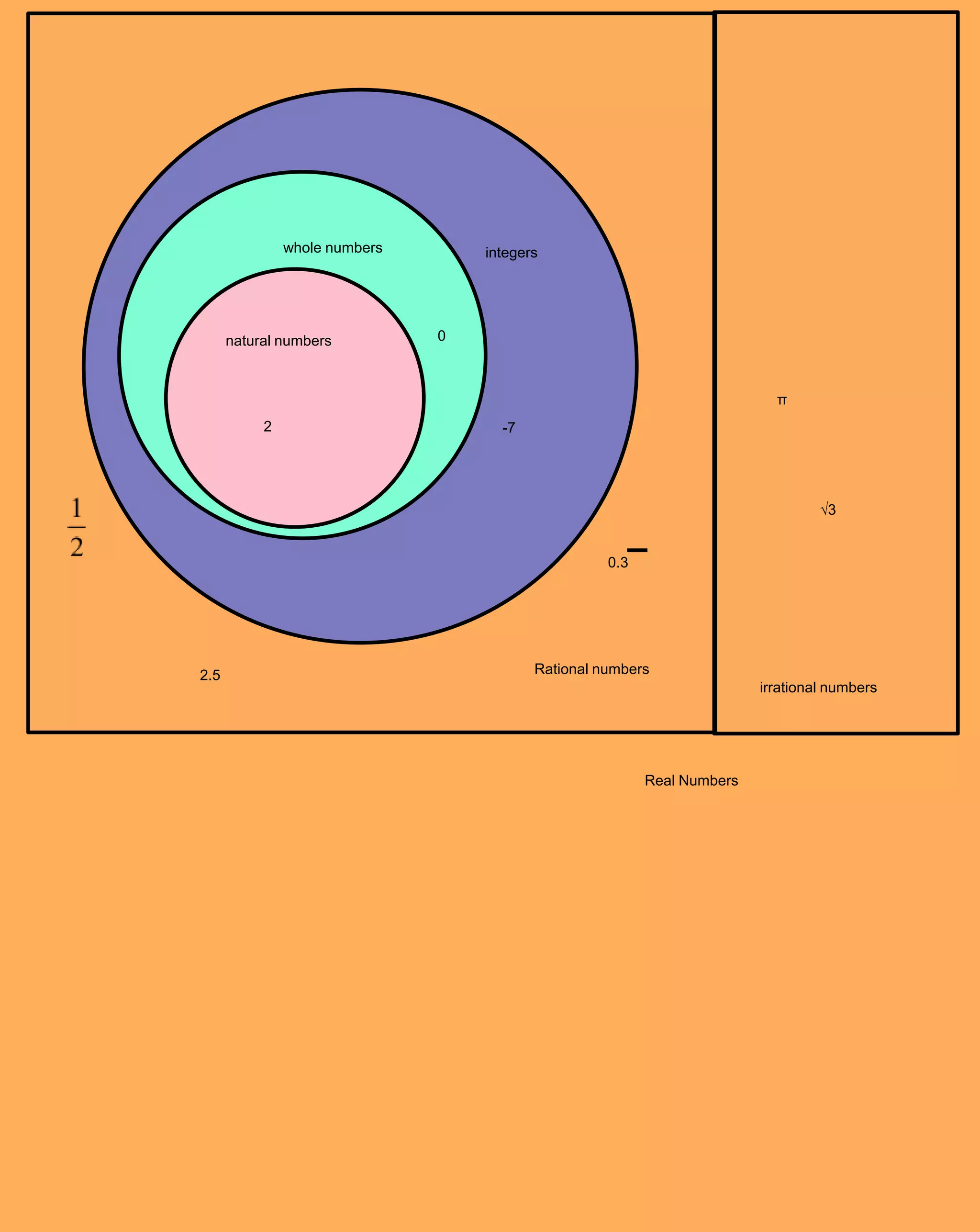
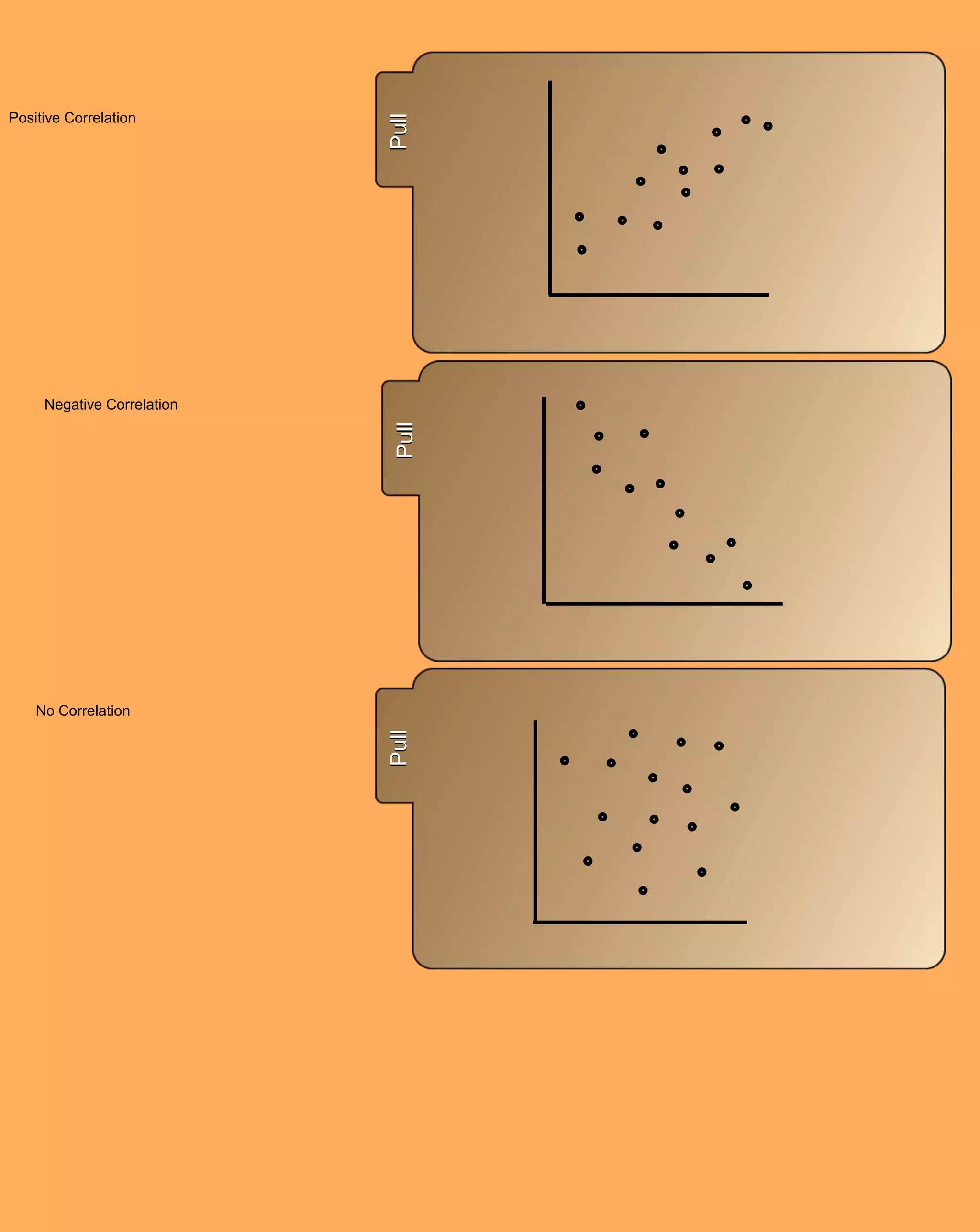
The document contains notes from Chapter 1 on algebra topics including: variables, expressions, equations, exponents, order of operations, real numbers, patterns and functions, scatter plots, and measures of central tendency. Lesson topics include using variables, exponents and order of operations, exploring real numbers, patterns and functions, scatter plots, and defining mean, median, mode, range and outliers. Examples are provided for writing expressions and equations, simplifying expressions, identifying functions, and calculating mean, median and mode.








![Examples
4[(2 * 9) + (15 ÷ 3)]
4[(18) + (5)]
4(23)
92
End](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algebra1chapter1completenotes-100919153859-phpapp02/75/Algebra-1-chapter-1-complete-notes-9-2048.jpg)