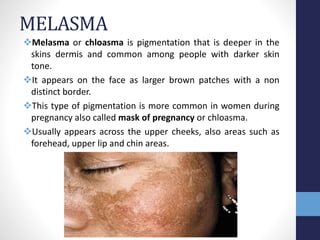
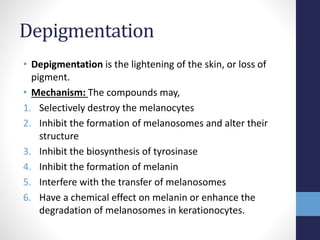
This document provides information on skin pigmentation and disorders of pigmentation. It discusses the role of melanin and melanocytes in determining skin color. The types of melanin and factors influencing their production are described. Common types of hyperpigmentation like freckles, melasma, solar lentigines, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation are summarized. Methods of depigmentation including ingredients that inhibit tyrosinase or melanosome transfer are covered. Hydroquinone formulations and other depigmentation treatments are discussed along with their mechanisms and regulatory status.