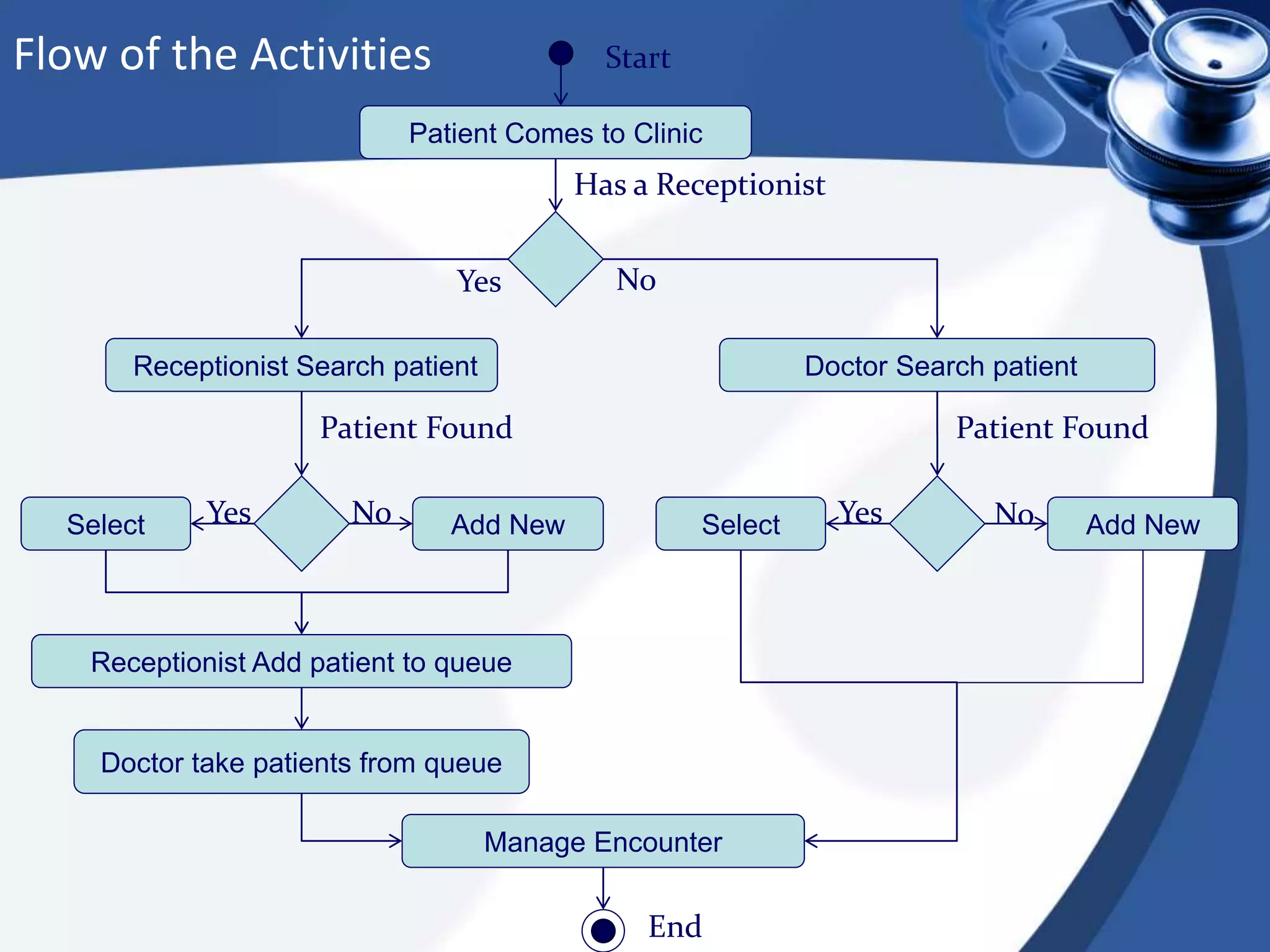
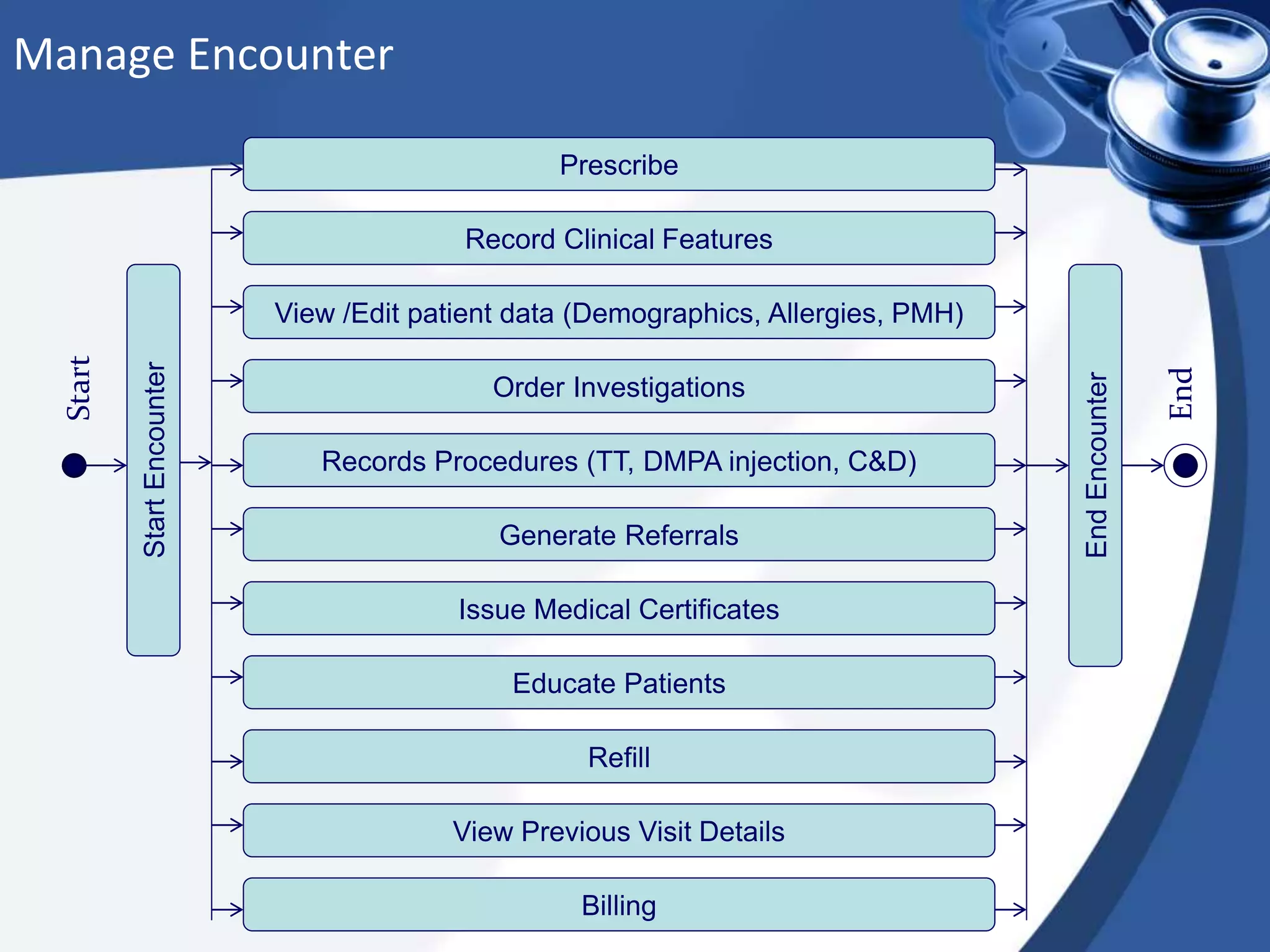
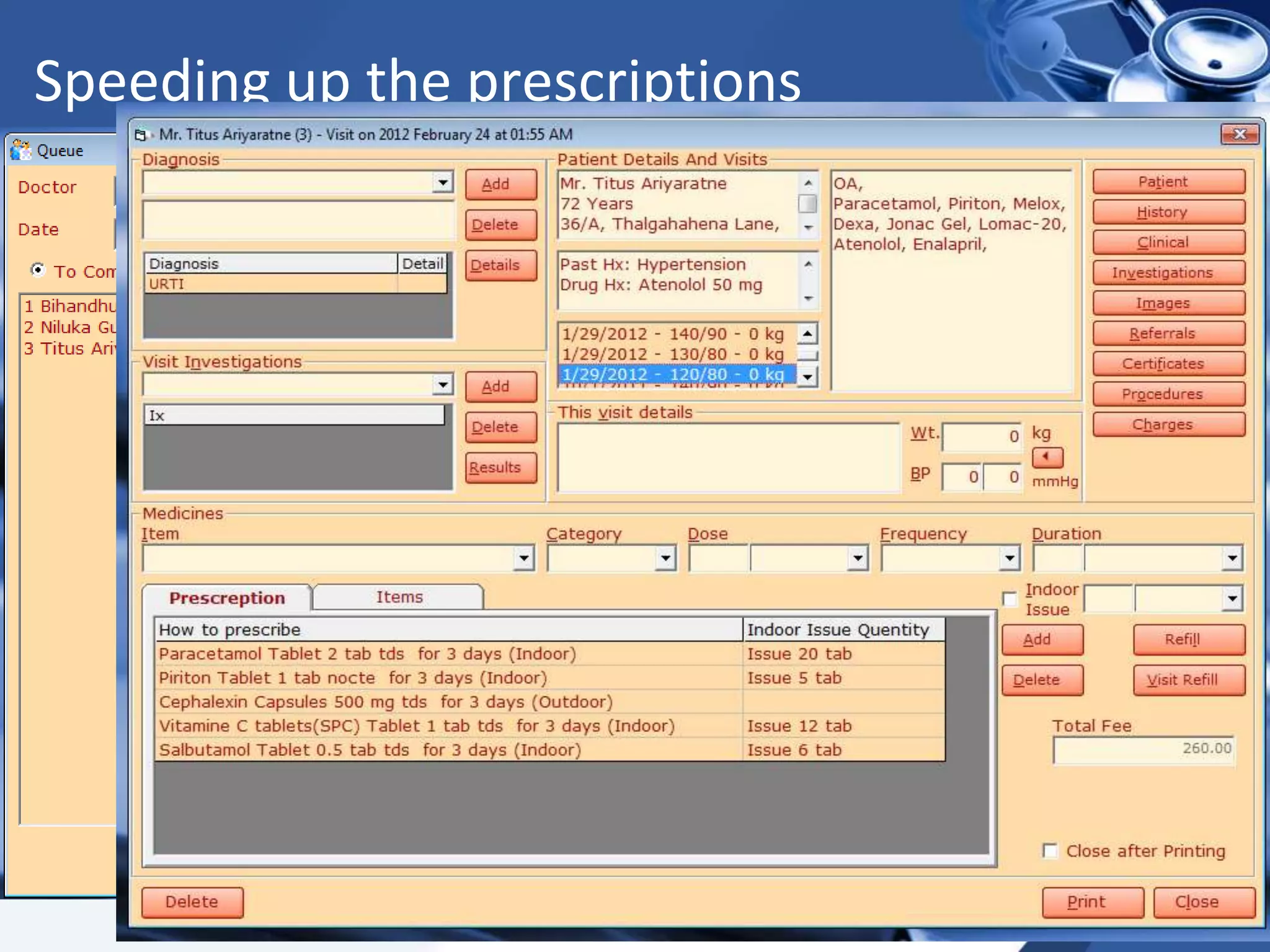
