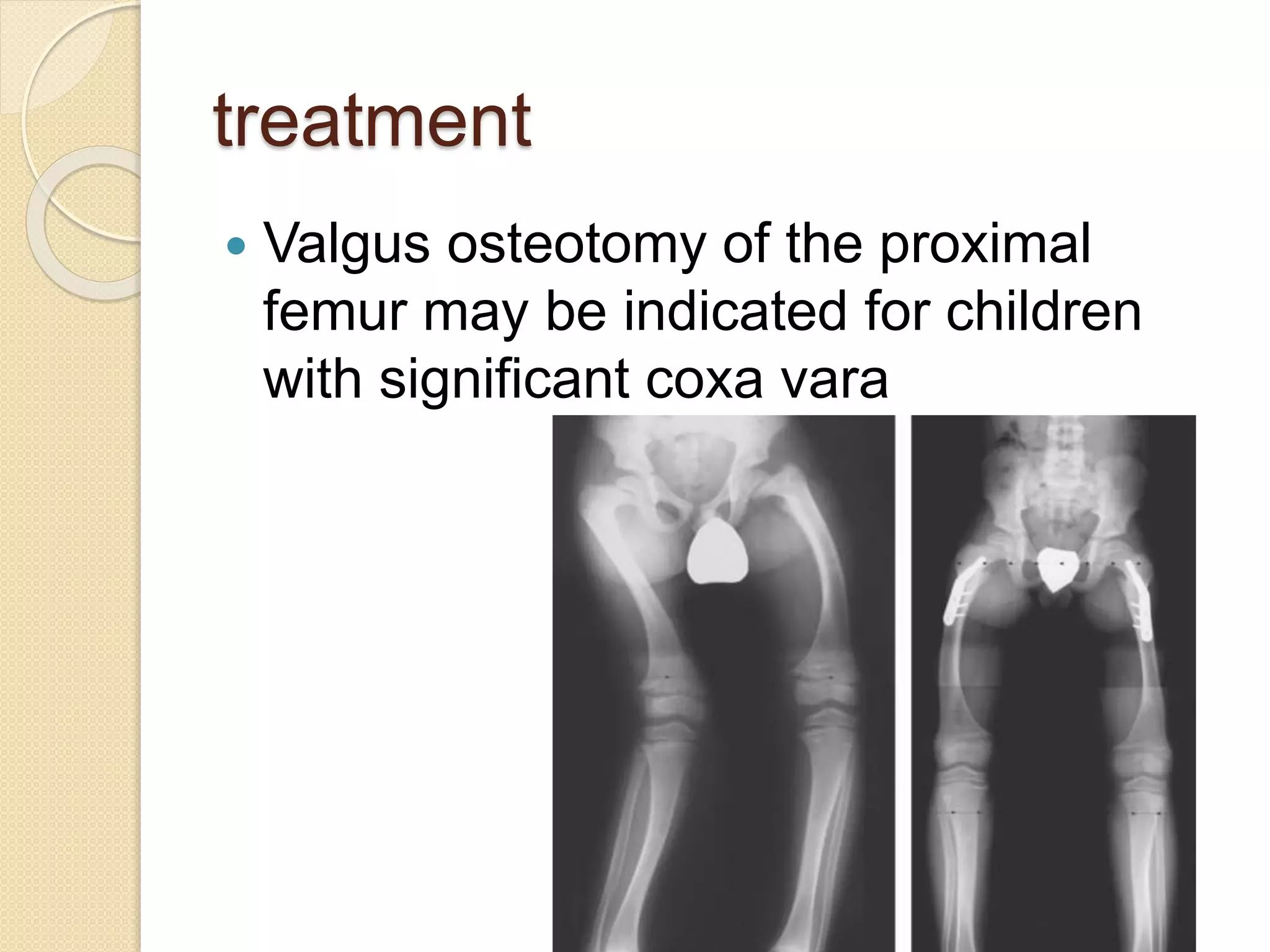
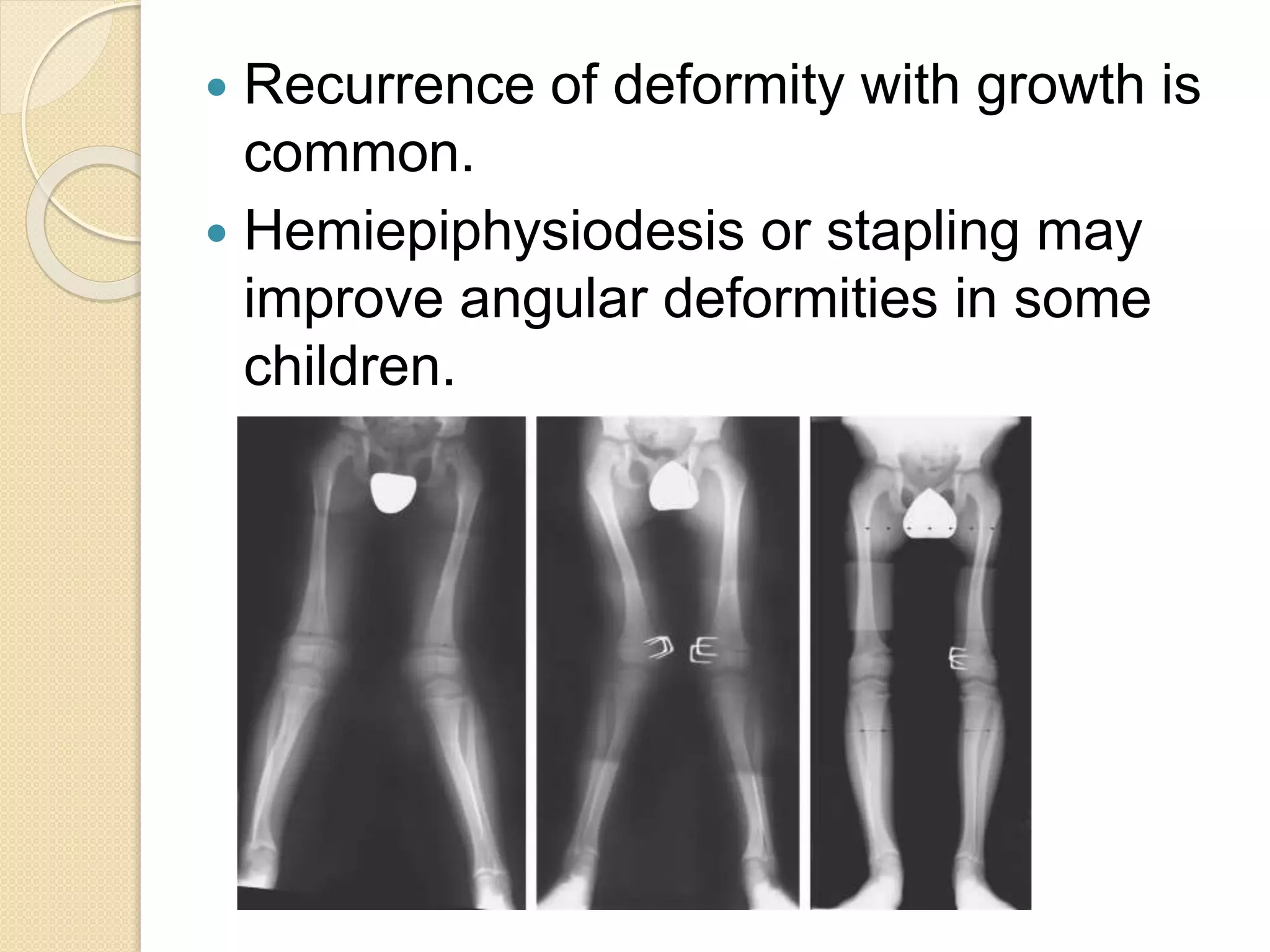
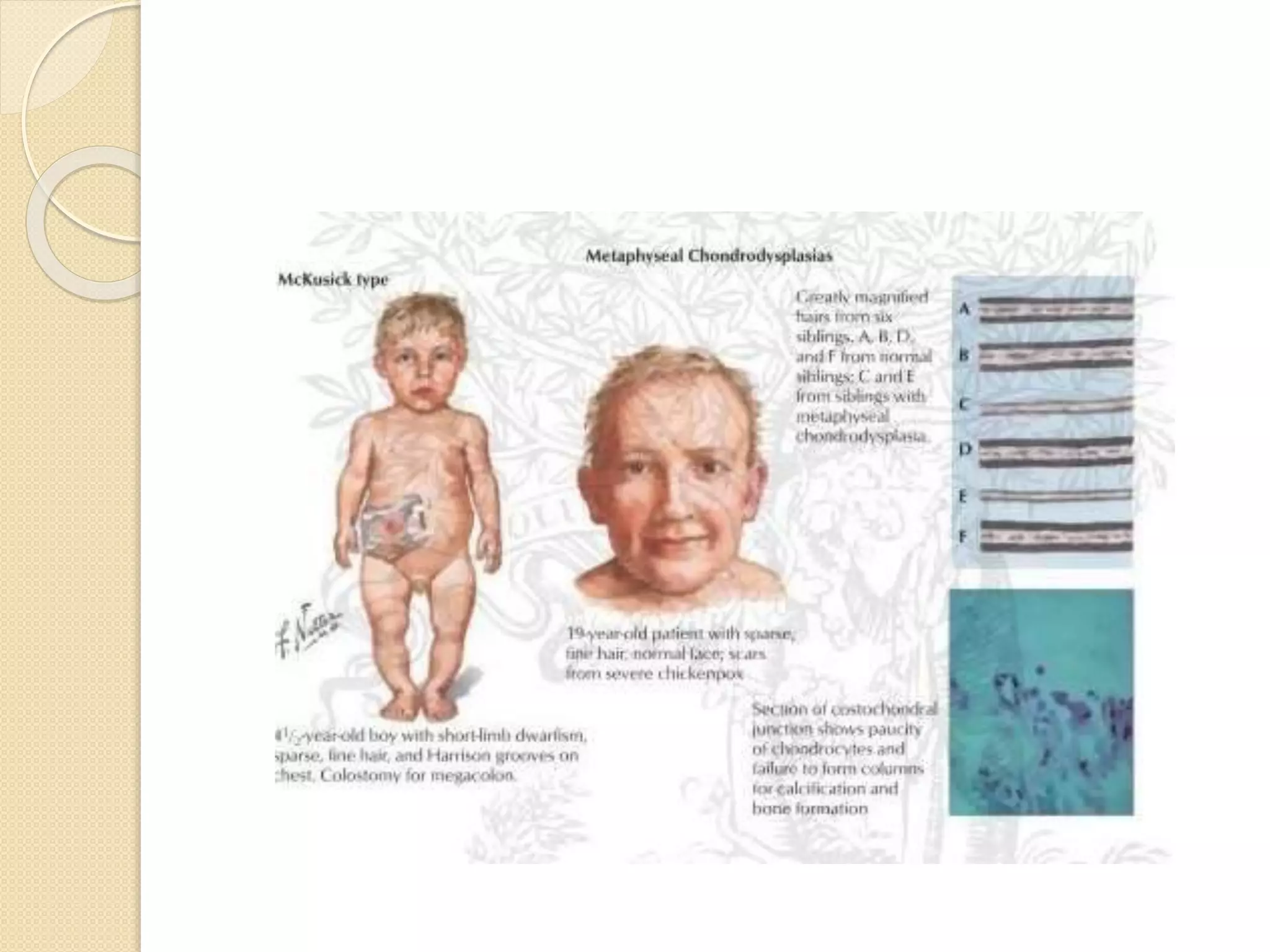
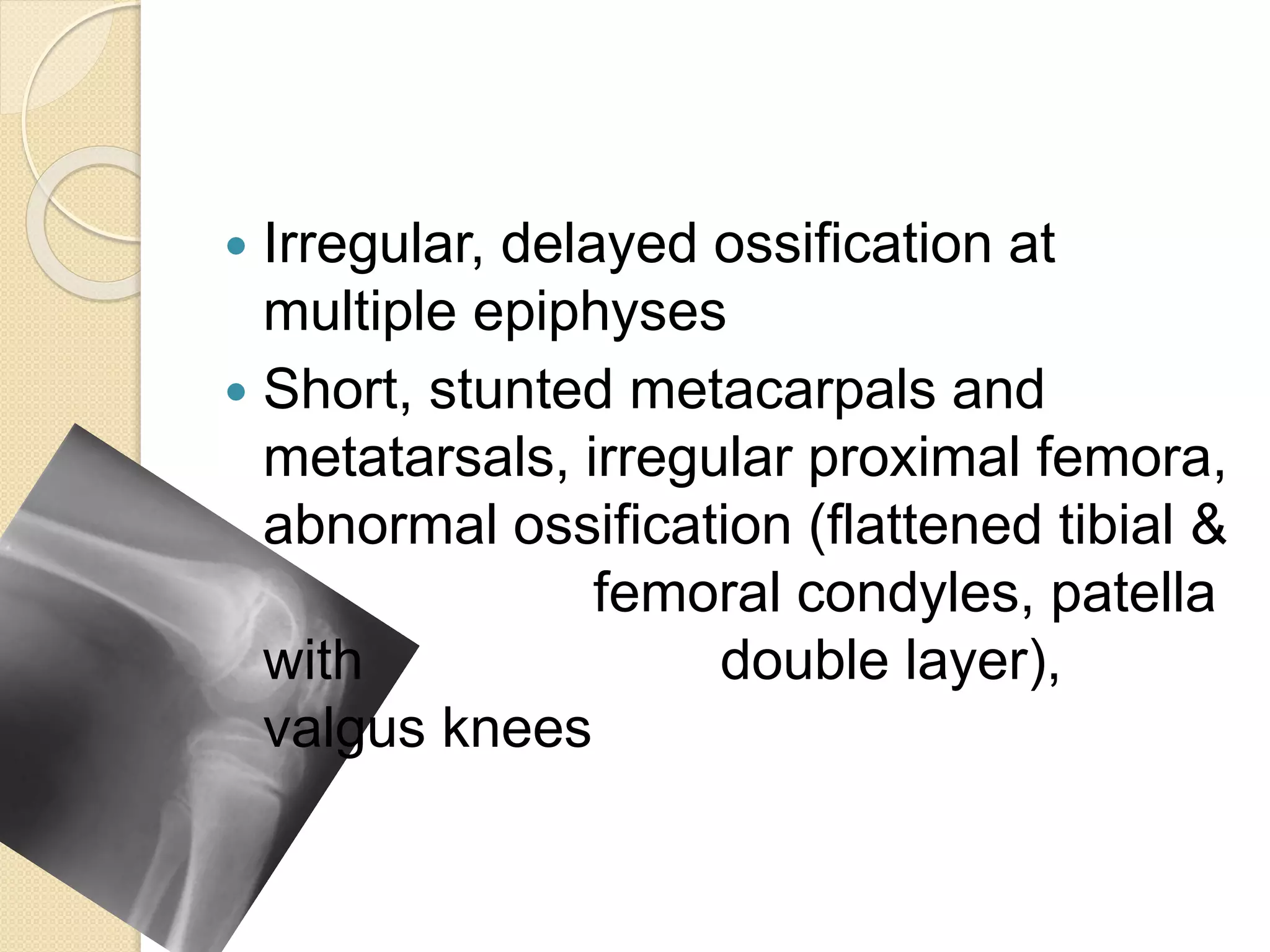
