1. Respiration is the process of oxidizing food substances to release energy in cells. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen to fully oxidize glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water. Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen, producing lactic acid or alcohol and less energy.
2. Oxygen debt refers to the oxygen required to later convert lactic acid produced during anaerobic respiration back into glucose.
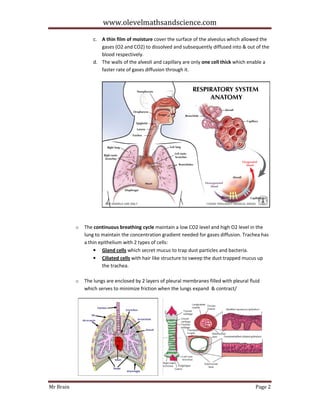
3. The passage discusses respiration in plants and animals, including methods to detect carbon dioxide, and gaseous exchange in animals via the lungs and diffusion across alveoli and blood capillaries.