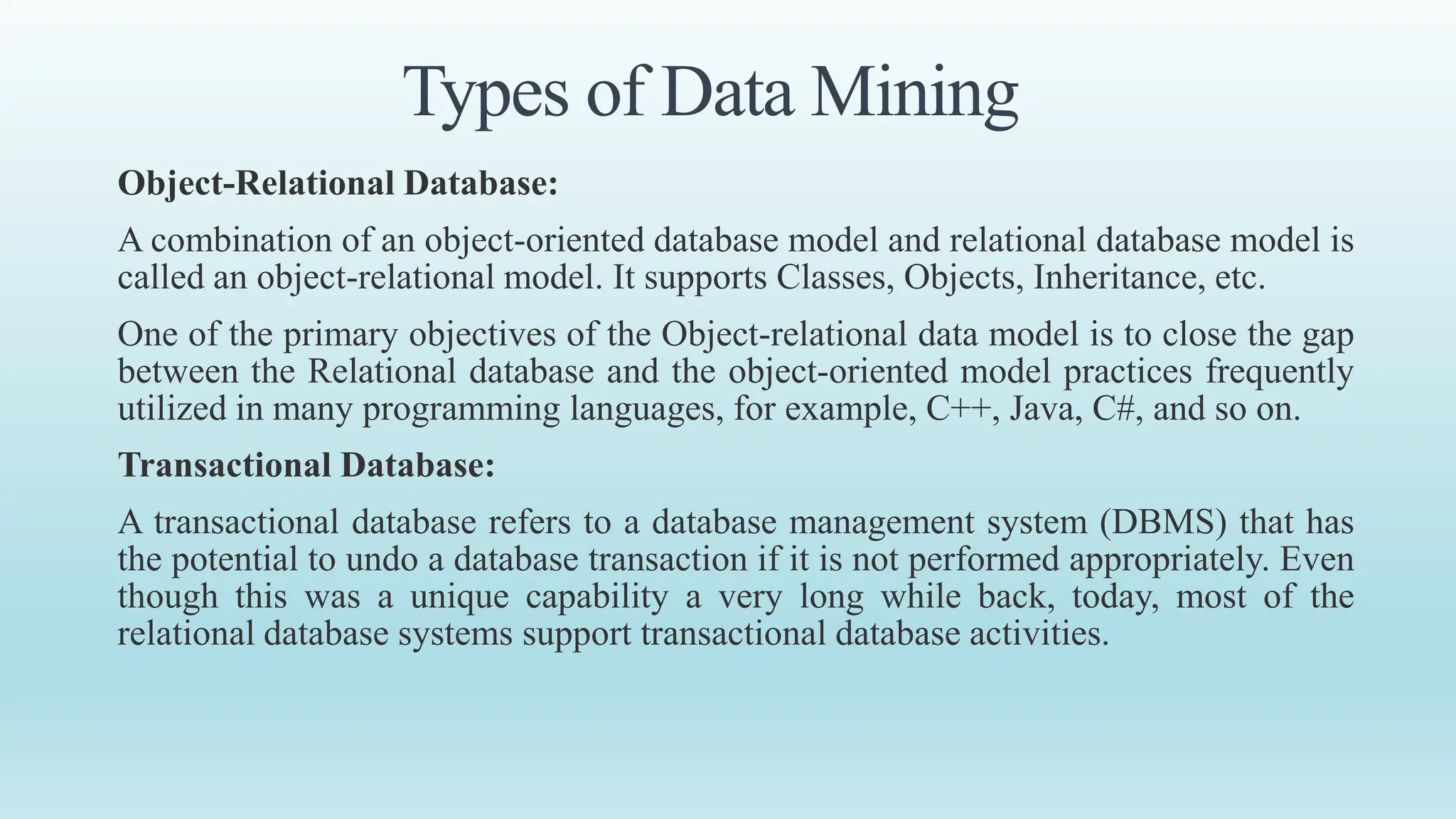
