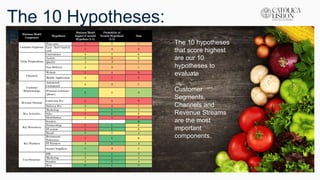
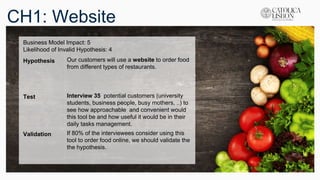
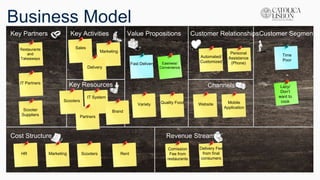
The document outlines a class presentation on validating hypotheses for a business model. It discusses 10 hypotheses for key elements of the business model like customer segments, value propositions, channels, and revenue streams. Each hypothesis is given an impact score and likelihood of being invalid. Methods for testing each hypothesis, such as interviews and surveys, are provided along with criteria for validation. The presentation also includes the business model canvas and lessons learned from developing the project.