The study aimed to investigate the hypothesis that the P protein influences tyrosine and tyrosinase localization. The results showed that tyrosine transport was not different between wild-type and P mutant melanocytes. While total tyrosinase activity was higher in P mutant cells, tyrosinase localization to melanosomes was impaired. This indicates that P protein plays an important role in localizing and stabilizing tyrosinase in melanosomes, rather than transporting tyrosine.

![The pink-eyed dilution phenotype in mice arises from mutations in the p gene; in
humans, analogous mutations in the P gene result in oculocutaneous albinism
type 2. Although the molecular mechanisms which underlie this phenotype remain
obscure, it has been postulated that mutations in p result in defective tyrosine
transport into murine melanosomes, resulting in hypopigmentation and
diminished coat color. However, we previously reported no difference in
melanosomal tyrosine transport in unpigmented, melanoblast-like pinkeyed
dilution (pcp/pcp), and in pigmented (melan-a) murine melanocytes. In this study,
we utilized melan-p1 cells, more differentiated pink-eyed dilution ( pcp/p25H)
melanocytes which can be induced to produce melanin, to characterize the
melanogenic lesion(s) more definitively. Uptake of [3H]tyrosine into melan-a
melanosomes did not differ significantly from uptake into melanosomes derived
from melan-p1 melanocytes, further arguing against its critical role as a tyrosine
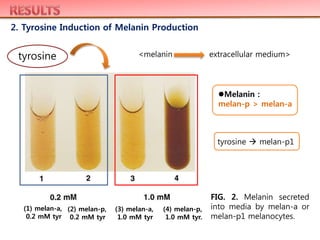
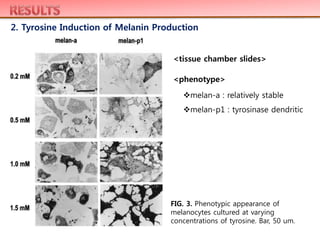
transporter. Pink-eyed dilution melanocytes incubated in high tyrosine
concentrations became extremely pigmented as they became confluent and
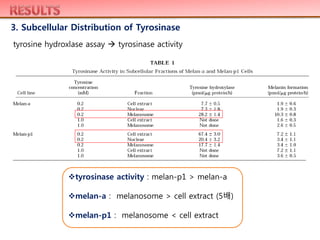
secreted large amounts of black material into the medium. Total cellular tyrosinase
activity in melan-p1 melanocytes was significantly higher than that in melan-a
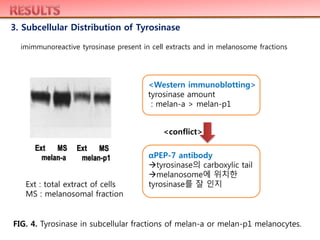
melanocytes (which are wild-type at the p locus), but the localization of tyrosinase
to melanosomes was impaired in melan-p1 melanocytes compared to melan-a
melanocytes. These results indicate that mechanisms other than deficient tyrosine
transport are involved in the pink-eyed dilution phenotype and that this protein
may serve a chaperone-like or stabilizing function in melanocytes. © 1998
Academic Press](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/130323paperstudy-140516034140-phpapp01/85/130323-paper-study-2-320.jpg)
![ Cell culture : wild-type : Melan-a (a/a, p/p) C57BL/6 mice
P mutant : Melan-p1 (a/a, pcp/p25H) pink eyed dilution mice
Tyrosine transport assays : [3H-tyrosine]
Subcellular fractionation : tyrosine transport assay, tyrosinase activity
Light microscopy
Enzyme assays and protein determinations : tyrosine hydroxylase assay
Western immunoblotting analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/130323paperstudy-140516034140-phpapp01/85/130323-paper-study-5-320.jpg)
![1. Tyrosine Transport Studies
FIG. 1. [3H]Tyrosine uptake
into melanosomes derived
from melan-a or melan-p1
melanocytes.
darker bars : melan-a
lighter bars : melan-p1
melan a와 melan-p는 별 차이가 없다.
tyrosine transport : 50uM이 10uM 약 2배
tyrosine transport X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/130323paperstudy-140516034140-phpapp01/85/130323-paper-study-6-320.jpg)