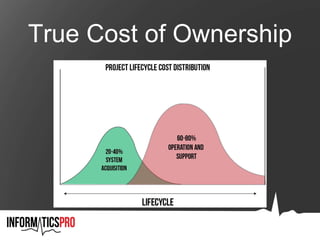
The document outlines the system selection and implementation lifecycle, detailing the critical steps from determining requirements to transitioning or decommissioning the system. It emphasizes the importance of an RFP process, assembling an implementation team, and developing a comprehensive plan, including user training and evaluation methods. It concludes with guidelines for obtaining feedback and assessing the system's effectiveness in meeting organizational goals.