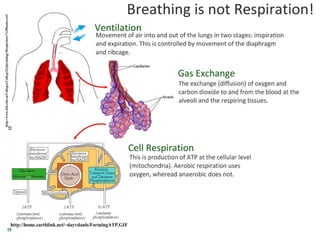
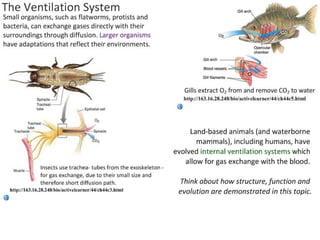
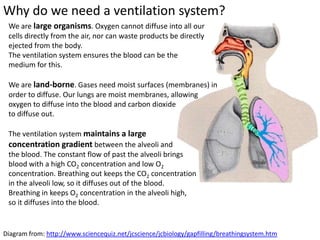
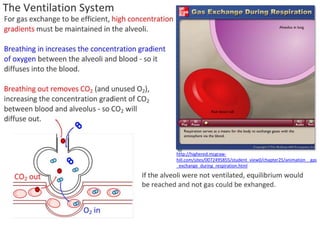
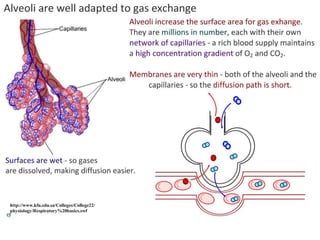
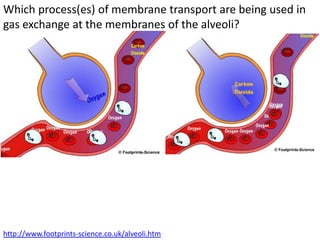
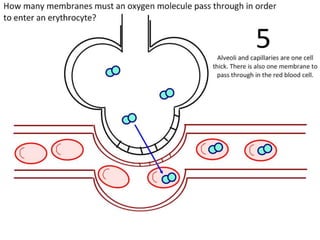
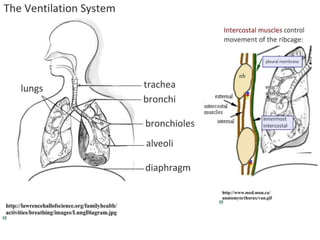
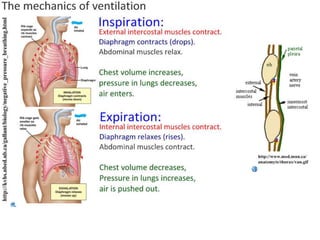
Ventilation refers to the process of moving air in and out of the lungs. Respiration is the cellular process of gas exchange that occurs in the lungs, where oxygen diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide diffuses out. The ventilation system, which includes the trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli, facilitates gas exchange through its features that maximize surface area for diffusion and maintain concentration gradients between the alveoli and blood. The diaphragm, intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles work together to change the volume and pressure of the lungs during breathing to ventilate air in and out.