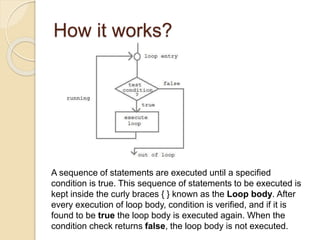
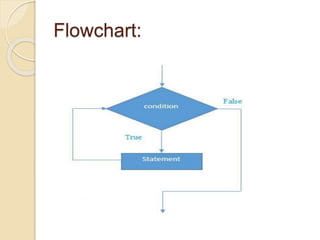
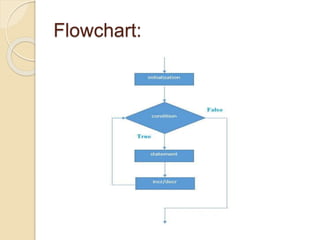
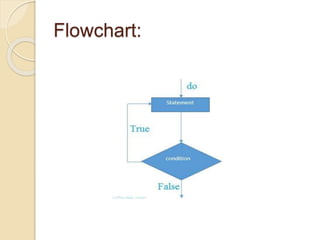
Loops in C are used to execute a block of code repeatedly until a specified condition is met, allowing for more efficient coding by reducing the number of lines required. There are three types of loops: while, for, and do-while, each with distinct structures and uses. While loops check the condition before executing, for loops allow more control with initialization and increments, and do-while loops ensure the body executes at least once before checking the condition.