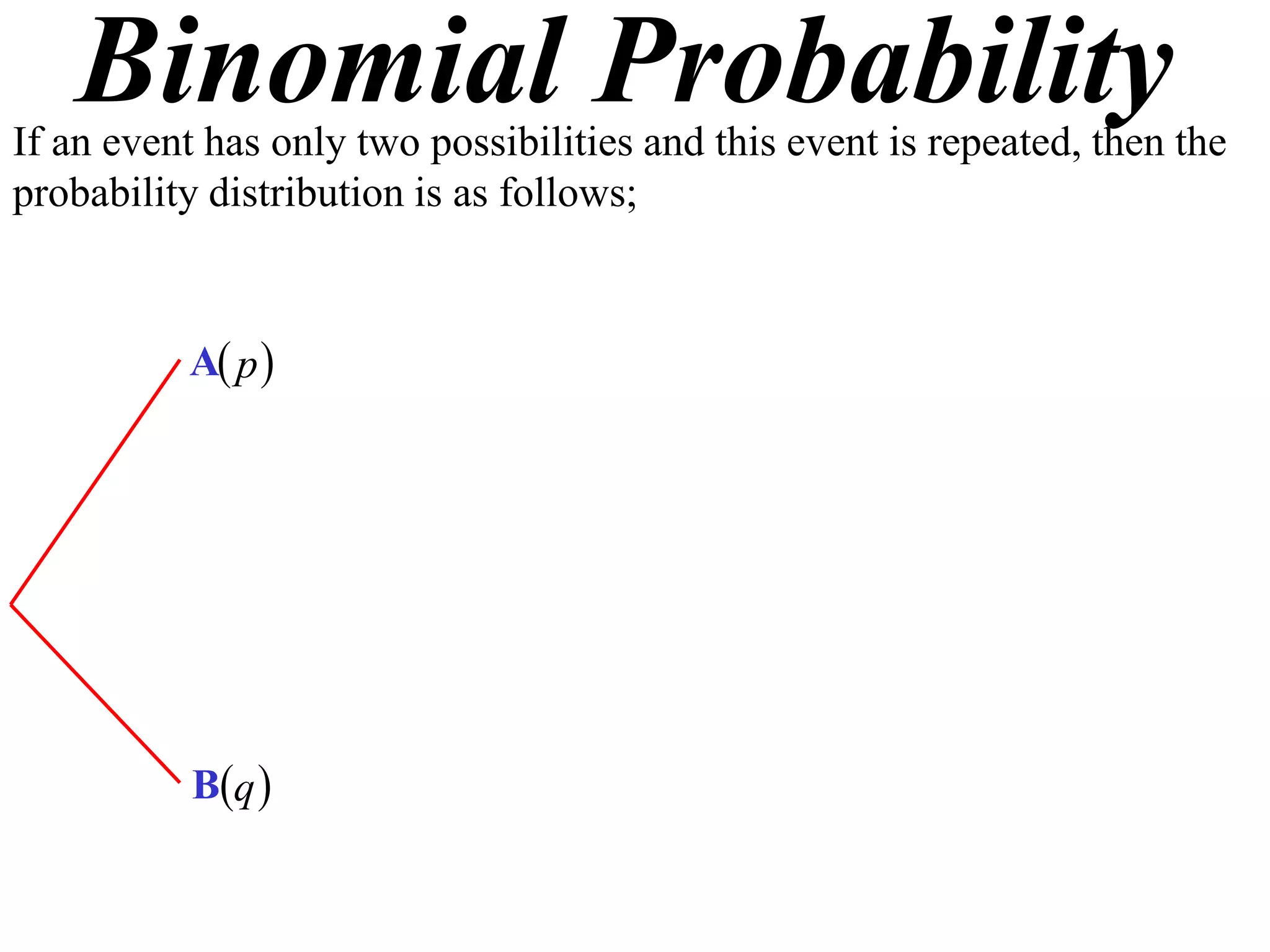
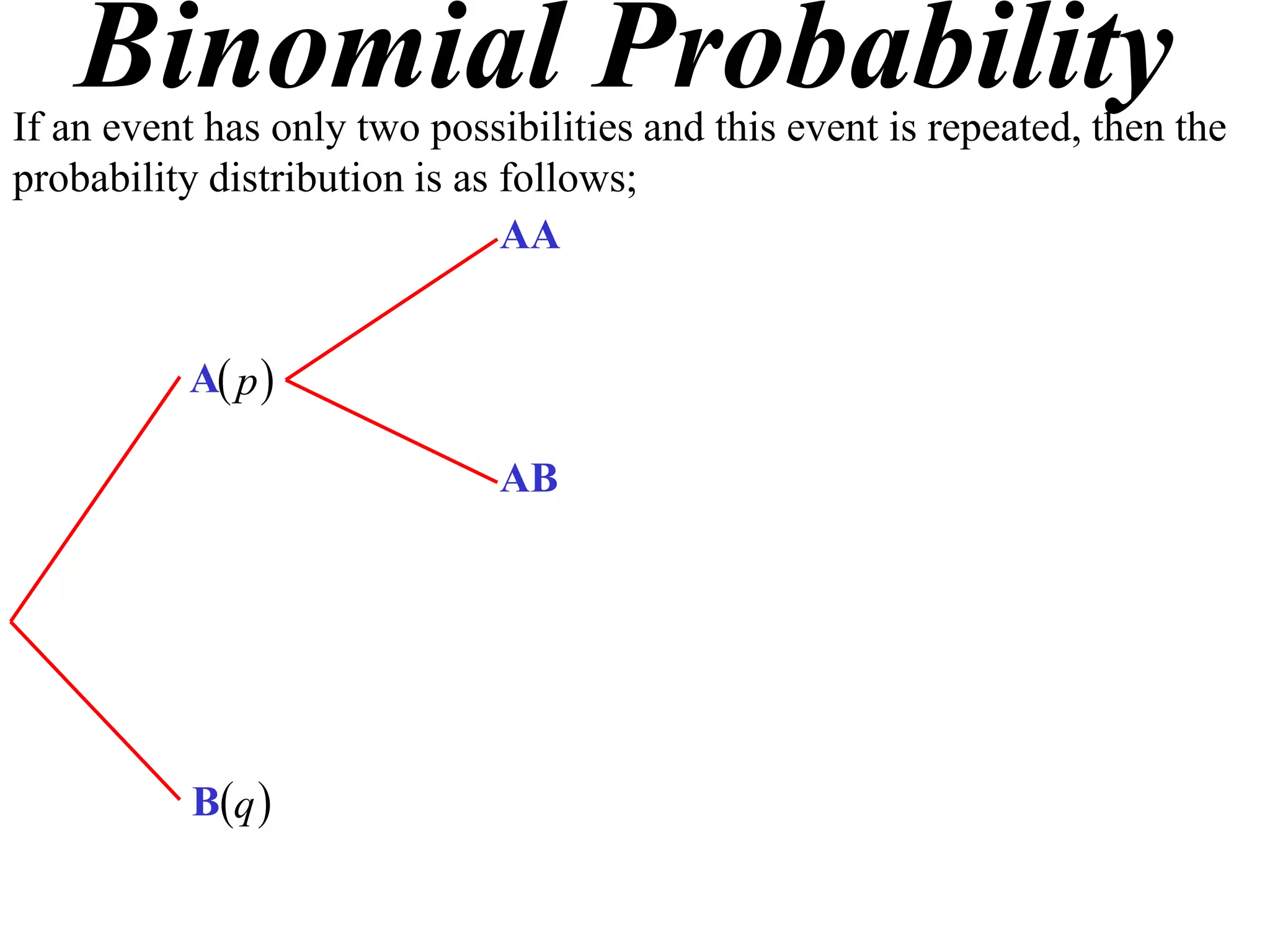
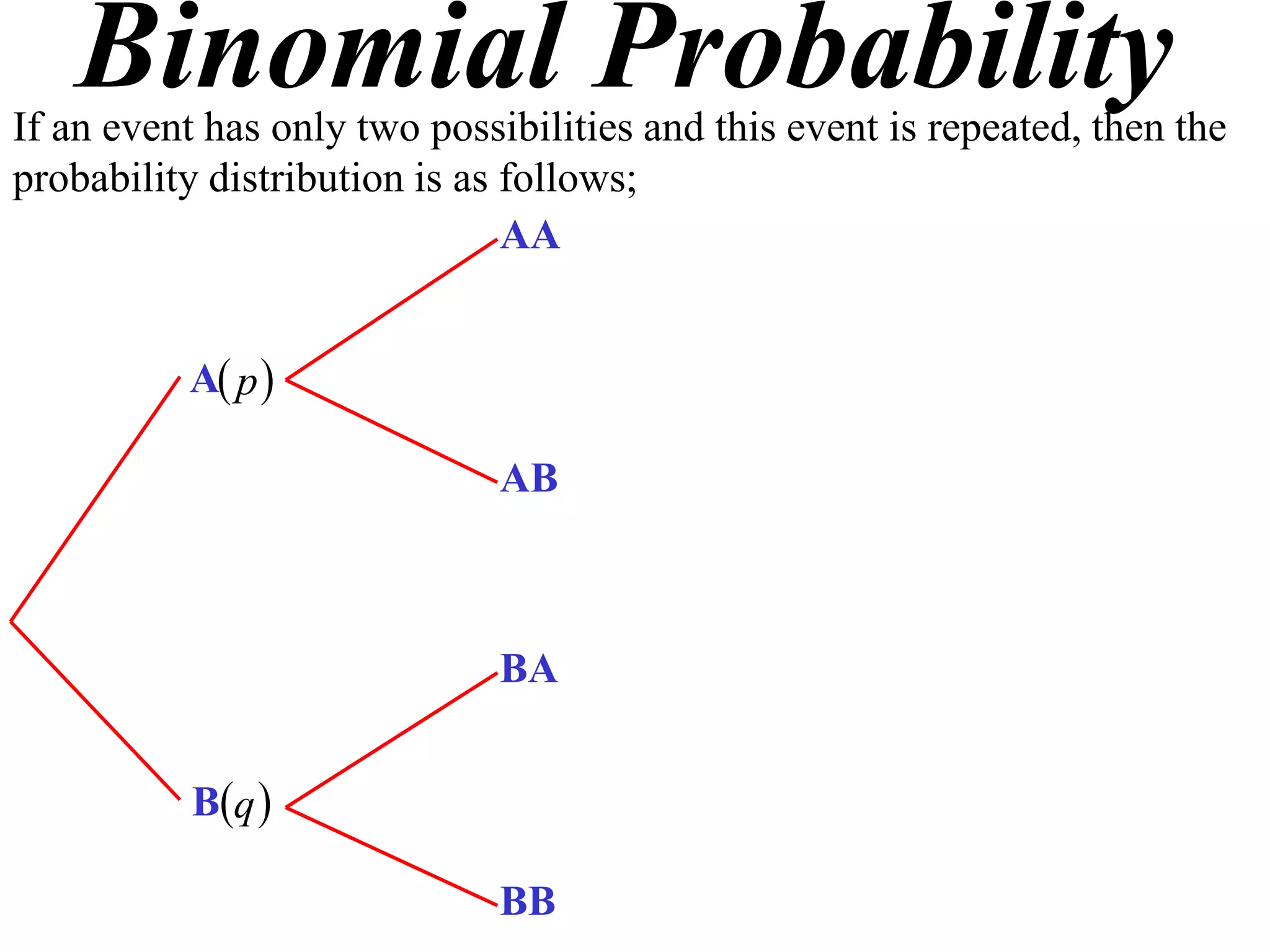