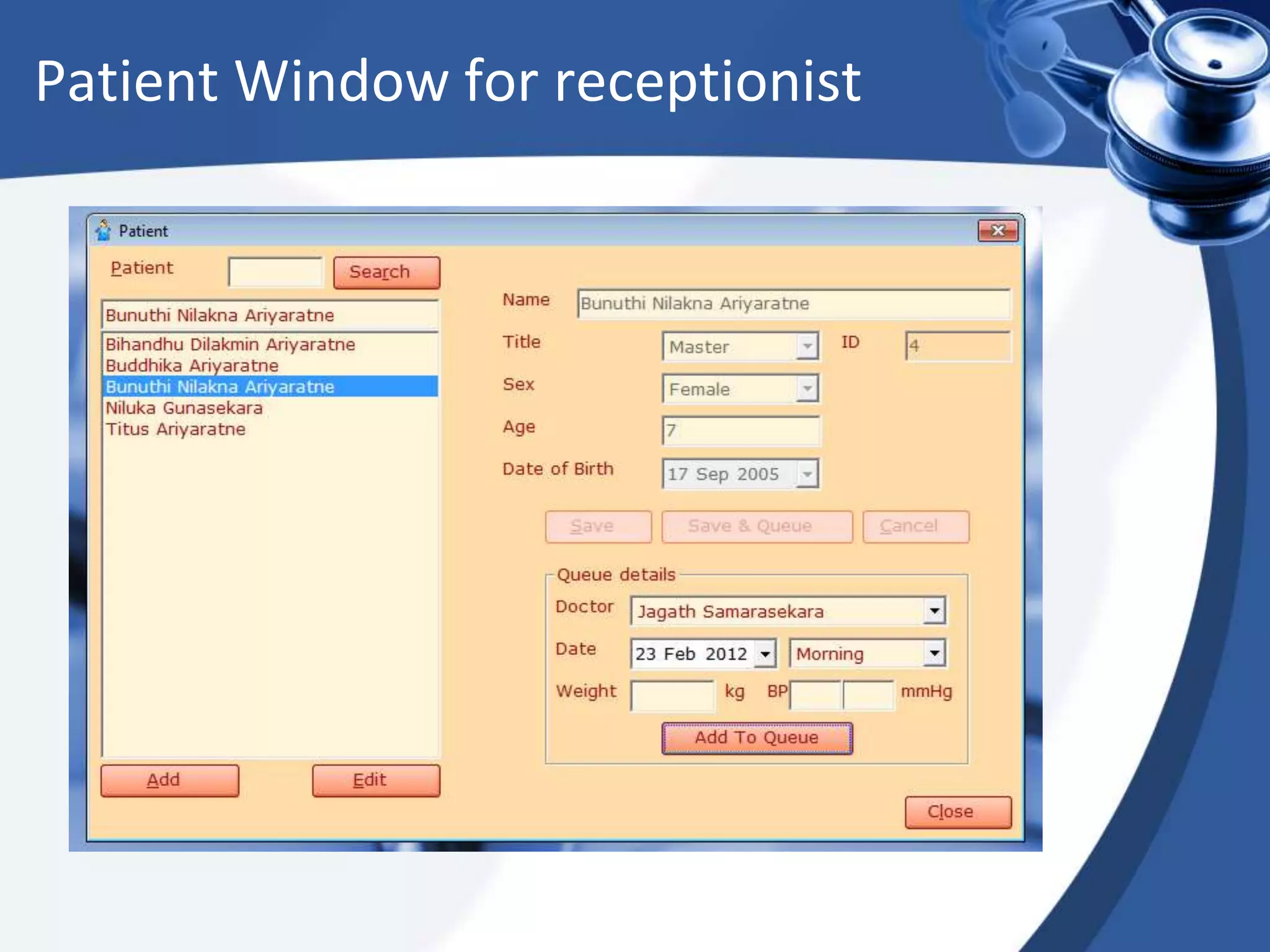
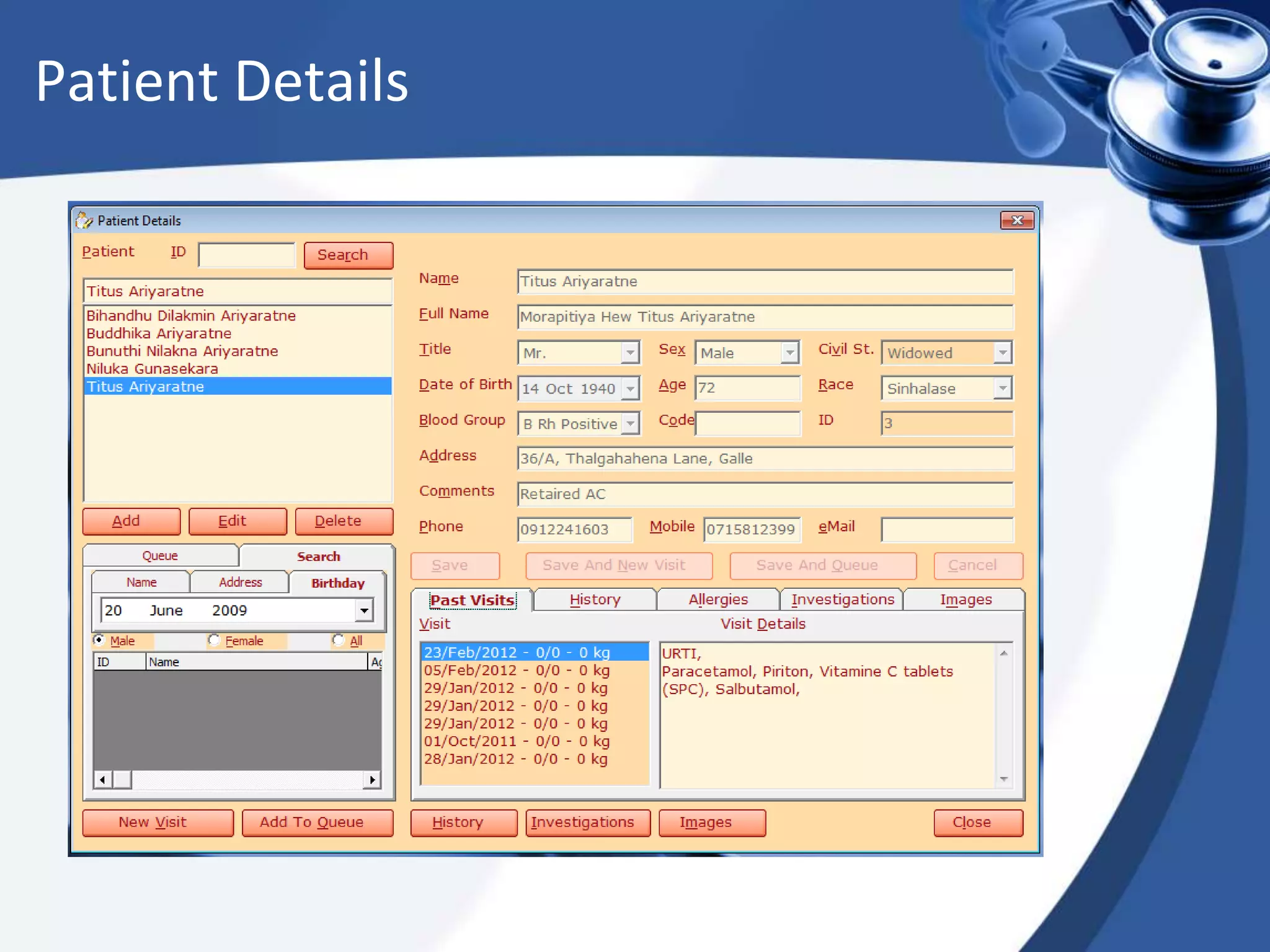
