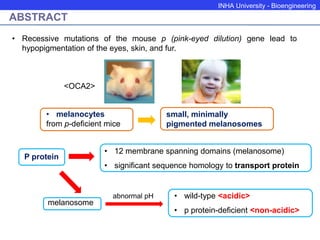
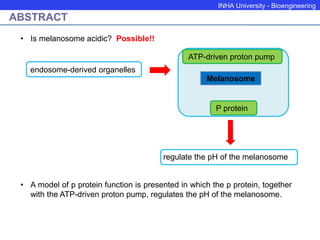
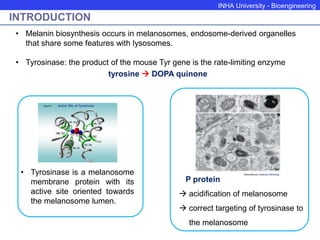
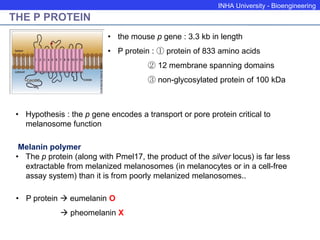
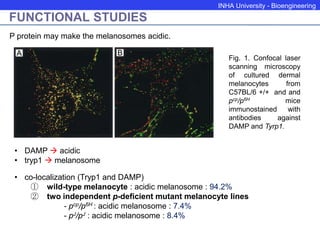
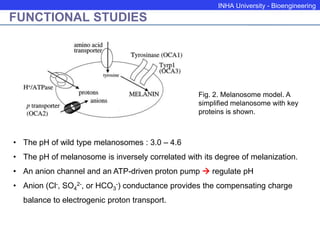
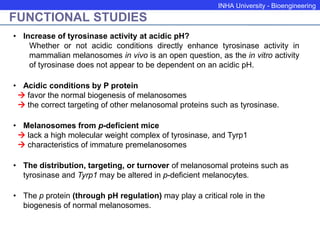
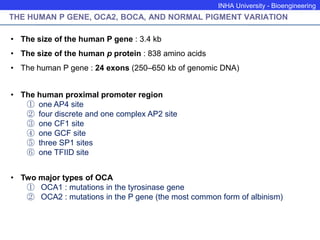
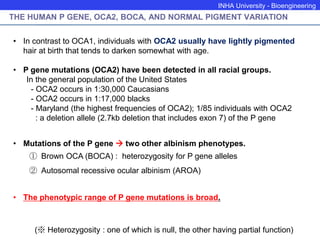
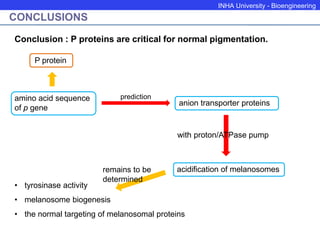
The P protein regulates melanosomal pH through proton transport. Recessive mutations in the P gene lead to hypopigmentation by disrupting melanosomal acidification. The P protein likely functions with a proton pump to acidify melanosomes, favoring tyrosinase activity and melanosome biogenesis. Abnormal pH in P-deficient mice prevents proper targeting of proteins like tyrosinase, resulting in underpigmented melanosomes. The human P gene is homologous and causes oculocutaneous albinism when mutated.