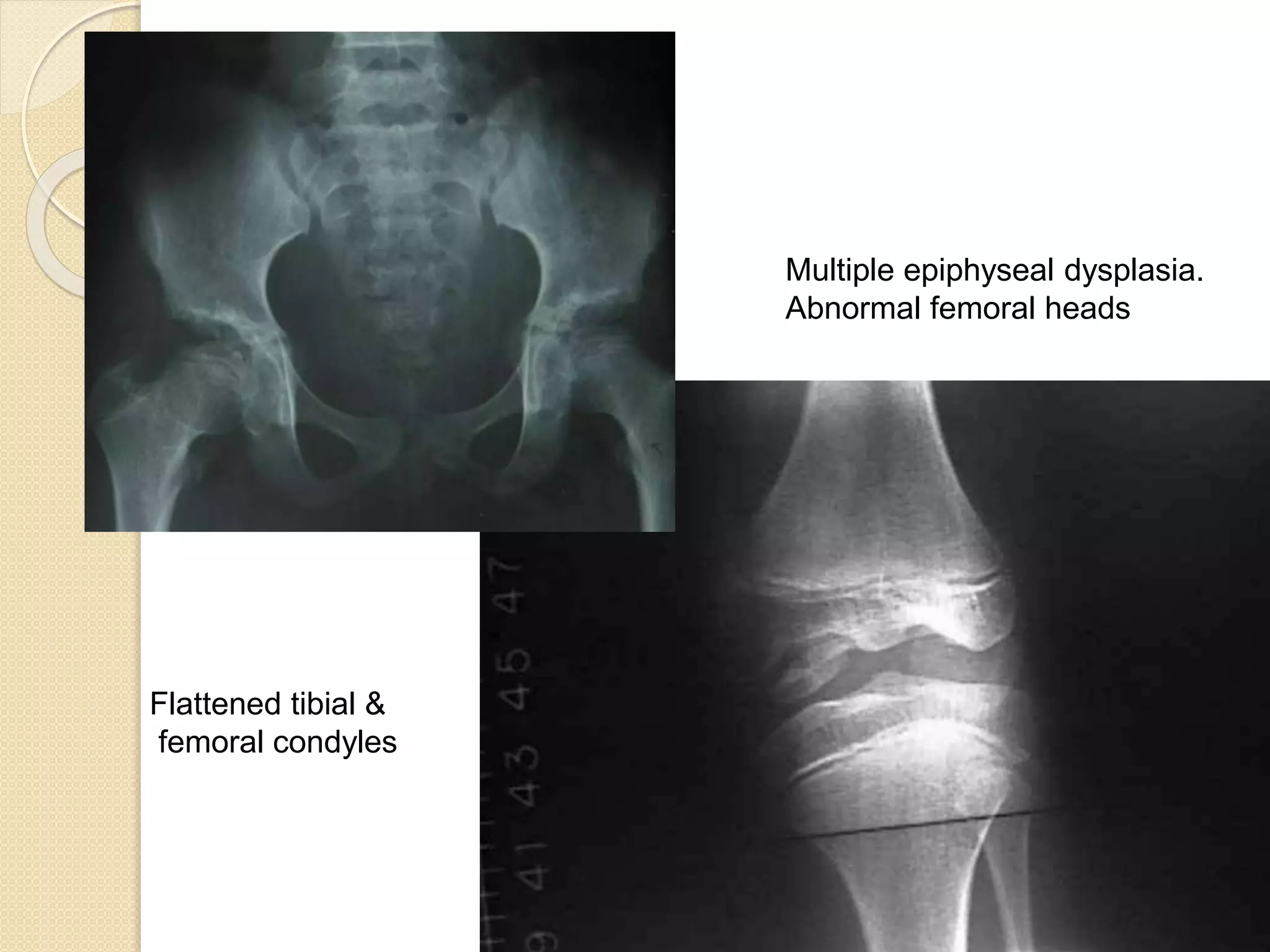
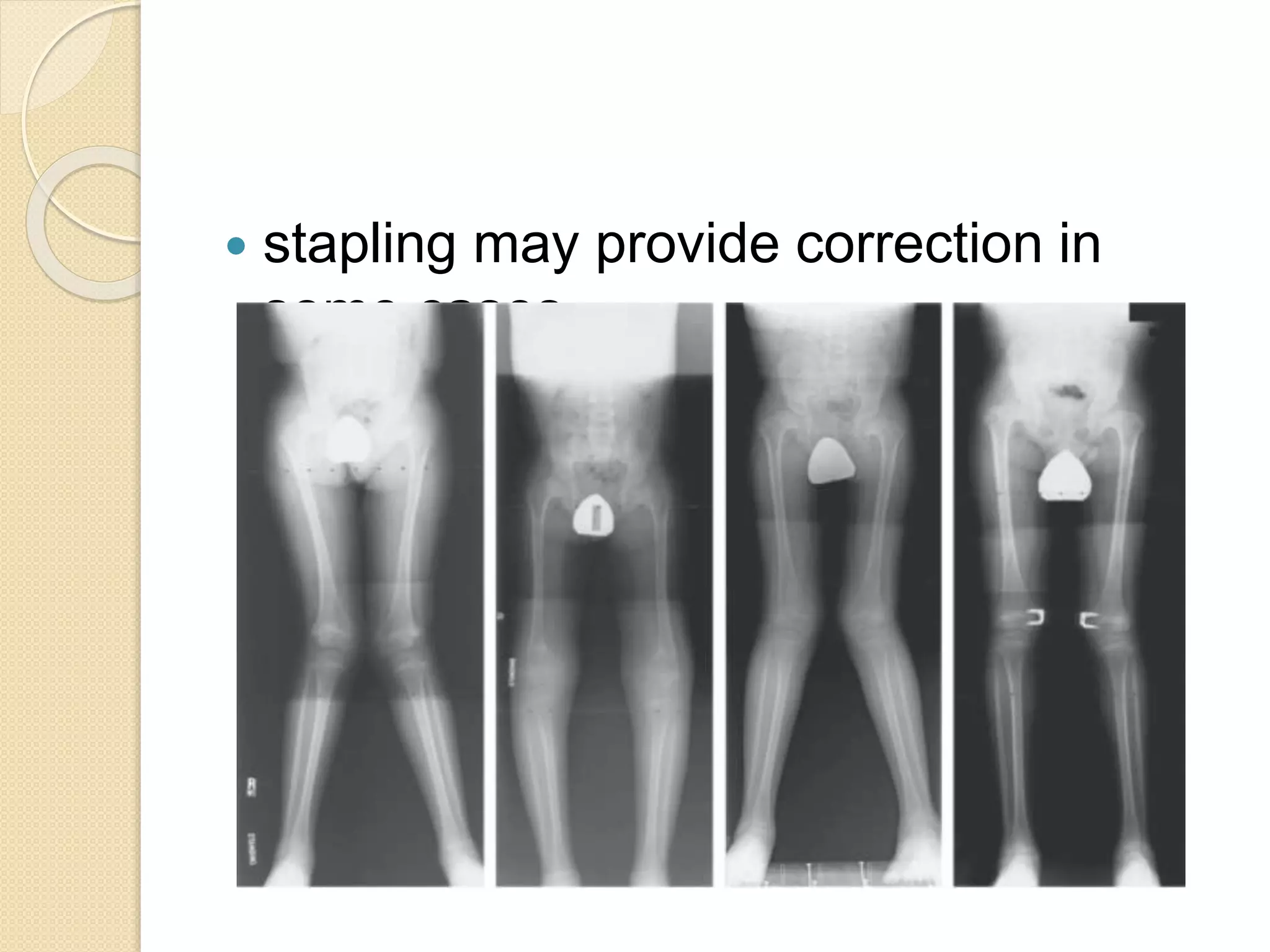
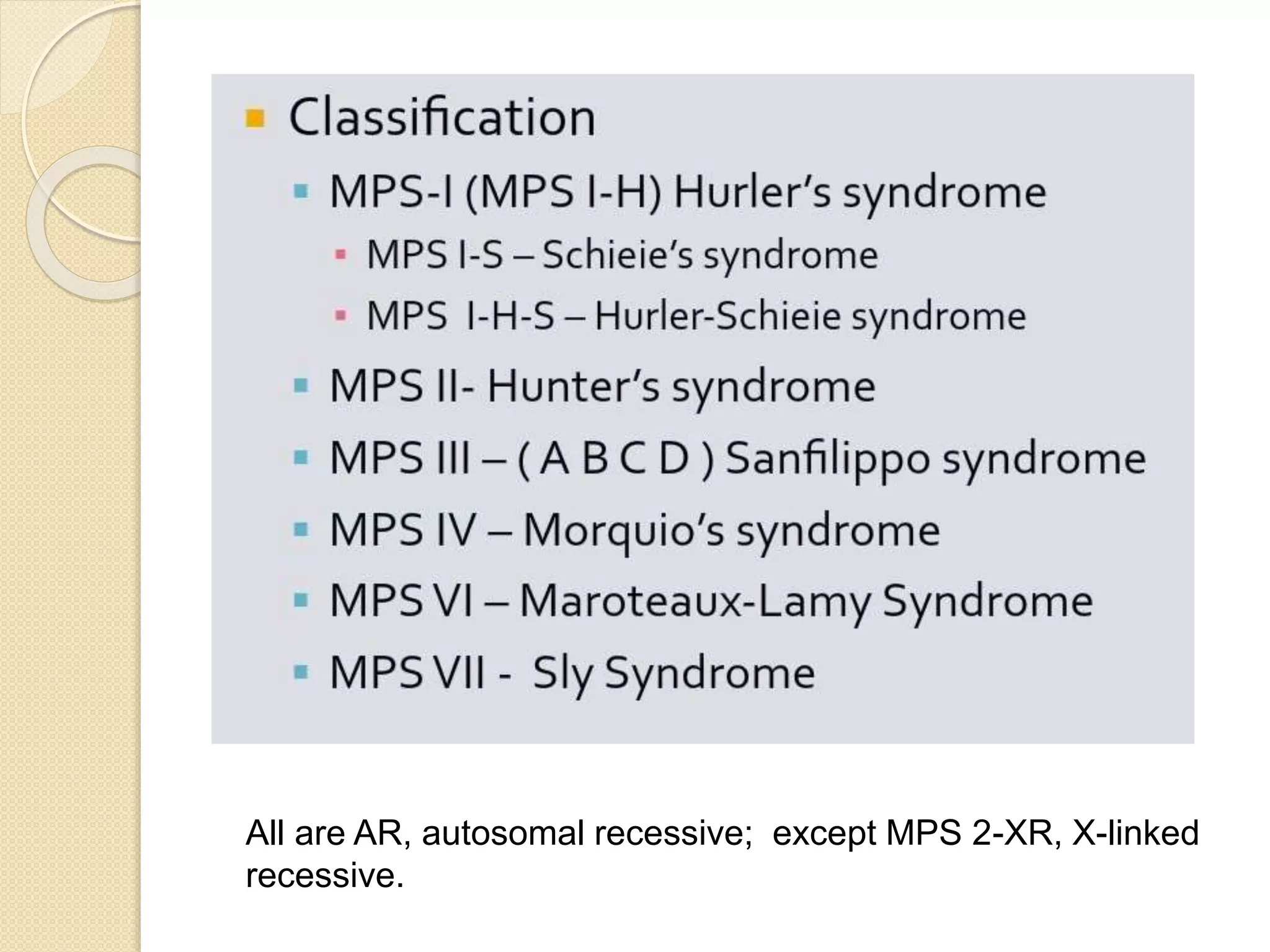
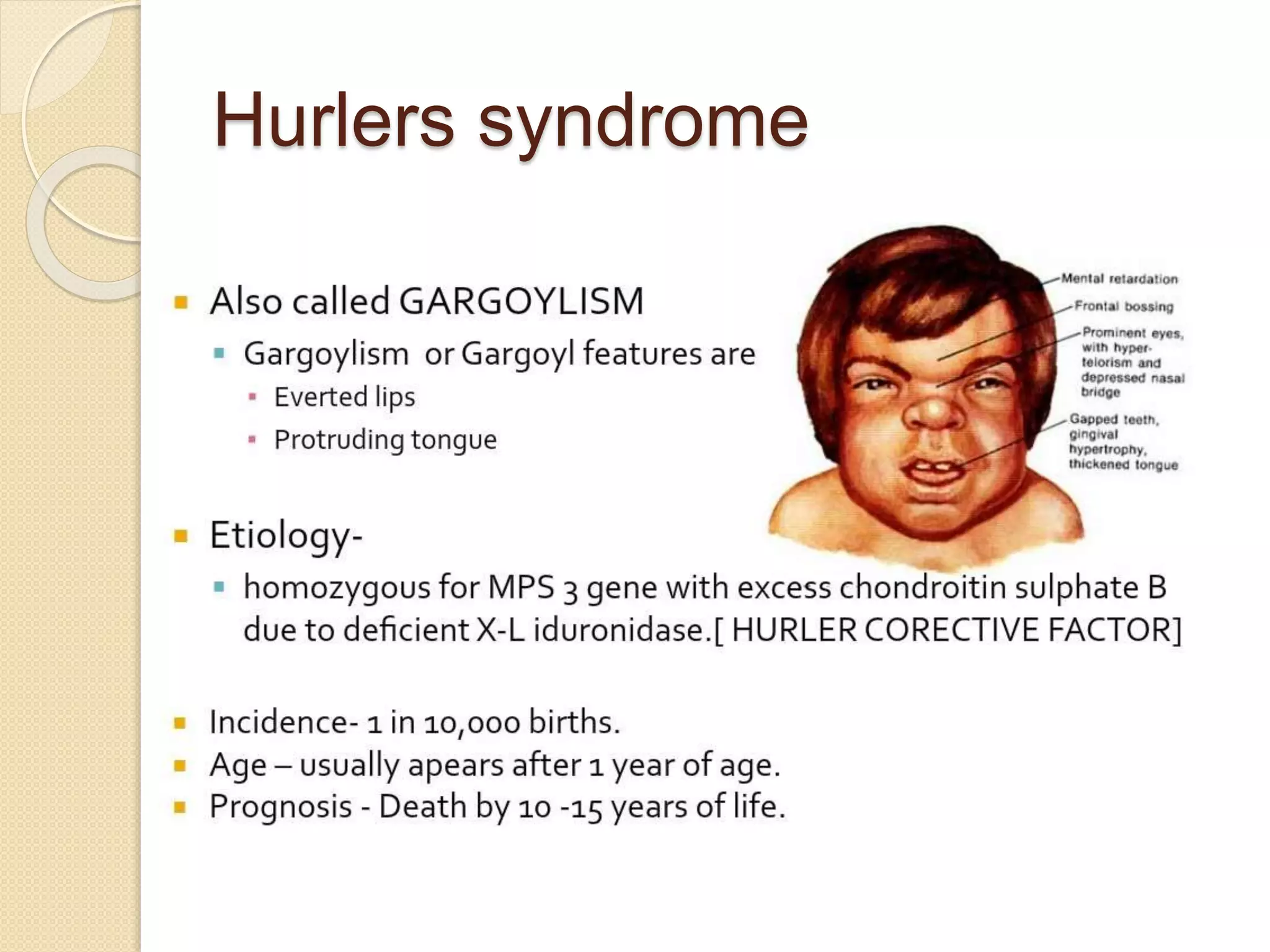
