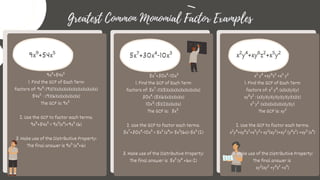
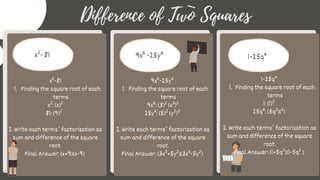
El documento detalla técnicas de factorización de polinomios, incluyendo trinomios cuadráticos, factores comunes monomiales, diferencia de cuadrados y trinomios cuadrados perfectos. Se explican los pasos necesarios para identificar y aplicar estas técnicas a diferentes tipos de polinomios, así como ejemplos de cada método. Además, se proporcionan ejercicios prácticos y claves de respuesta para mejorar la comprensión.