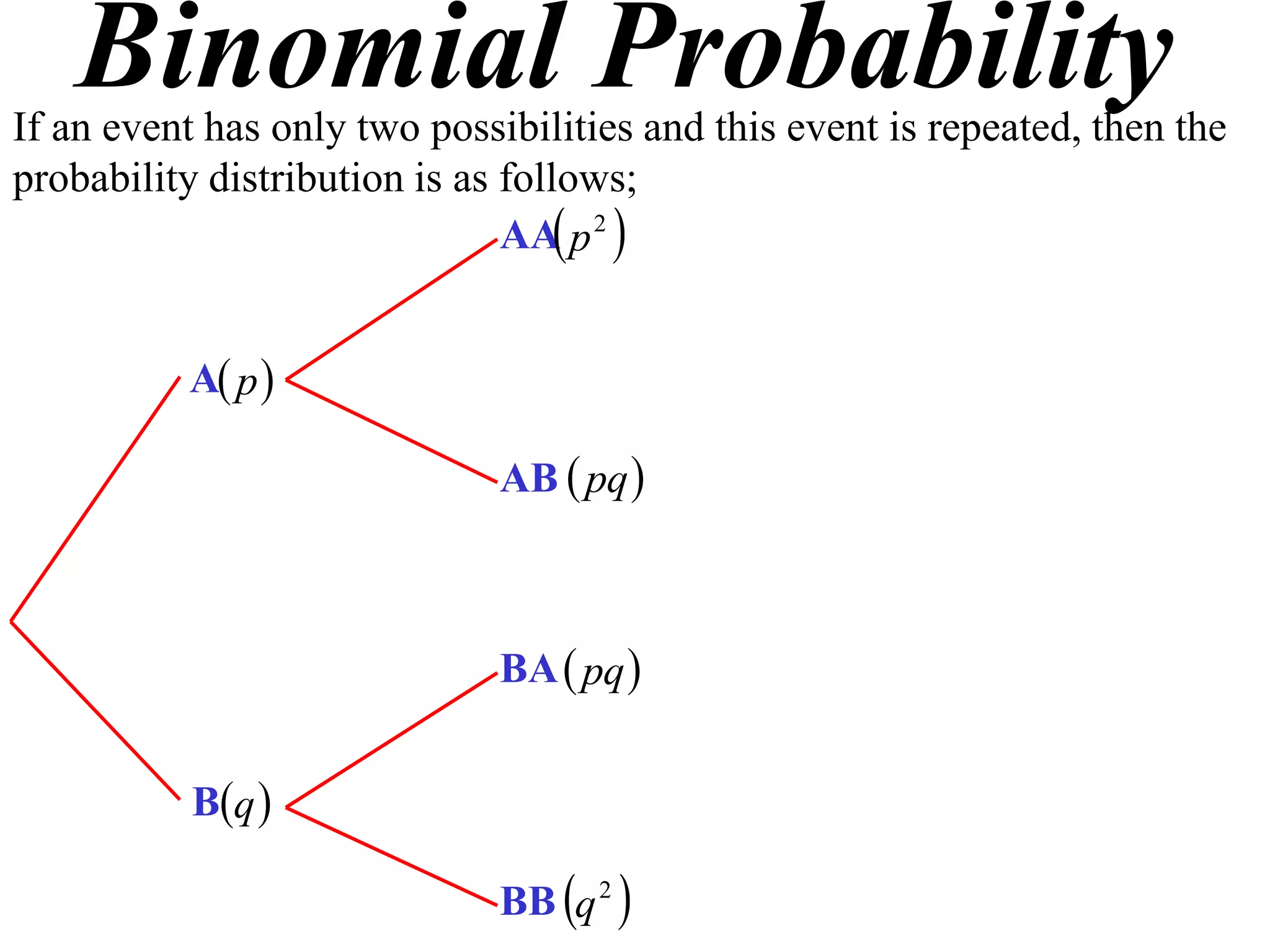
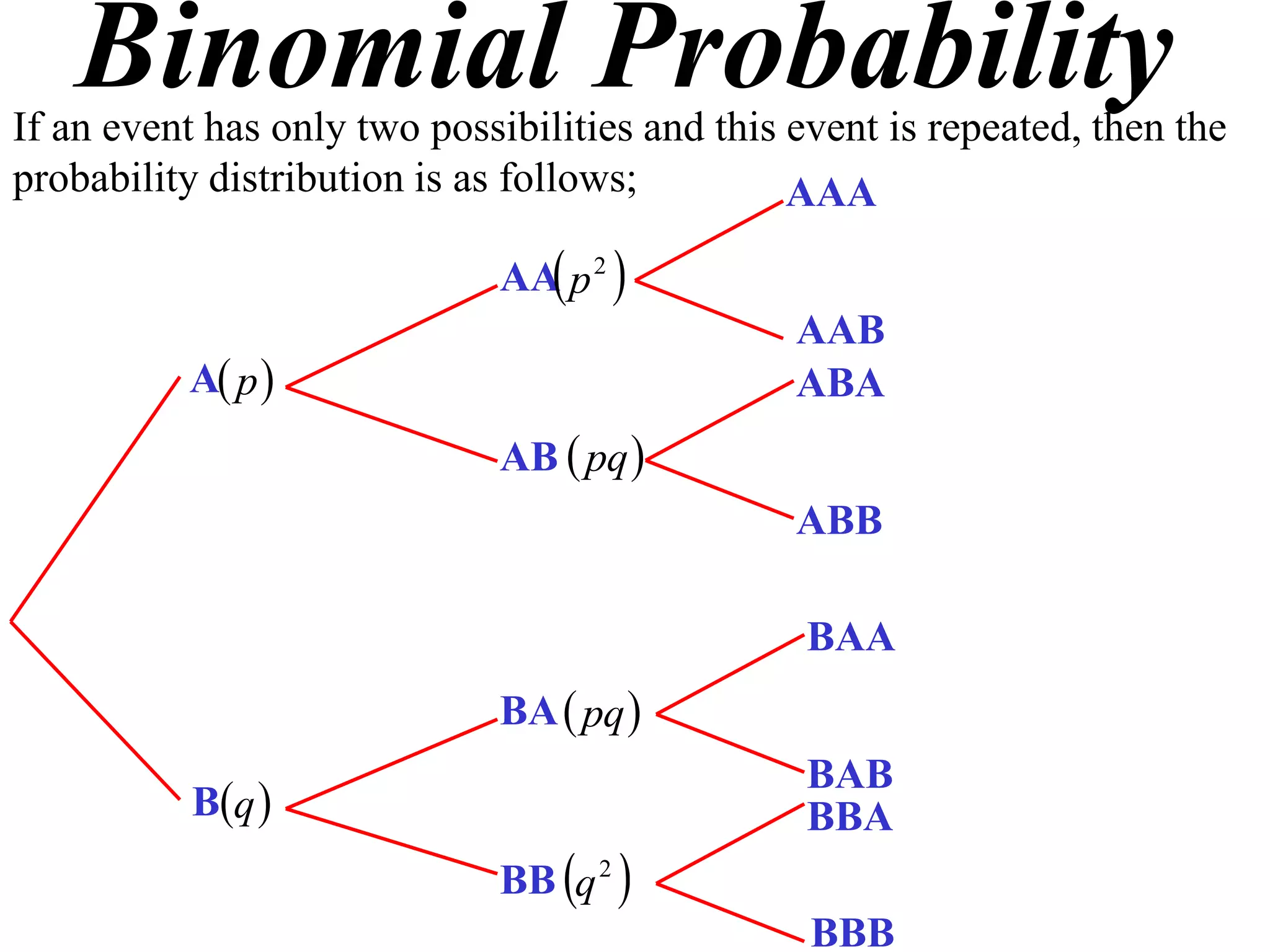
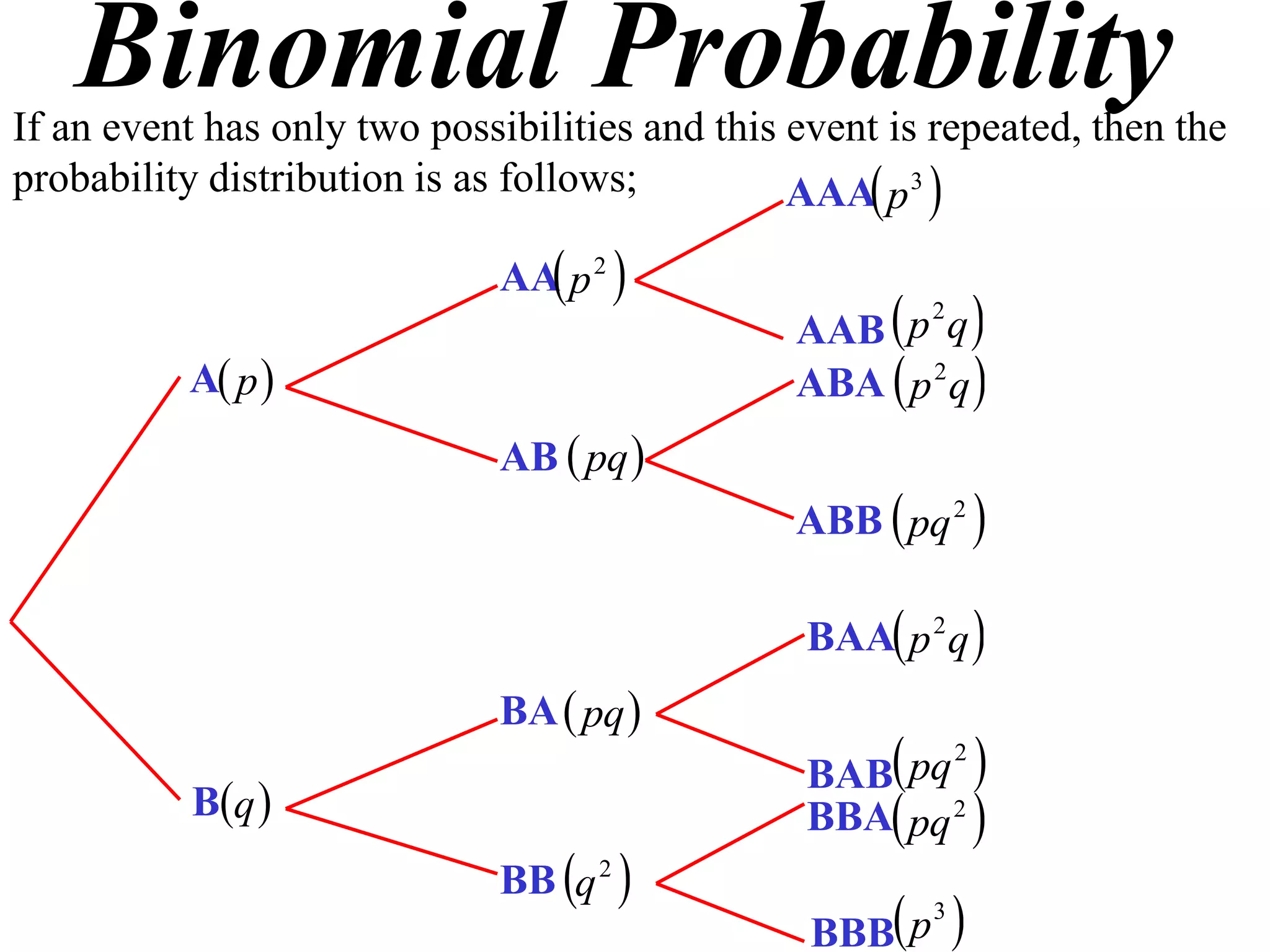
