Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times




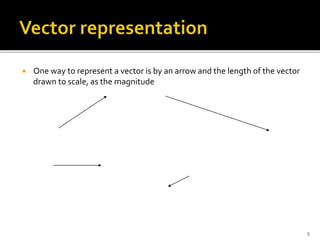


A scalar quantity only has magnitude and no direction, with examples including mass, temperature, and distance. Scalar quantities are added together simply by adding their values. A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction, with examples like force, velocity, and electric current. Vectors can be represented by arrows with length corresponding to magnitude.