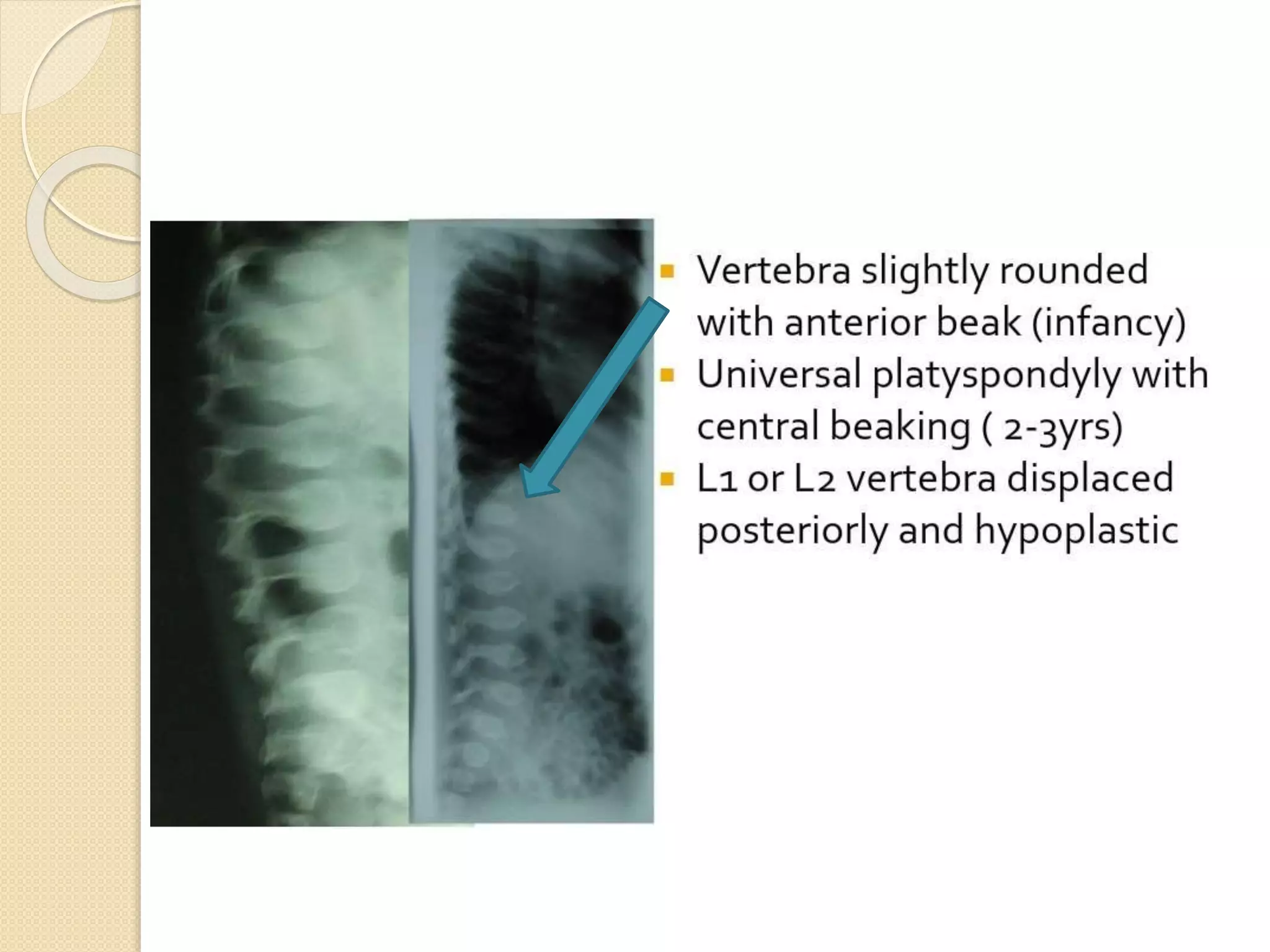
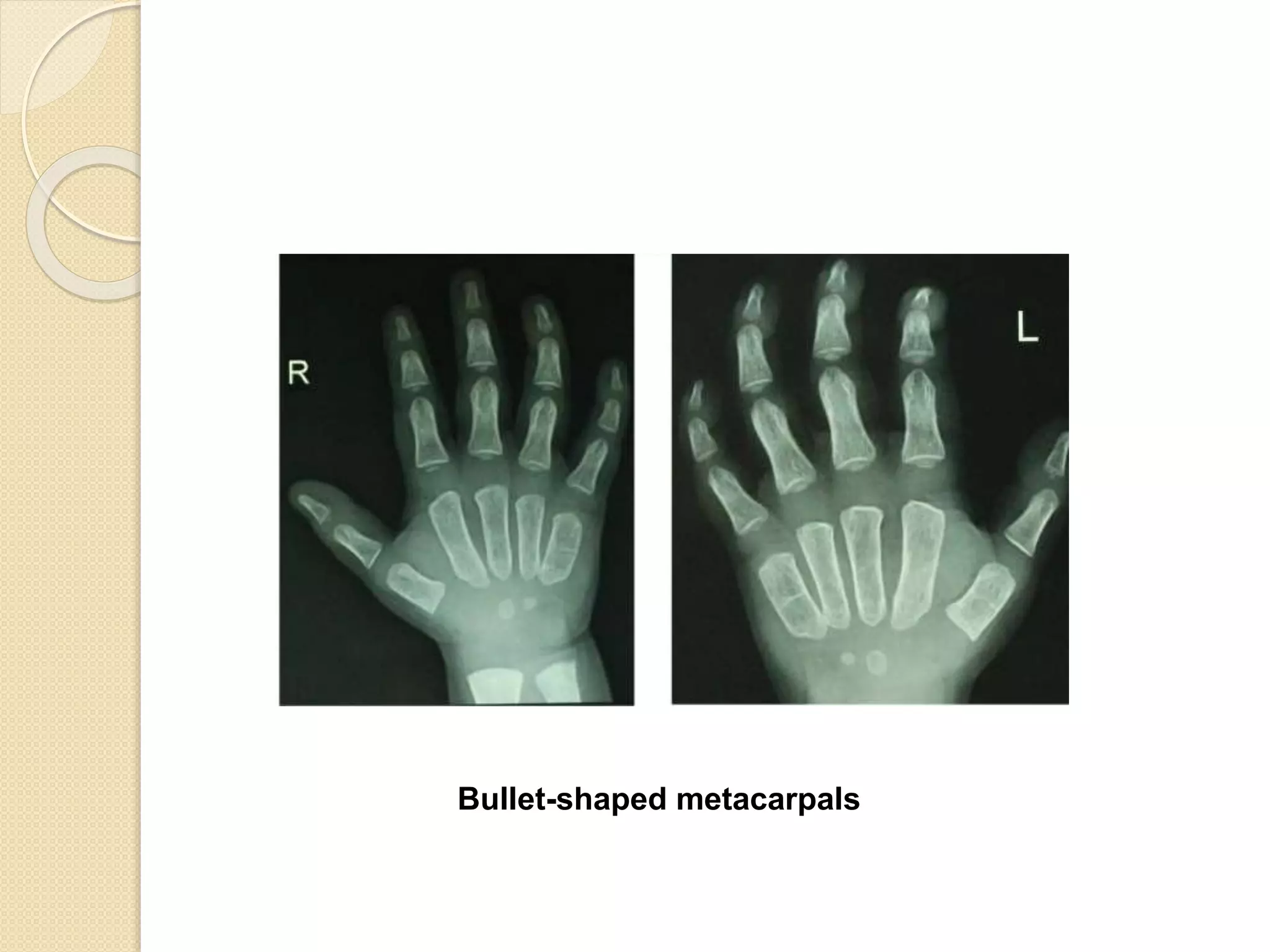
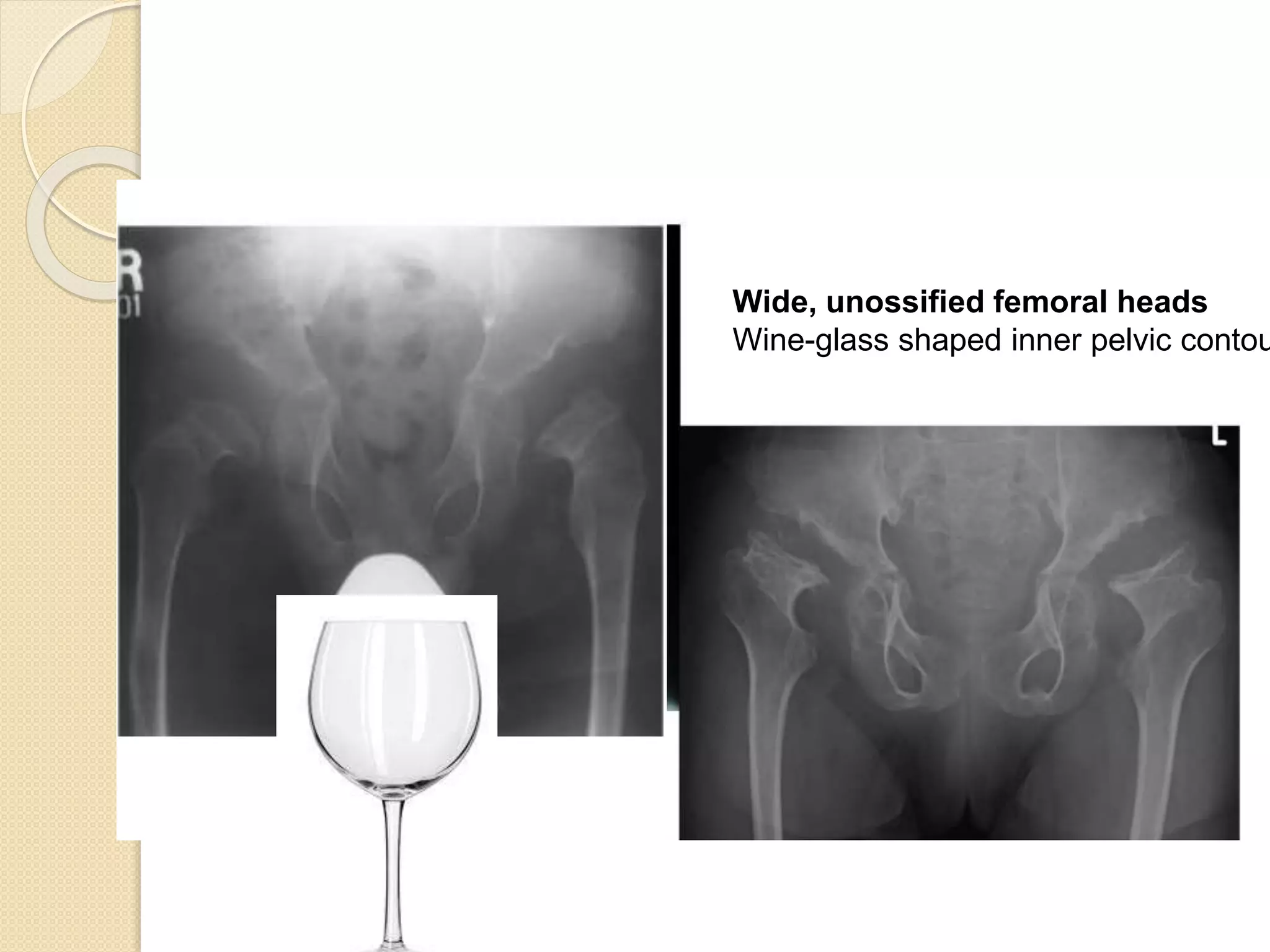
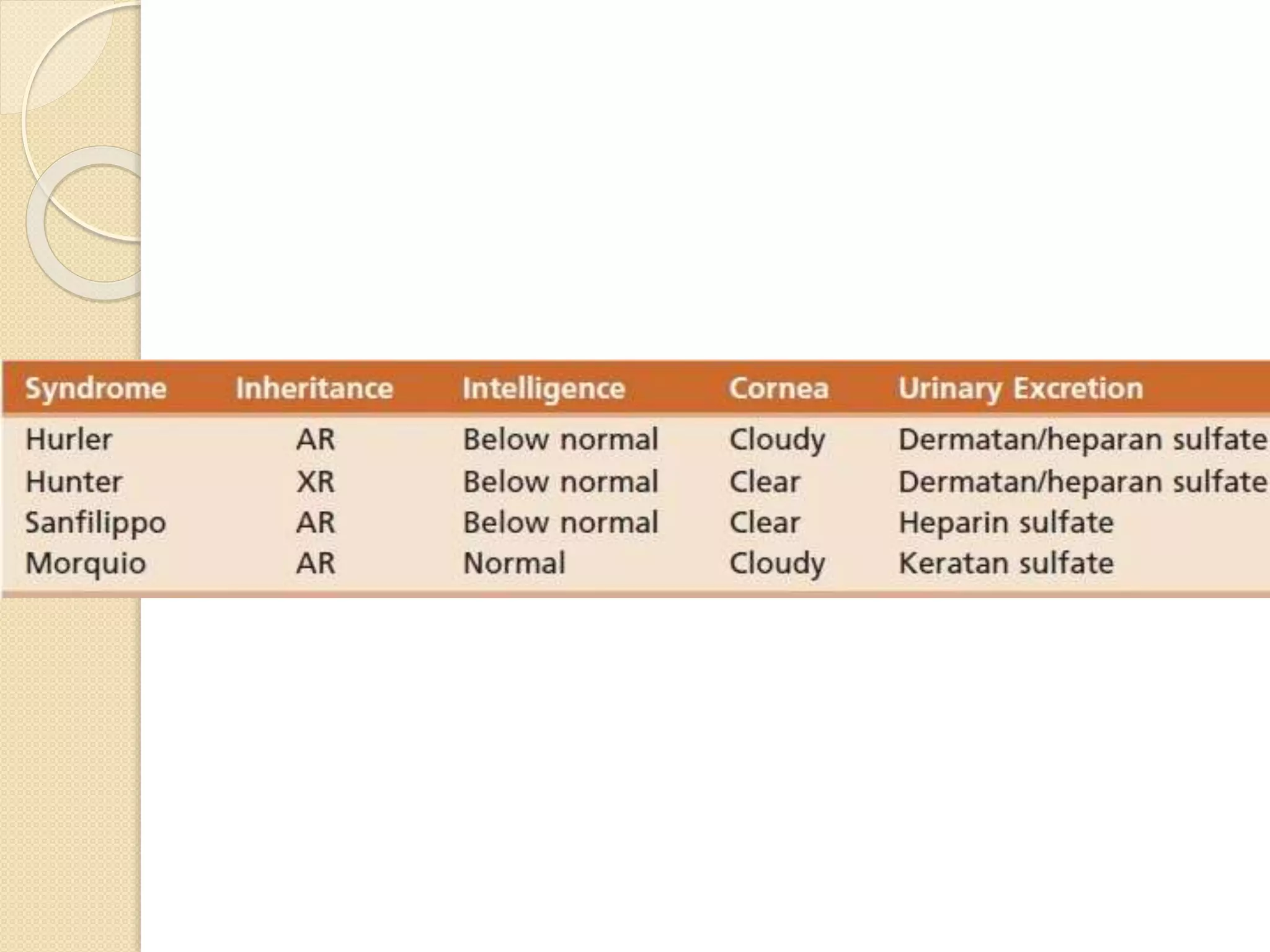
