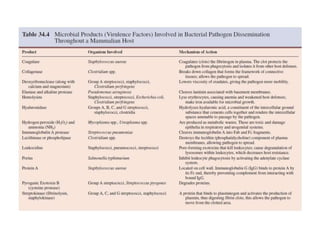
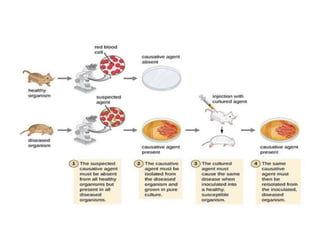
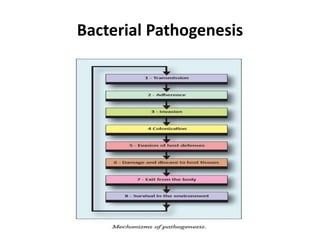
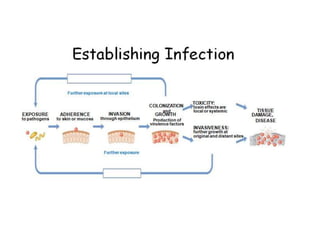
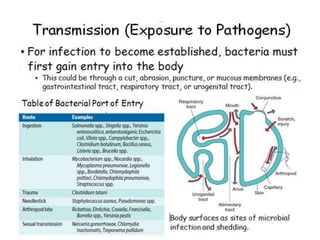
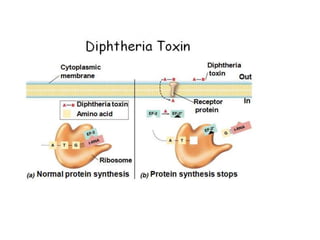
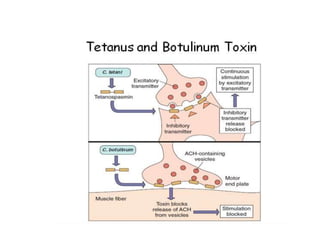
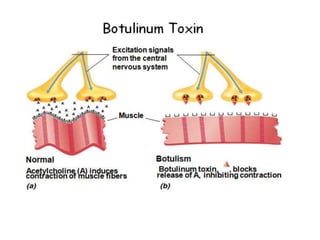
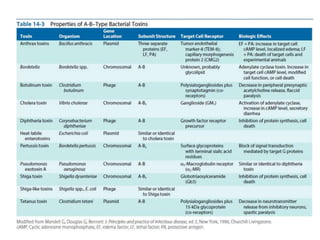
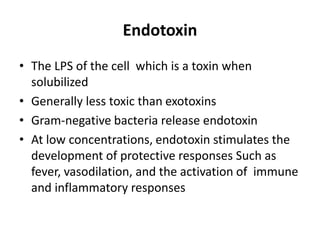
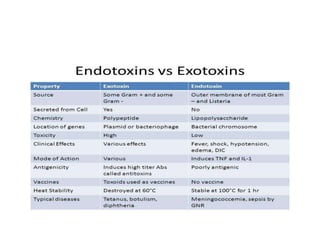
This document discusses host-microbe relationships and microbial pathogenesis. It begins by defining key terms like pathogenicity, virulence, and toxigenicity. It then describes how most microbes do not cause harm, while a few contribute to health or pose threats. Pathogens can establish infections through various mechanisms like toxin production, tissue invasion, or evading host defenses. Toxins are categorized as exotoxins, endotoxins, or exoenzymes. Exotoxins like AB toxins directly damage tissues. Colonization, invasion, and evasion of host defenses allow pathogens to replicate and spread infection. Microbes cause disease through direct damage by toxins or indirect activation of the host immune response.