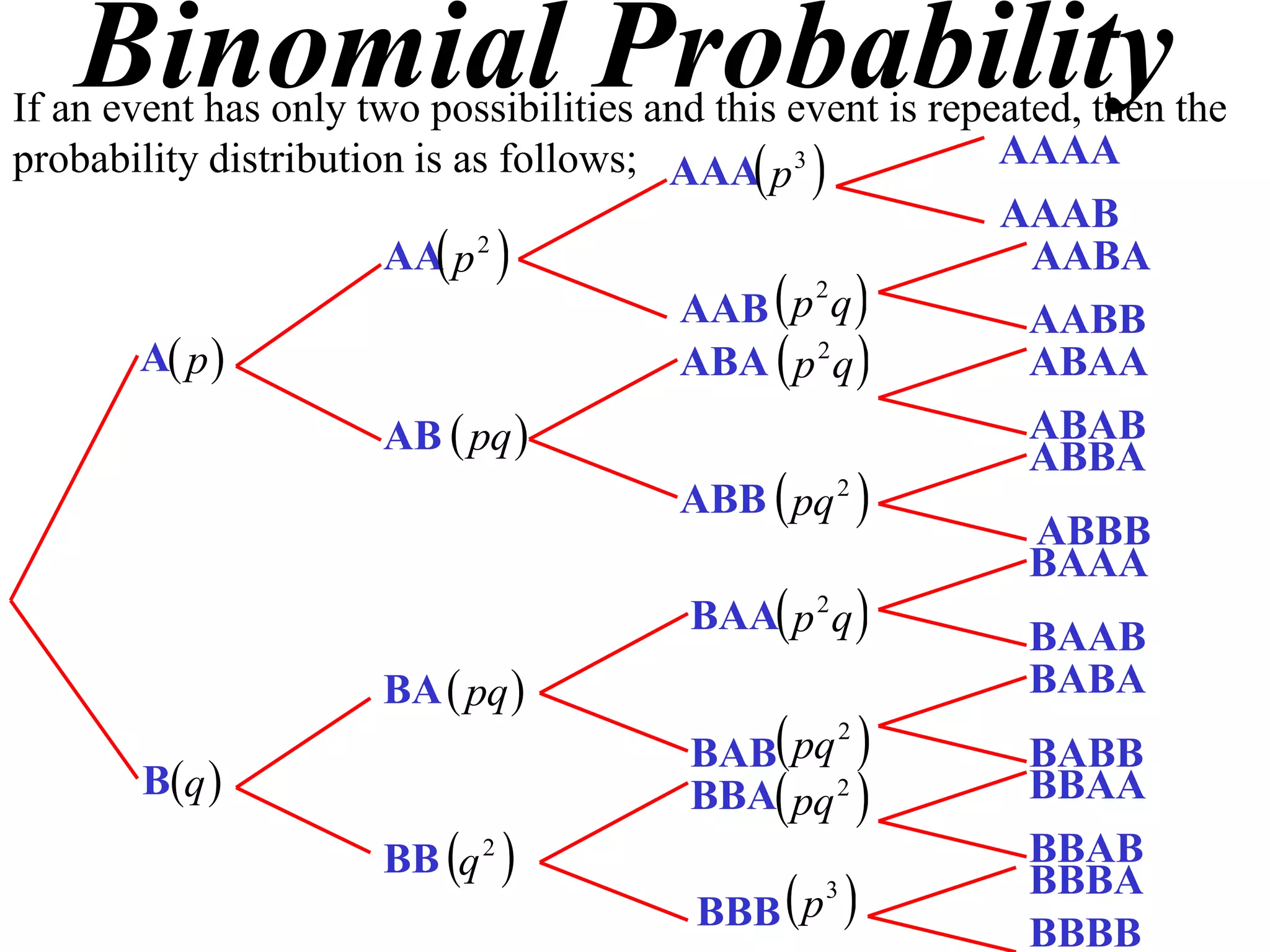
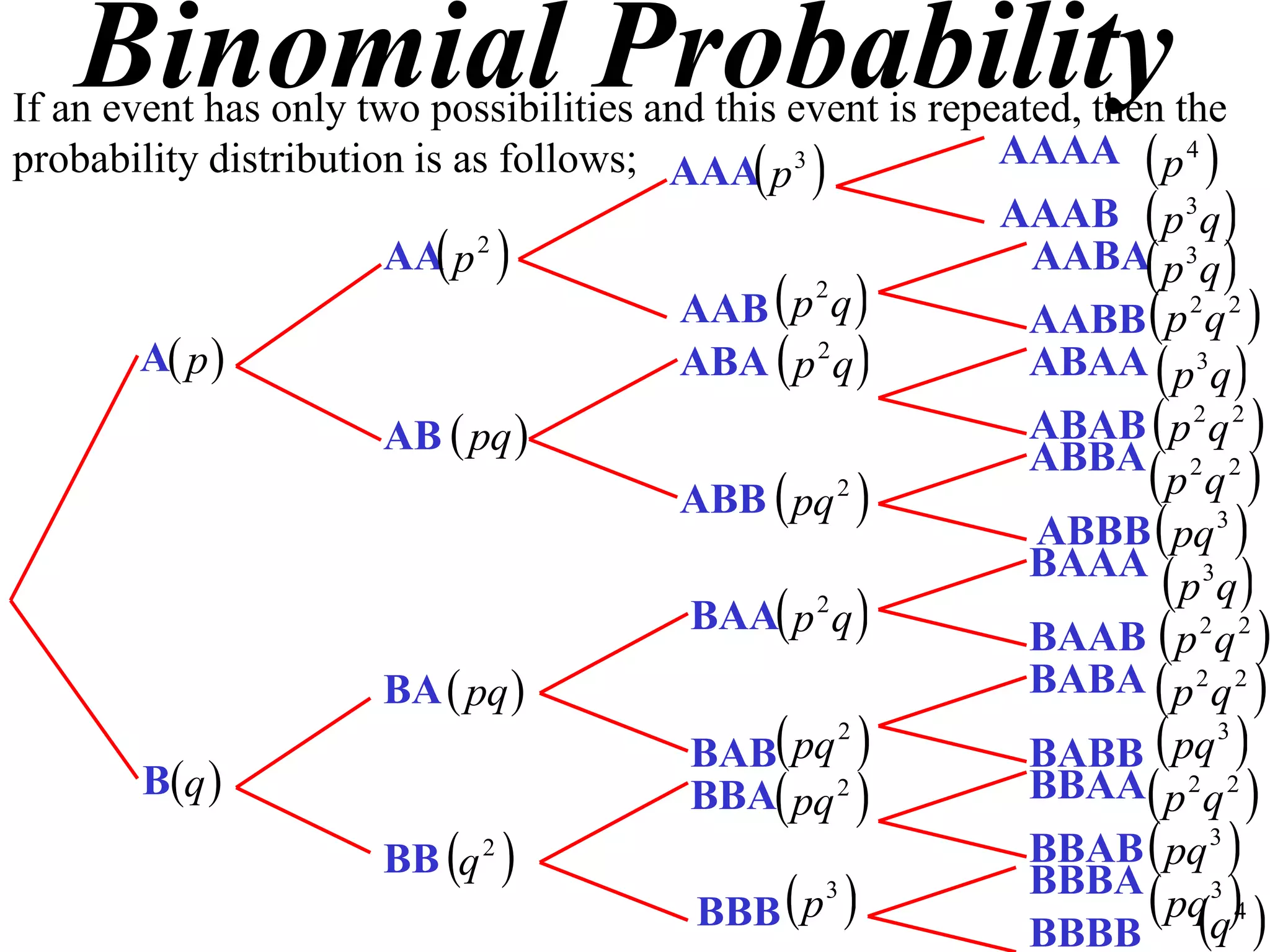
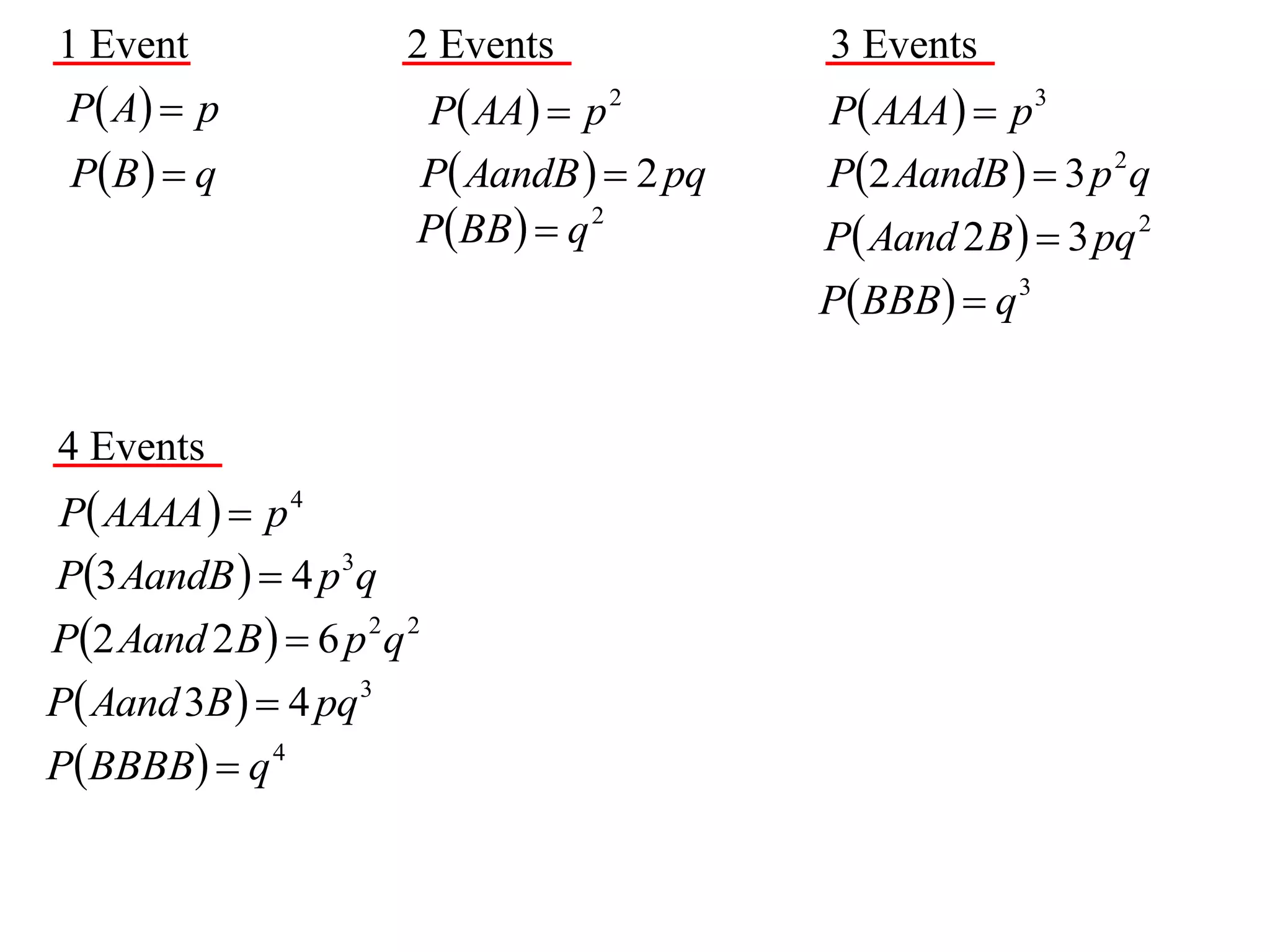
The document discusses binomial probability distributions. It explains that if an event has two possible outcomes and is repeated, the probability of each outcome follows a binomial distribution. It provides examples of calculating binomial probabilities for 1, 2, 3, and 4 events. The key points are:
- Binomial probabilities use the formula P(X=k) = nCk * pk * (1-p)(n-k)
- Where X is the number of successes, n is the number of trials, p is the probability of success on each trial, and q is the probability of failure.
- It illustrates calculating binomial probabilities for examples like drawing balls from a bag.