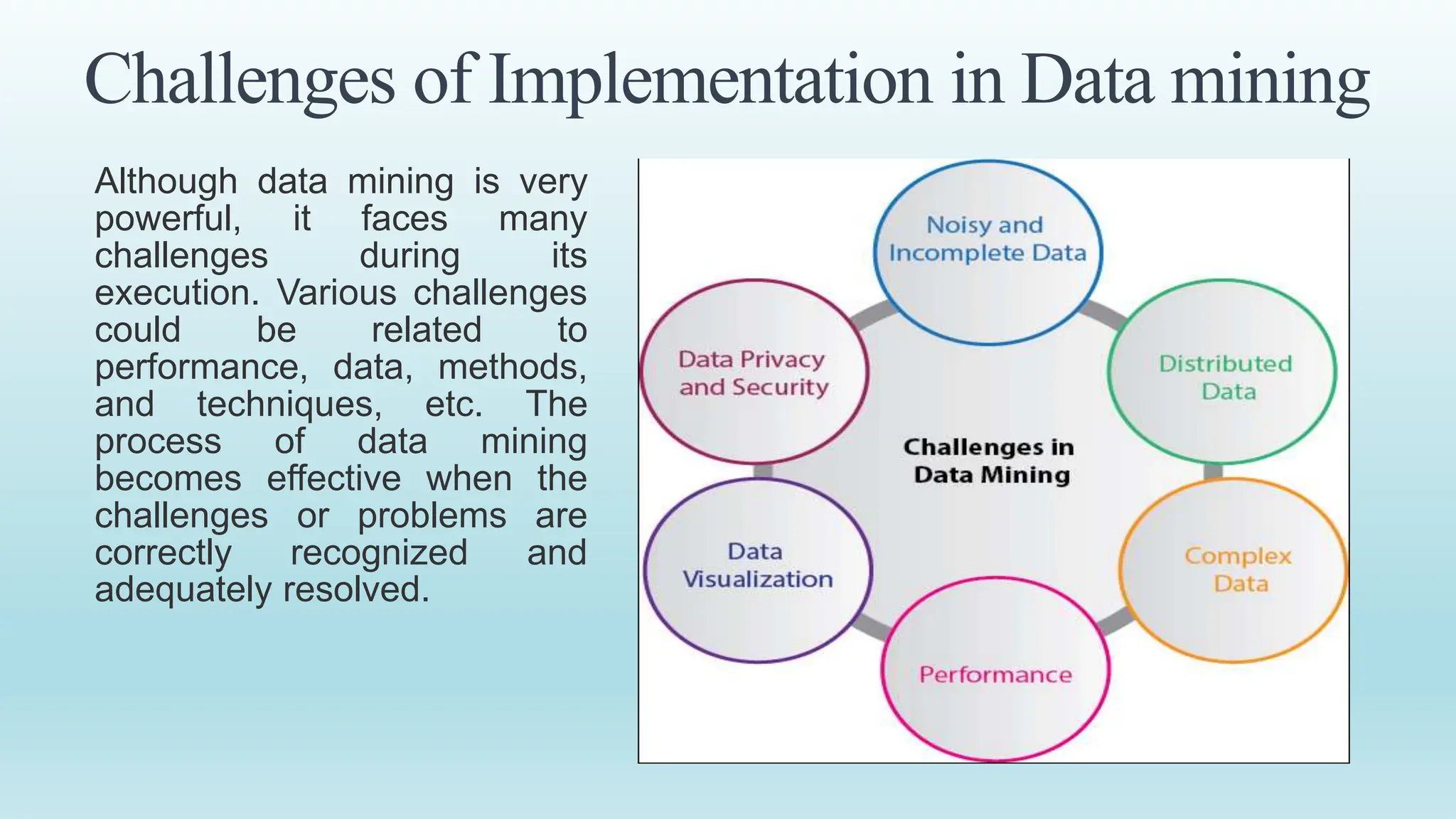
