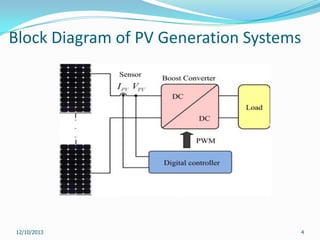
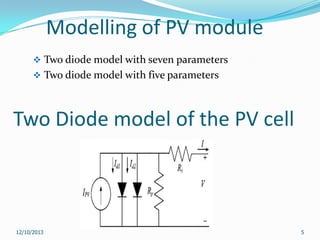
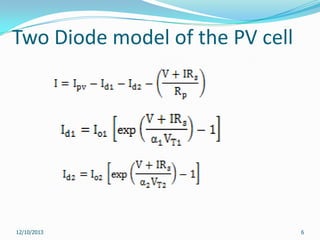
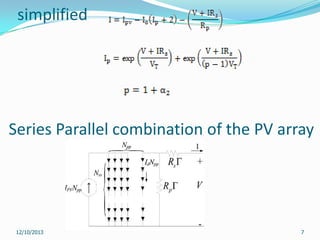
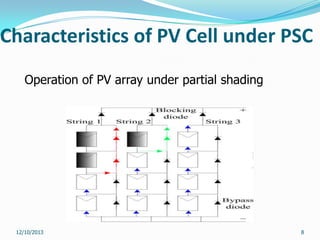
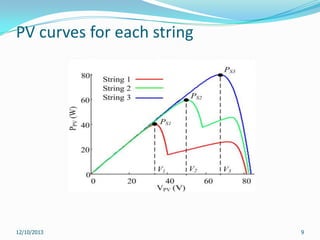
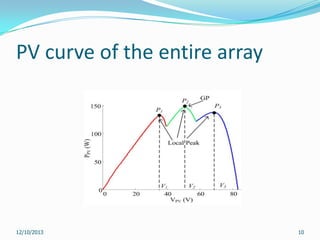
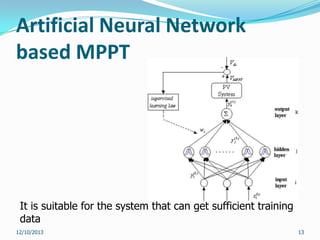
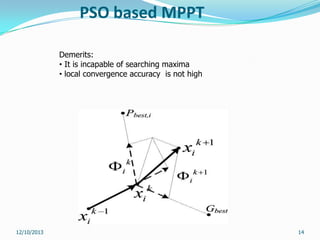
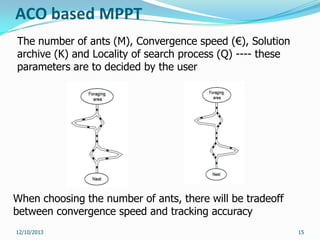
This document reviews maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms for photovoltaic systems. It discusses conventional MPPT techniques like perturb and observe and incremental conductance. It also examines intelligent MPPT techniques using fuzzy logic, artificial neural networks, particle swarm optimization, ant colony optimization, and firefly algorithms. The firefly algorithm is proposed as suitable for partial shaded conditions due to its ability to find the global maximum power point. The document concludes that while conventional MPPT methods have limitations, intelligent techniques have merits and drawbacks, and further research is needed.