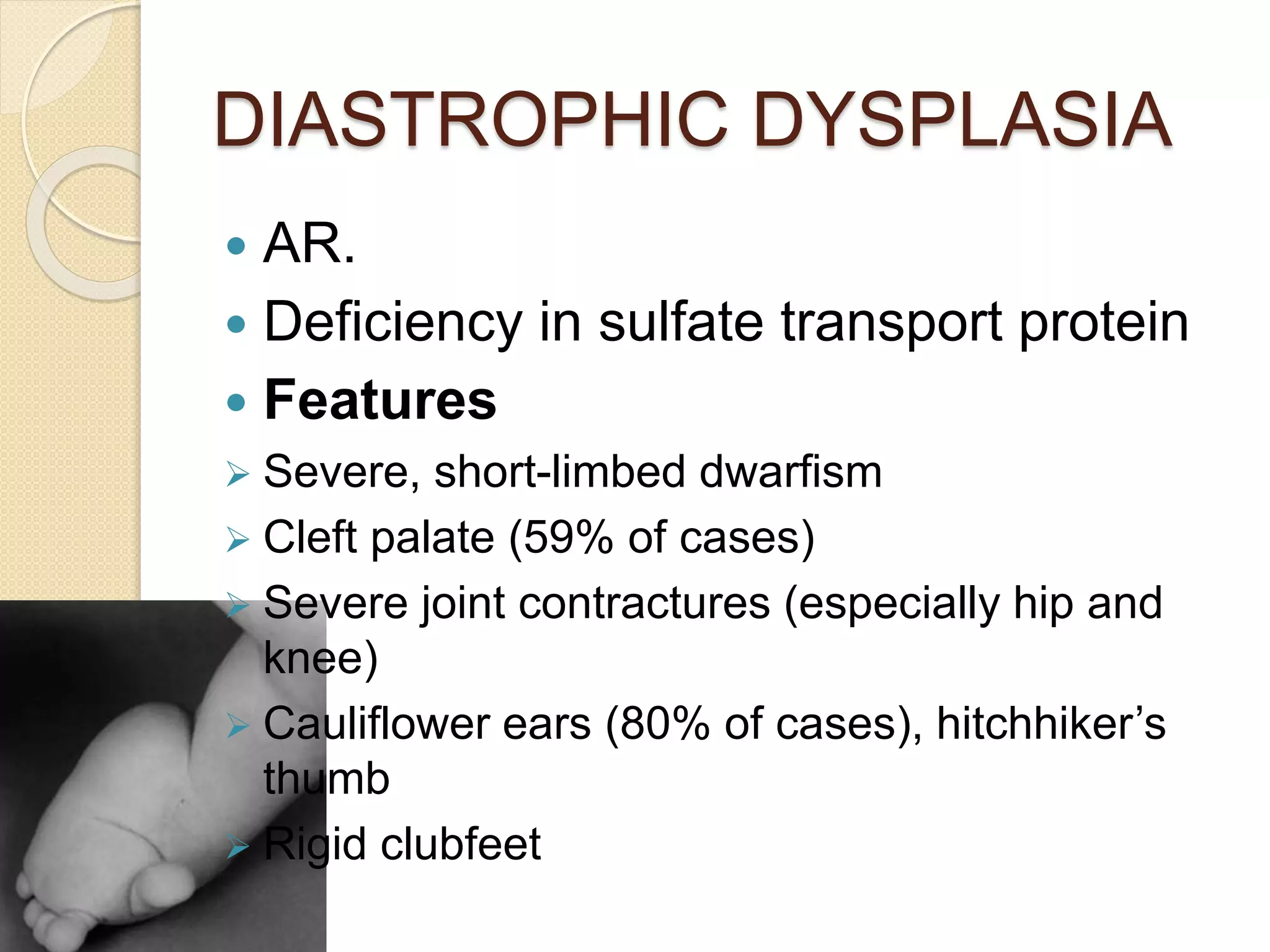
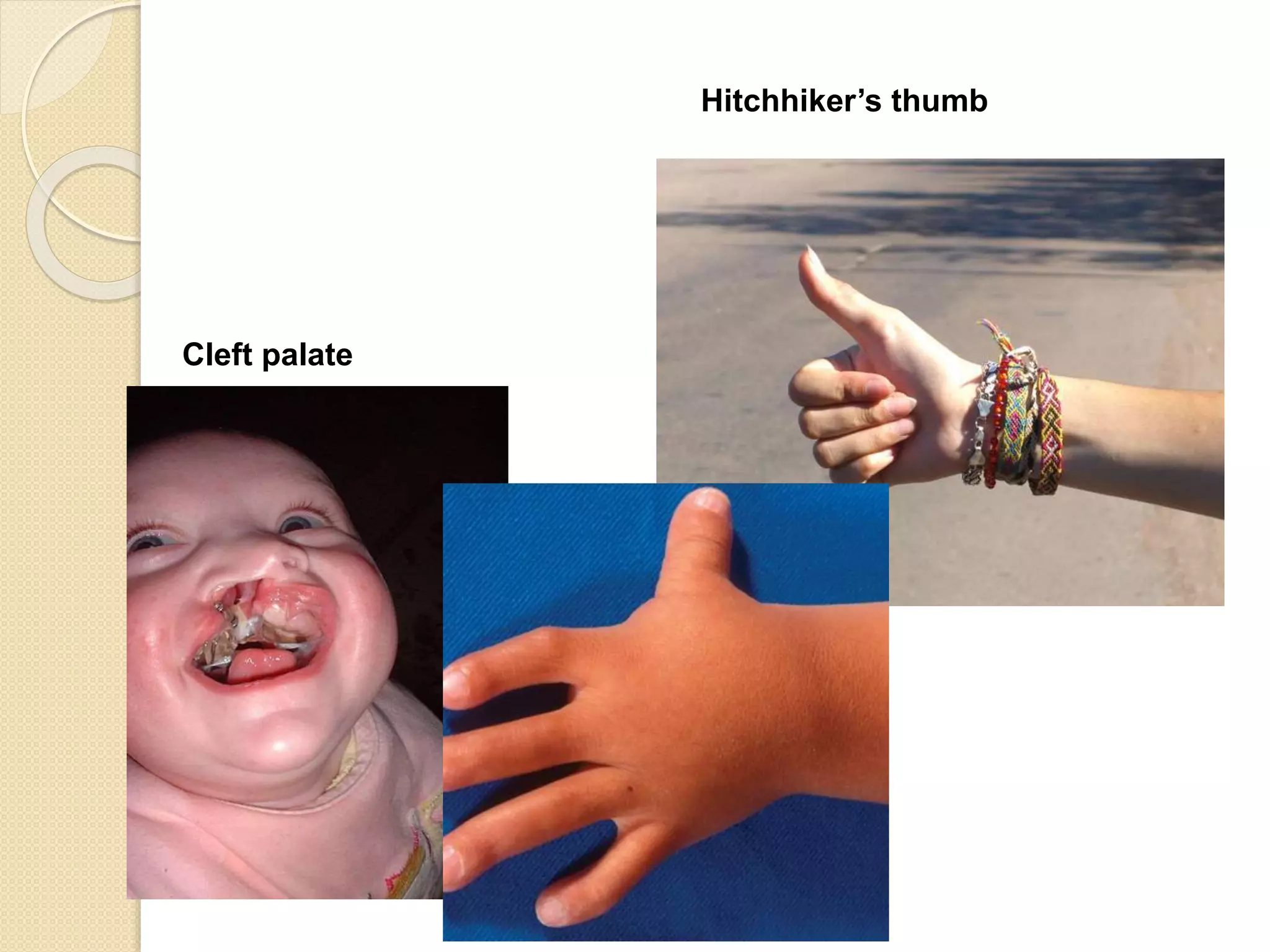
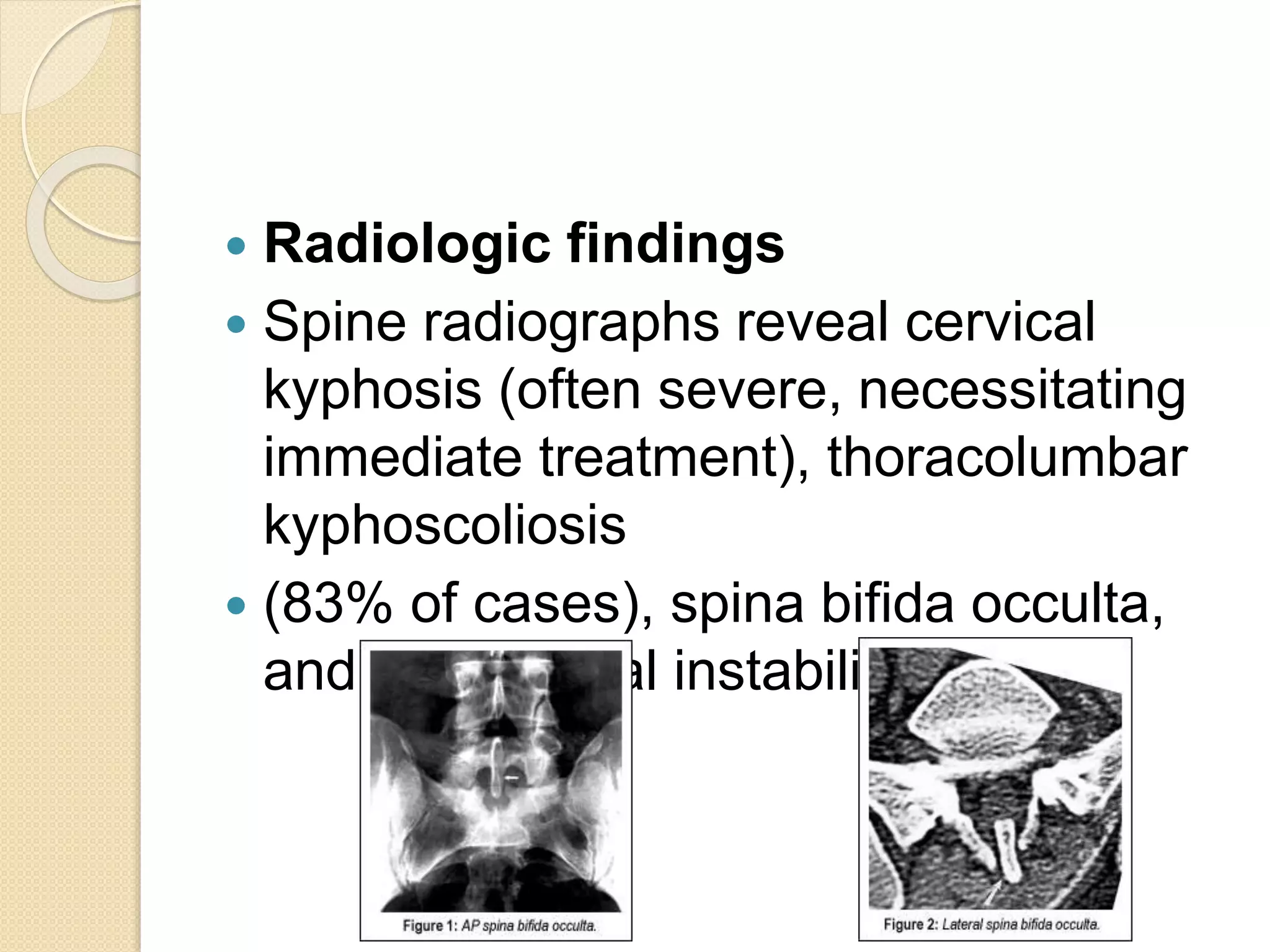
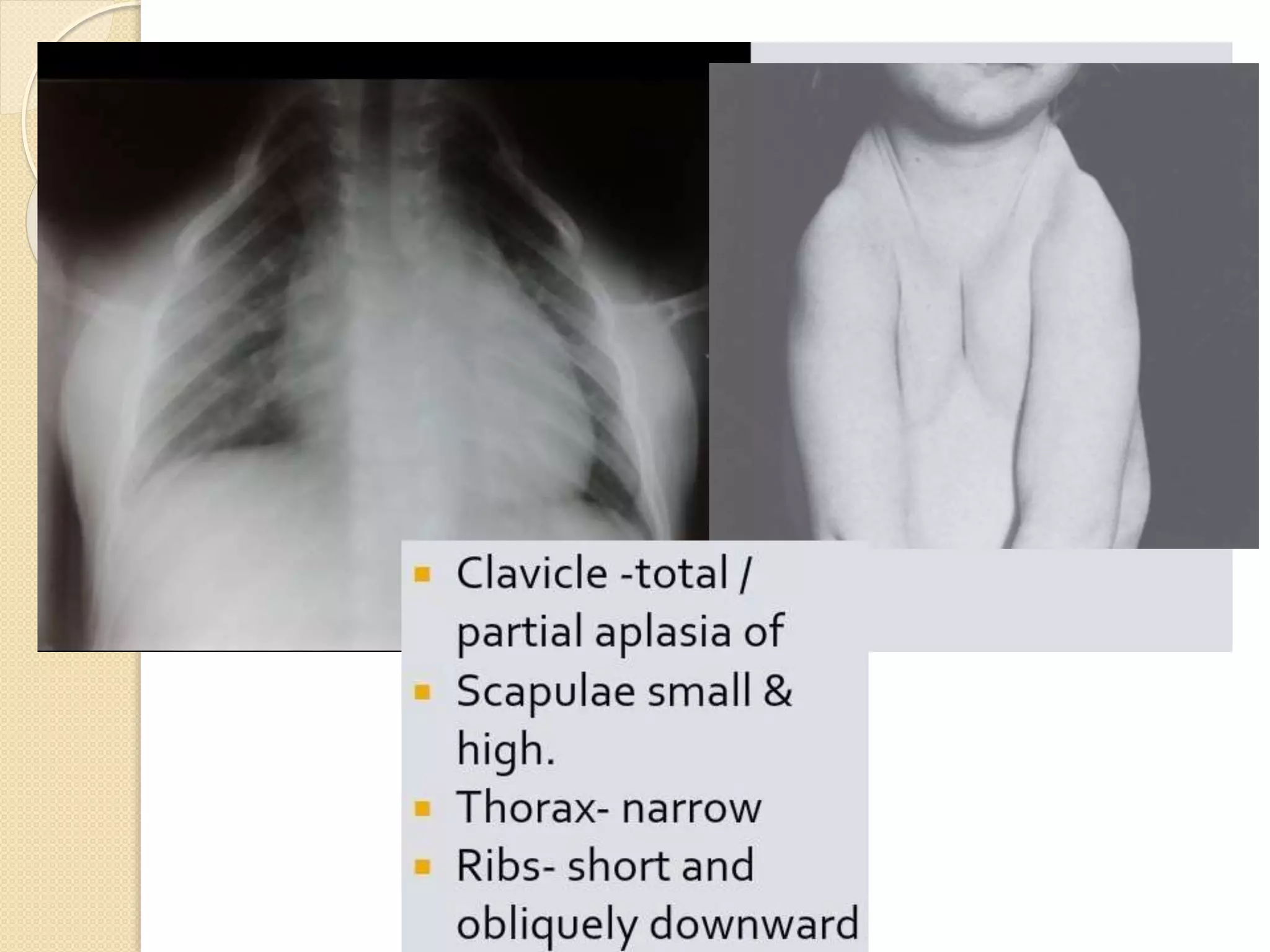