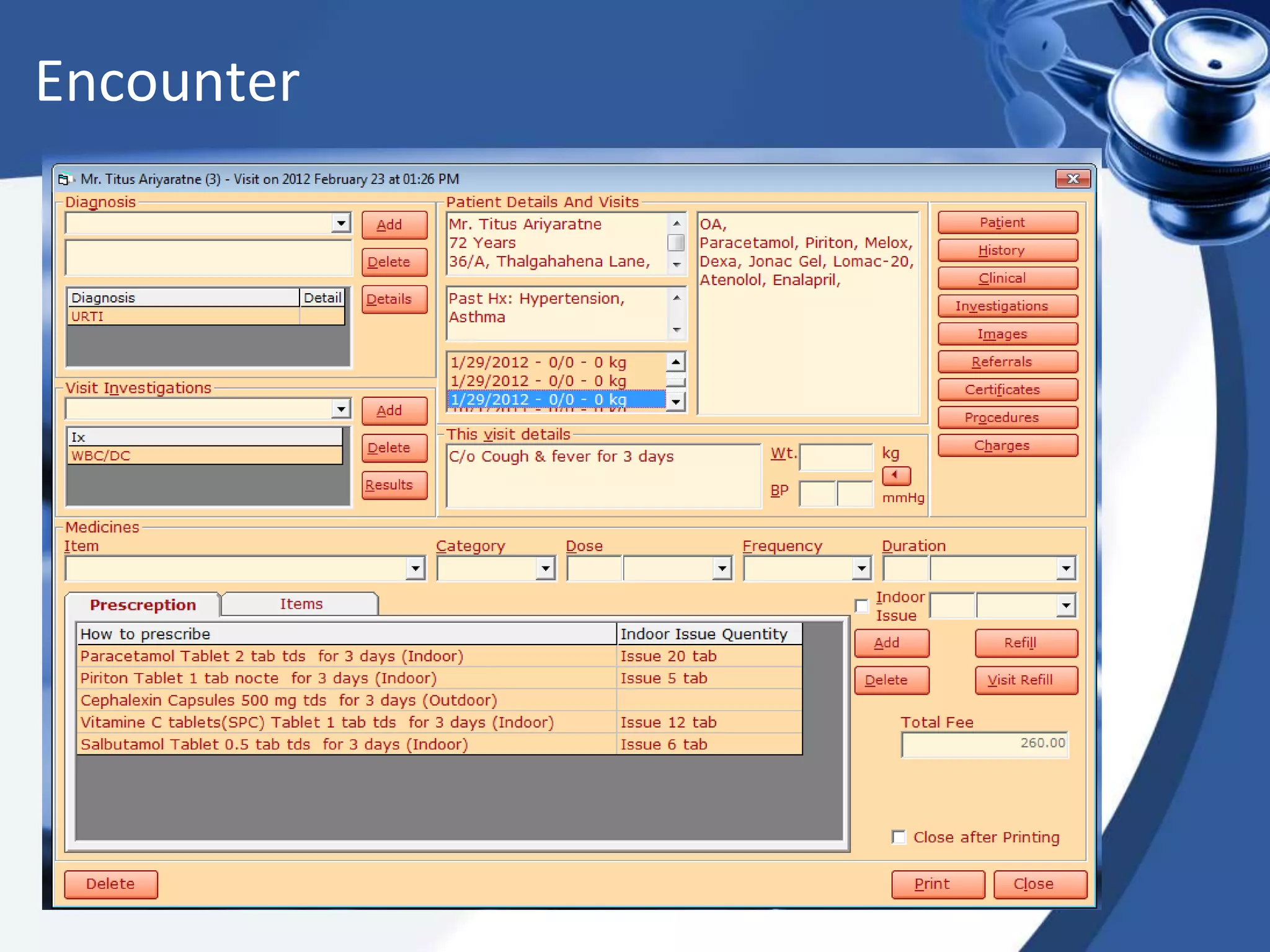
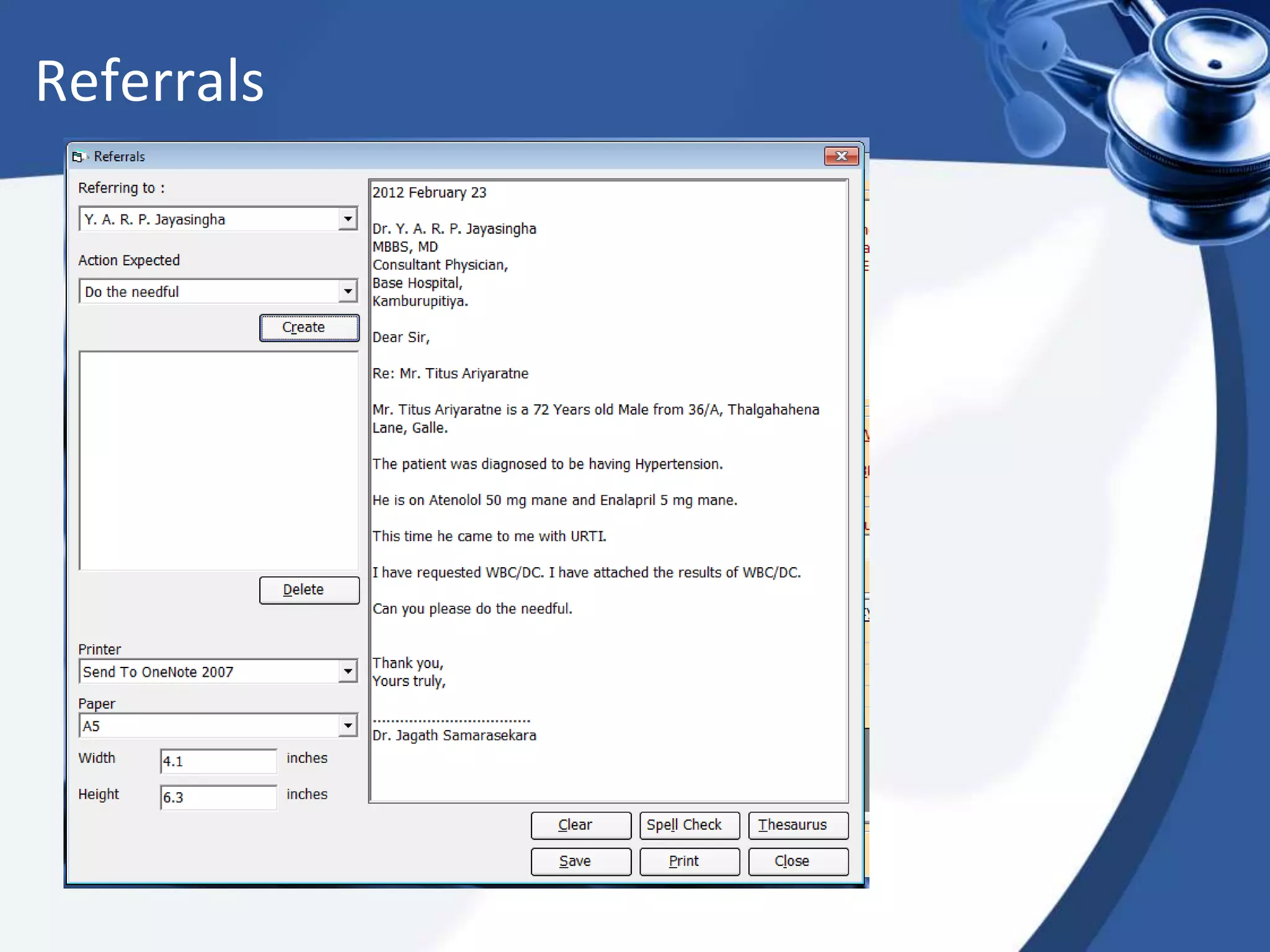
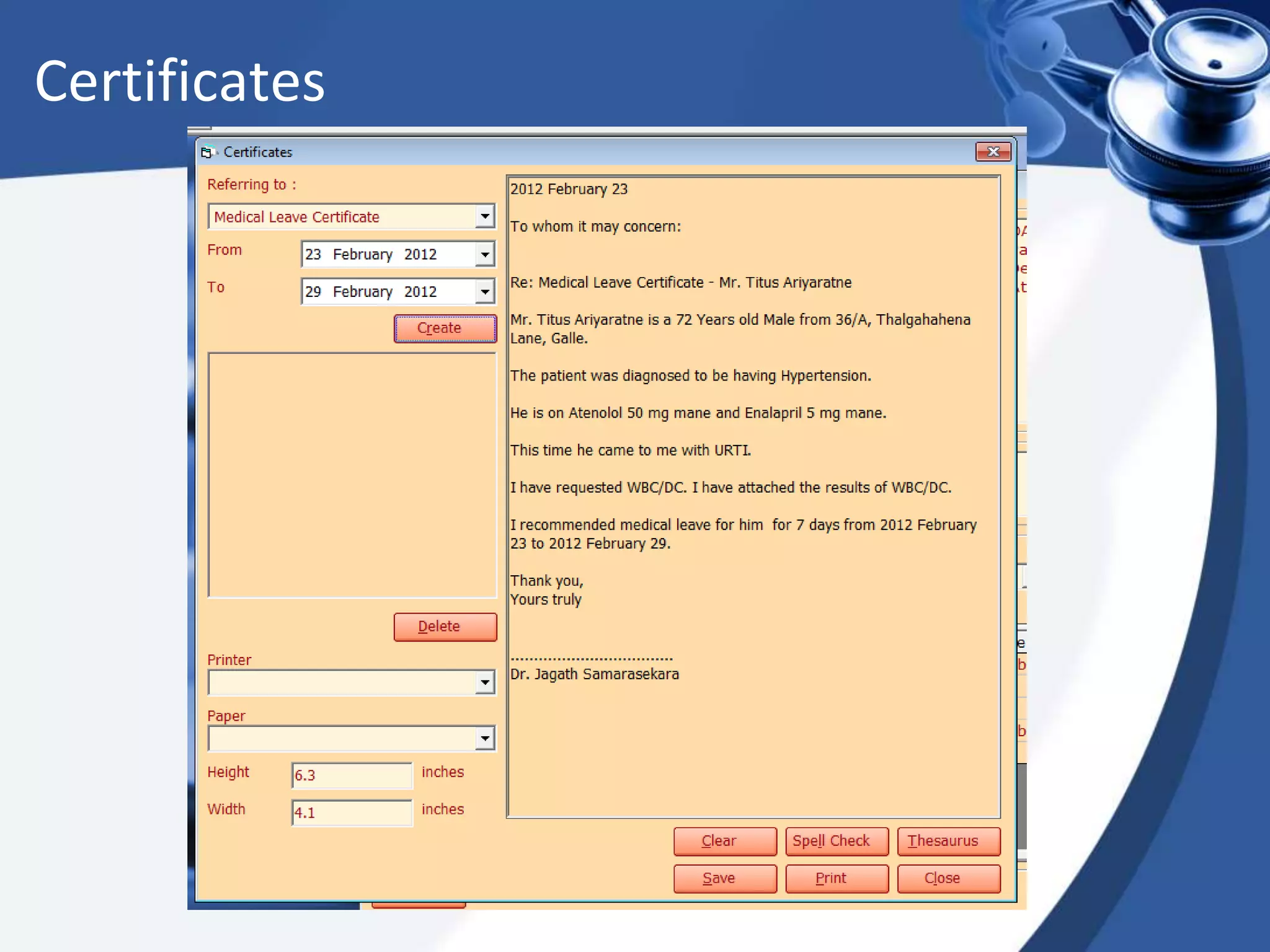
