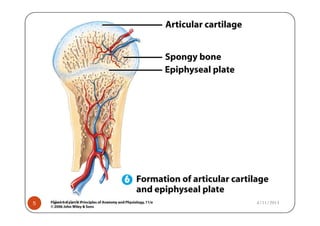
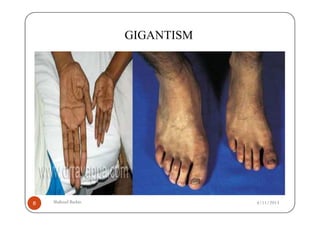
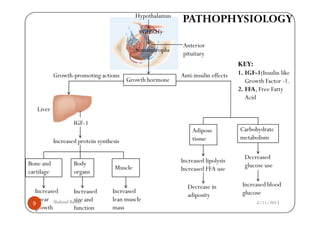
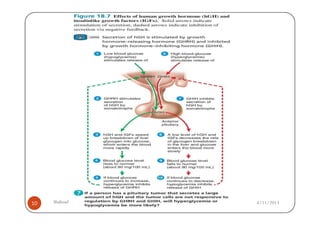
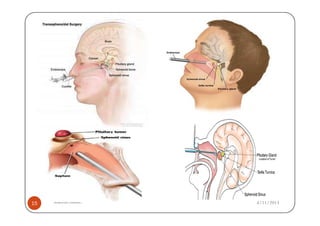
The document defines gigantism as abnormally large growth due to excess growth hormone during childhood, before growth plates close. It describes the pathophysiology of gigantism as being caused by overproduction of growth hormone from a pituitary adenoma, which leads to increased insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels. The clinical features of gigantism include excessive growth, delayed puberty, headaches, and enlarged hands and feet. Diagnostic tests include CT/MRI scans showing a pituitary adenoma, and high levels of growth hormone and IGF-1. Treatment involves surgery to remove the adenoma, radiation therapy, and drug therapy such as bromocriptine.