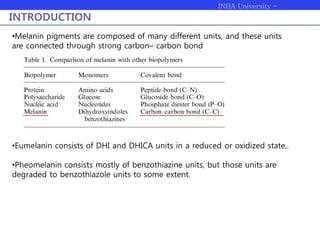
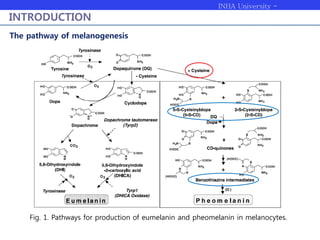
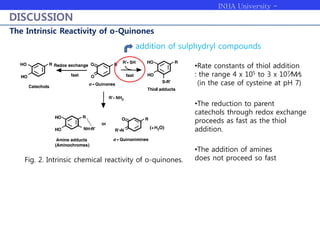
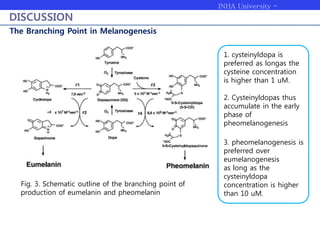
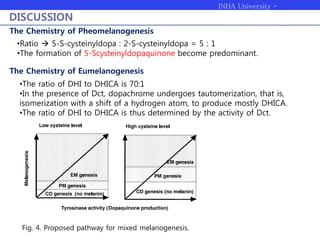
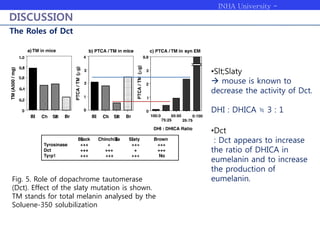
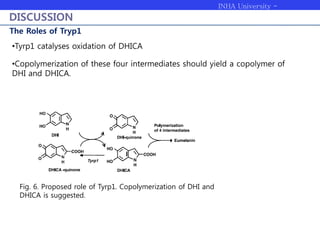
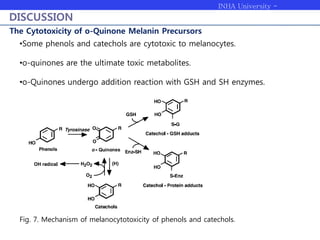
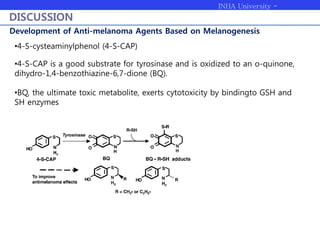
Melanogenesis proceeds in three steps: production of cysteinyldopas, oxidation to pheomelanin, and production of eumelanin. Dopachrome tautomerase (Dct) catalyzes the tautomerization of dopachrome to increase the ratio of DHICA in eumelanin and eumelanin production. The initial production of cysteinyldopas and subsequent pheomelanin favors pheomelanogenesis over eumelanogenesis as long as cysteinyldopa levels remain high. The reactivity of o-quinones, which are highly reactive, chemically controls the early melanogenesis process.