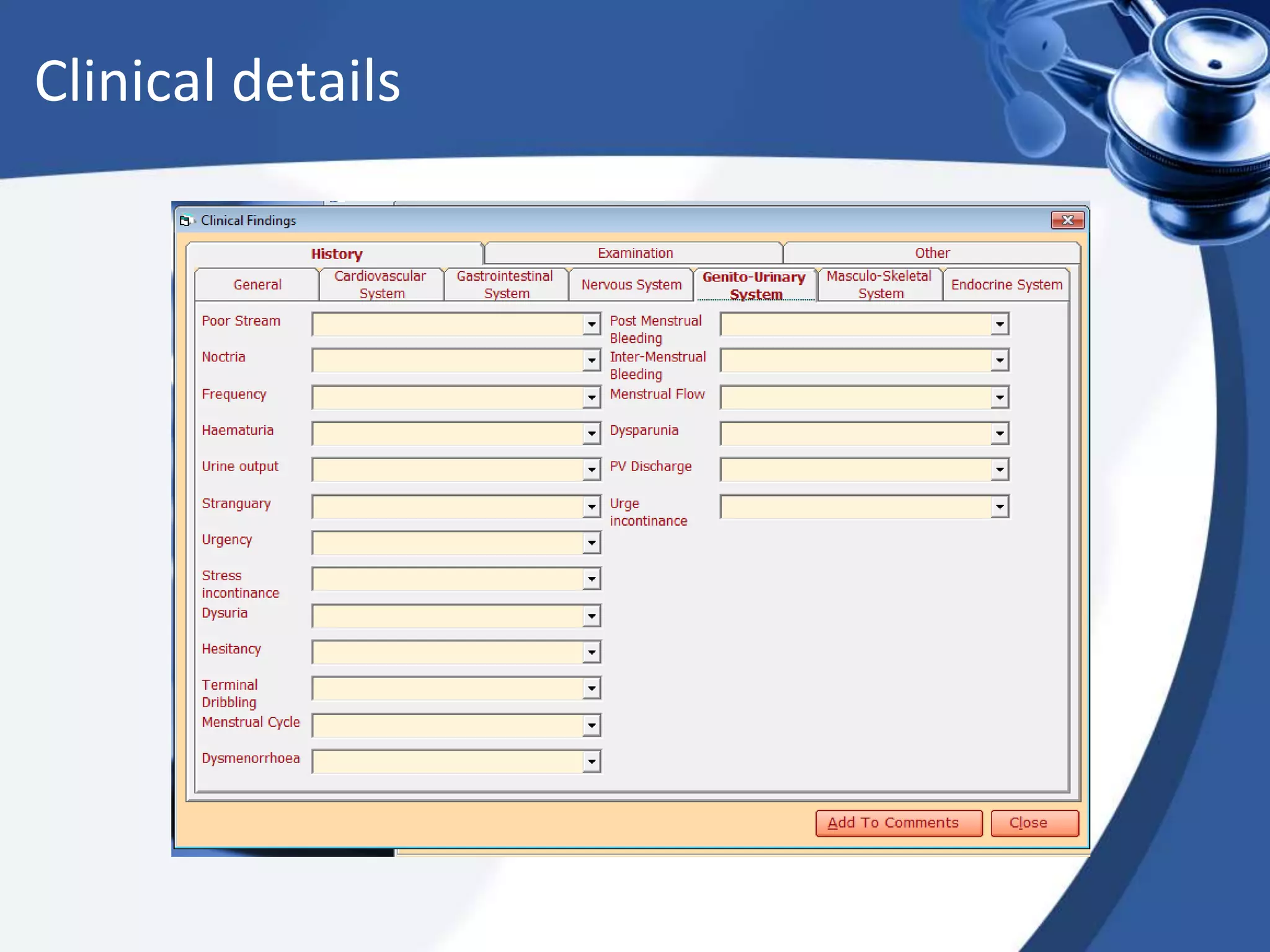
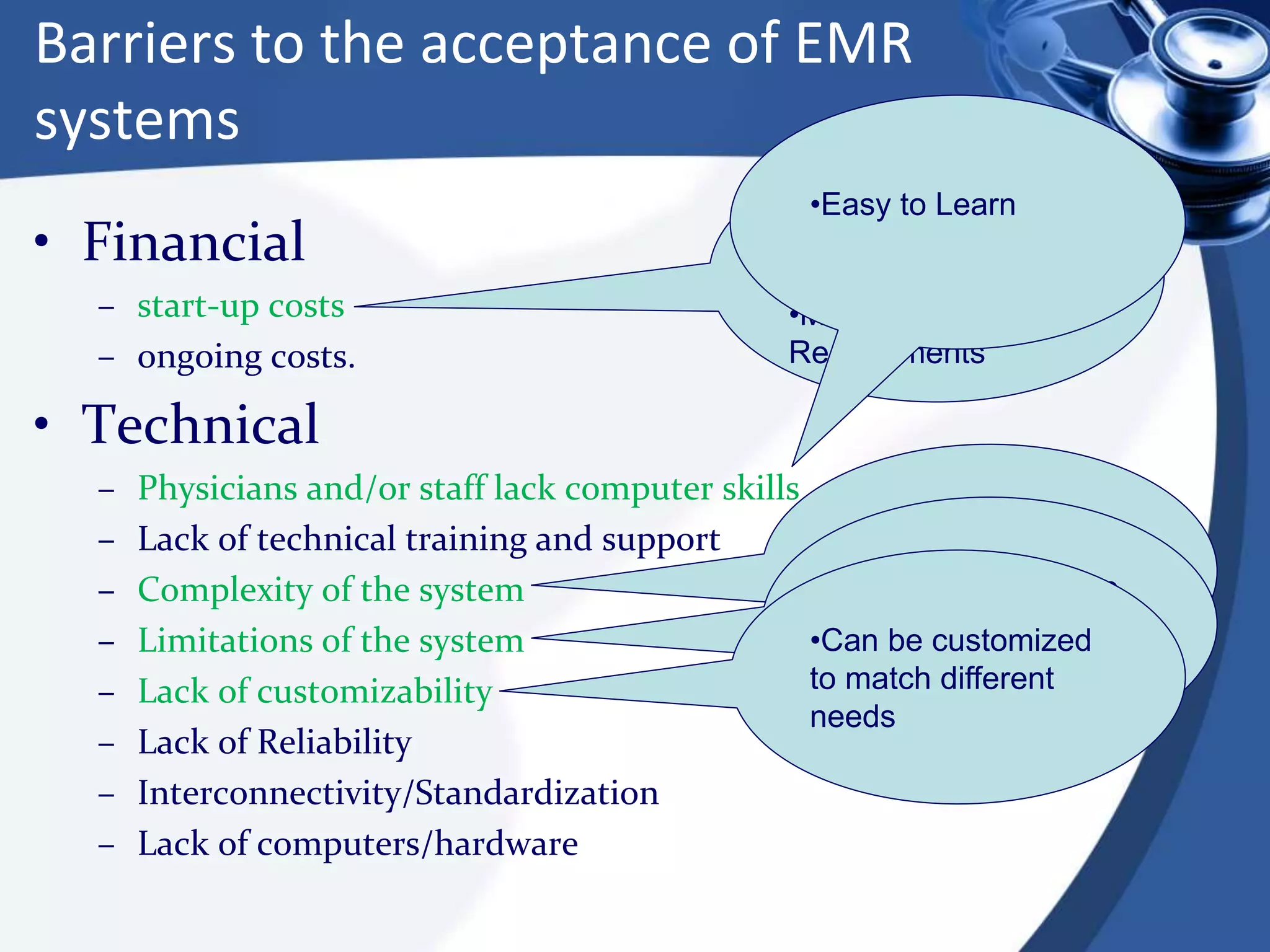
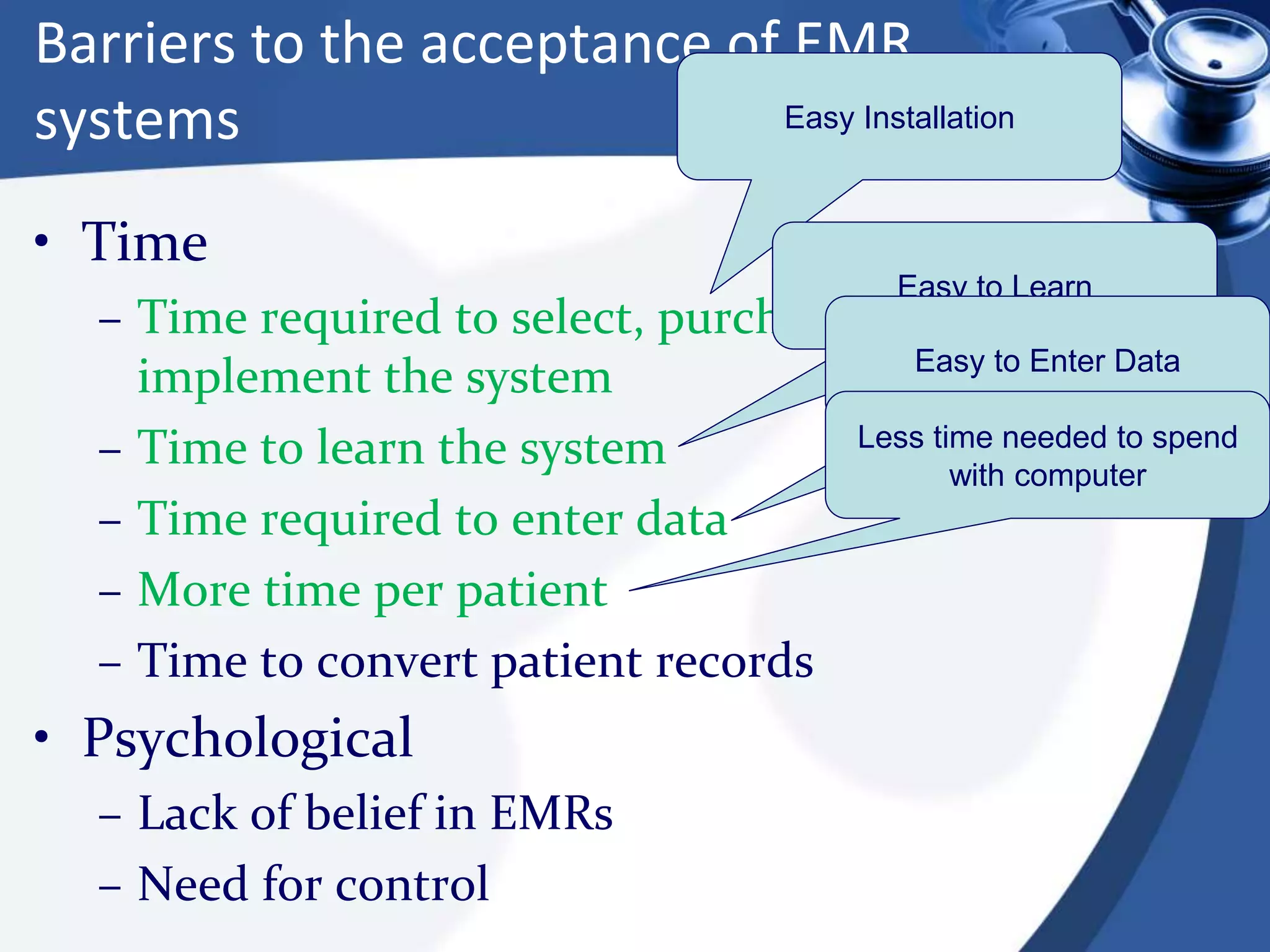
The document discusses the integration of electronic health records (EHR) into general practice, outlining their definitions, components, benefits, and concerns. It emphasizes the importance of EHR in improving patient safety and efficiency while identifying barriers to adoption, such as costs and technical challenges. The future of EHR is envisioned to include better interoperability and patient collaboration.