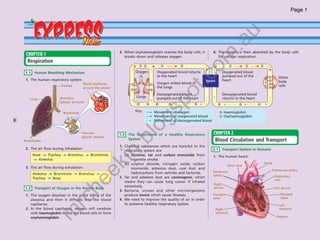
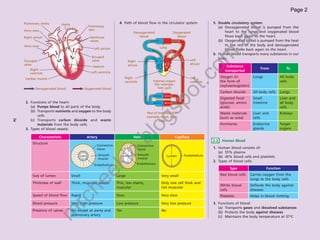
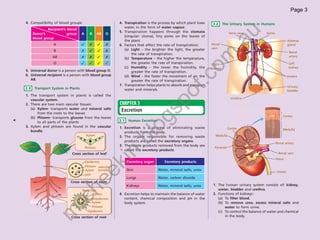
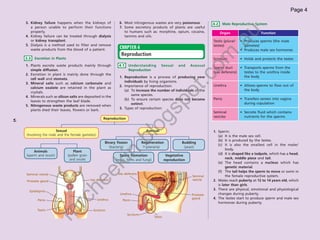
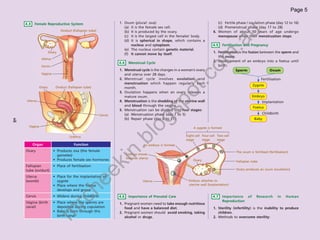
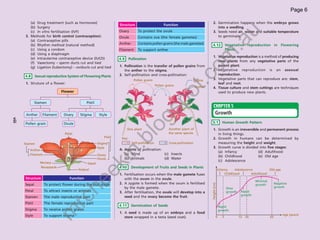
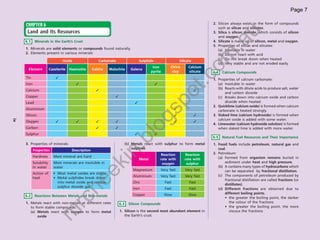
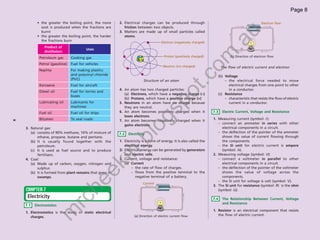
The document provides information about human anatomy and physiology related to respiration, circulation, excretion, and reproduction. It contains detailed descriptions and diagrams of the structures and processes involved. The document is authored by Ng Chee Kin and copyrighted in 2012.