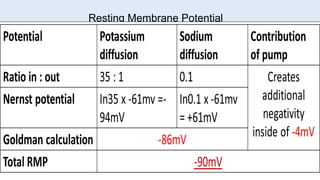
The document discusses the resting membrane potential of cells. It begins by explaining that cells actively transport ions across their membranes through pumps and channels to establish concentration gradients. This separation of charge results in a transmembrane potential. Specifically:
1) The sodium-potassium pump actively transports 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions into the cell, making the intracellular environment negatively charged.
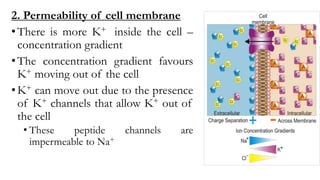
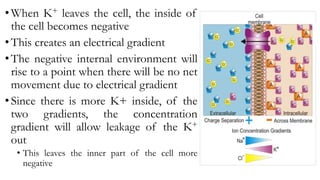
2) There are more potassium channels on the cell membrane that allow potassium to diffuse out down its concentration gradient. This further increases the negative charge inside the cell.
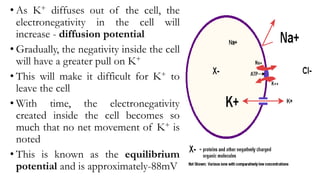
3) The resting membrane potential is the equilibrium point where the electrical and concentration gradients balance out, typically ranging from -70mV to -90mV in neurons. It results from

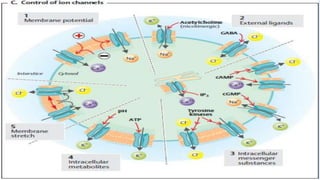


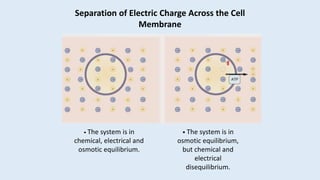
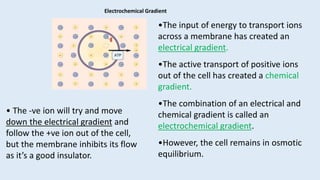


![Nernst Equation
ECl = equilibrium potential for Cl–
R = gas constant
T = absolute temperature
F = the faraday (number of coulombs per mole of
charge)
ZCl = valence of Cl– (–1)
[Clo
–] = Cl– concentration outside the cell
[Cli
–] = Cl– concentration inside the cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230510173150-3e7ad319/85/1-Resting-Membrane-Potential-pptx-12-320.jpg)