The document discusses different types of storage classes in C programming:
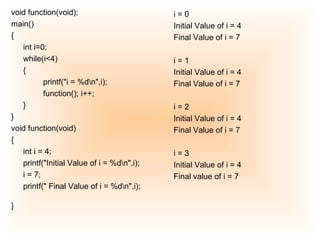
1) Auto variables are allocated on the stack and have block scope, being destroyed when the block exits. Register variables are a type of auto variable stored in CPU registers for faster access.
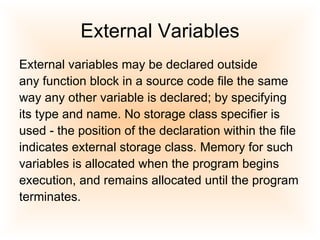
2) External variables are declared outside functions and remain in memory for the program duration.
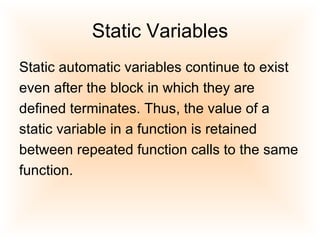
3) Static variables retain their value between function calls, stored in static storage duration. They are initialized only once.