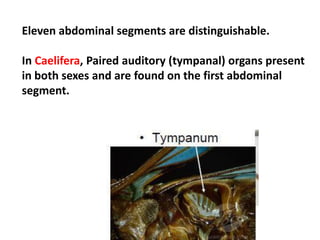
Orthoptera is an order of insects that includes grasshoppers, crickets, locusts, and mole crickets. It contains over 20,000 species worldwide and 900 species in India. They range in size from 2 to 200 mm and have chewing mouthparts. Their antennae and legs can vary in structure between suborders and among species for tasks like digging, walking, running or jumping. Most species have two pairs of wings but some are wingless. They exhibit diverse habitats, behaviors, and roles as herbivores, predators, or crop pests.














![Antennae consist of several segments [15 or more] Filiform,
comparatively short (suborder Caelifera) to very long (suborder
Ensifera).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1orthoptera-230507083107-f0e91d66/85/1-Orthoptera-pdf-15-320.jpg)








![Winged [2 pairs], with reduced wings or
wingless.
Forewings elongate, many-veined and
somewhat thickened – called tegmina.
Hind wings membranous, broad and many –
veined and folded fanwise beneath the front
wings while at rest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1orthoptera-230507083107-f0e91d66/85/1-Orthoptera-pdf-24-320.jpg)