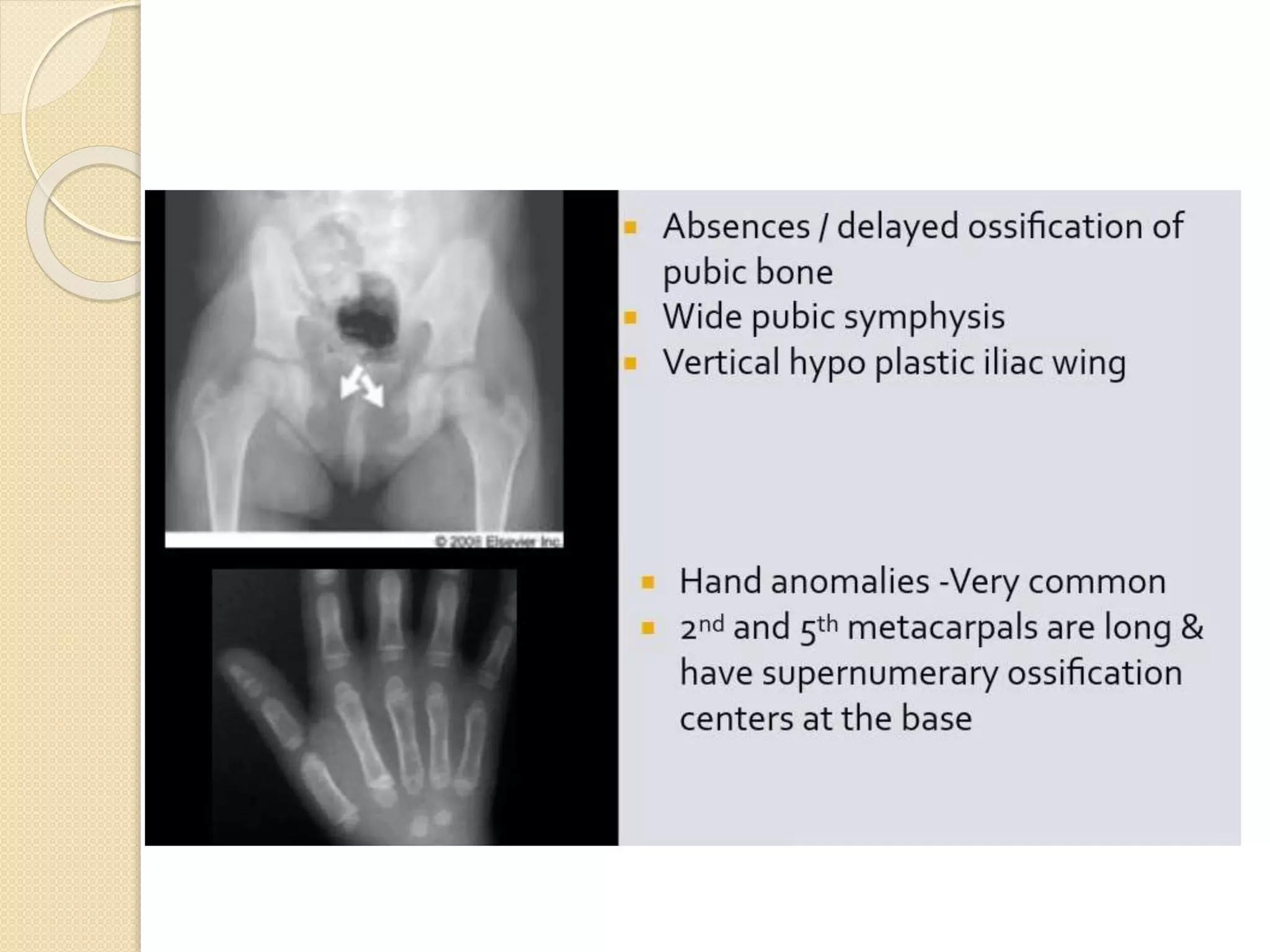
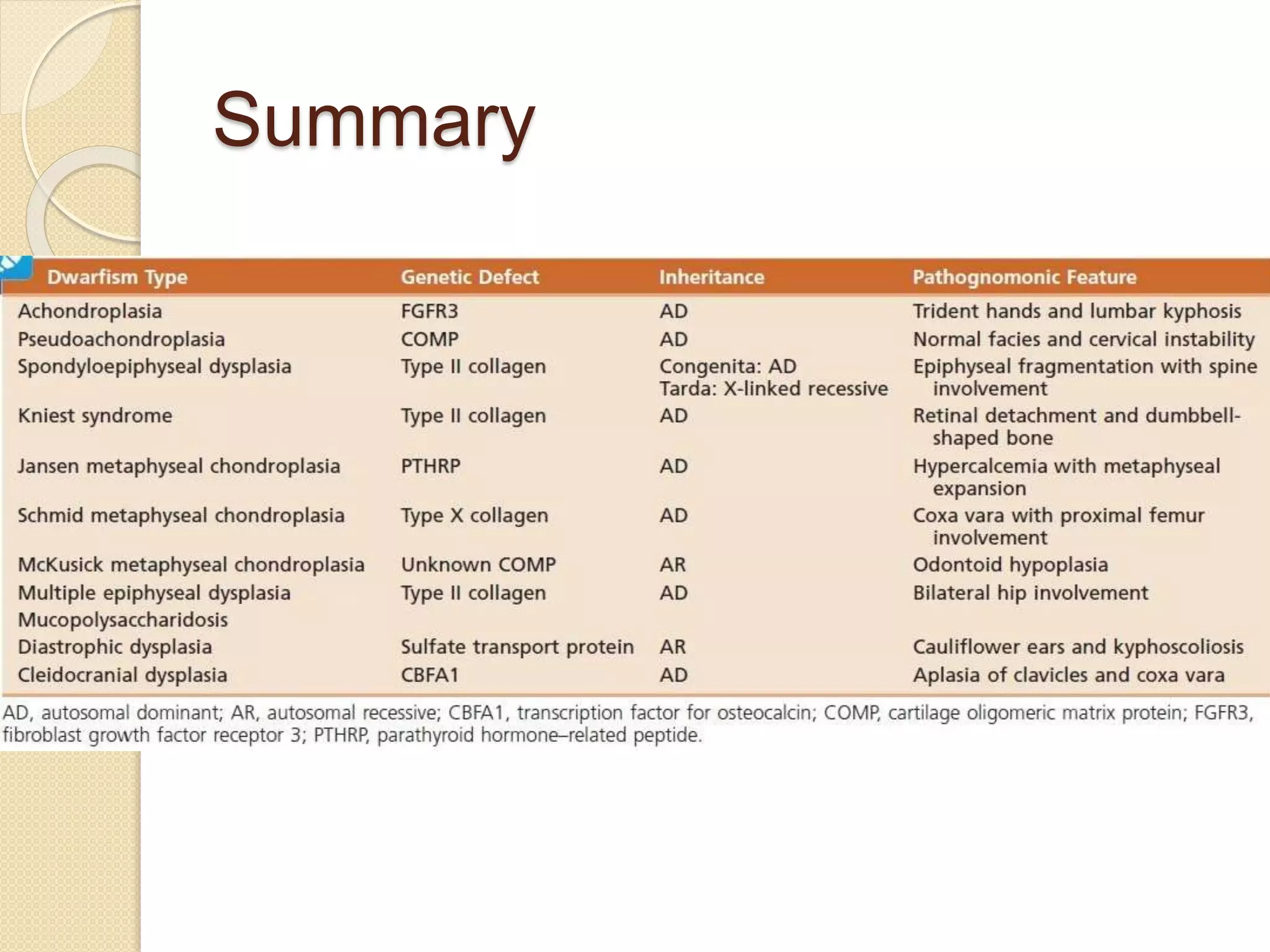
This document provides an overview of dwarfism (bone dysplasias), including classification, causes, signs and symptoms, radiographic findings, and treatment for various types. It discusses proportionate vs disproportionate dwarfism and classifications based on location and source. Specific types covered include achondroplasia, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, chondrodysplasia punctata, Kniest syndrome, metaphyseal chondrodysplasia, multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, and mucopolysaccharidoses. Treatment focuses on managing skeletal deformities and complications.