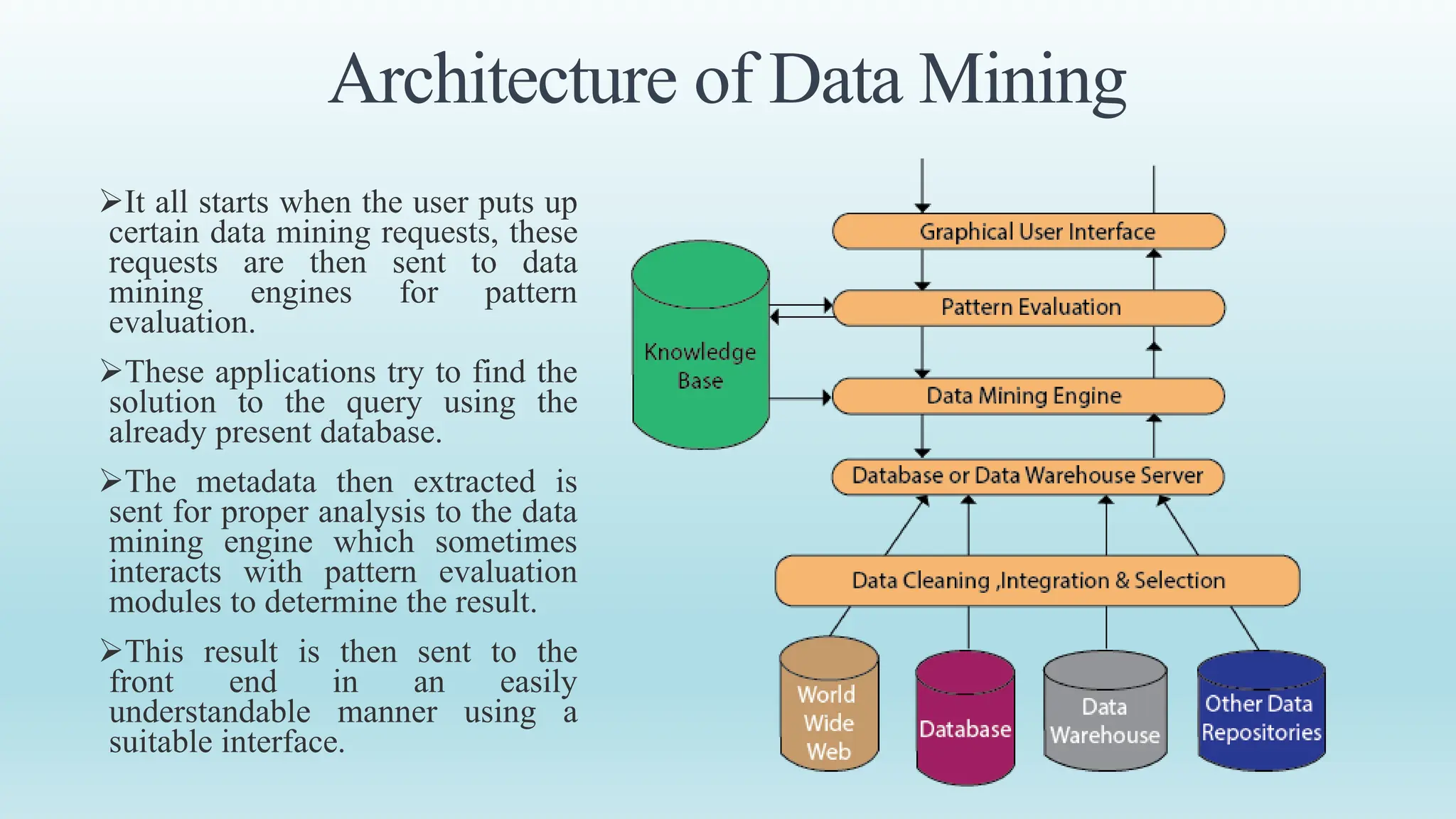
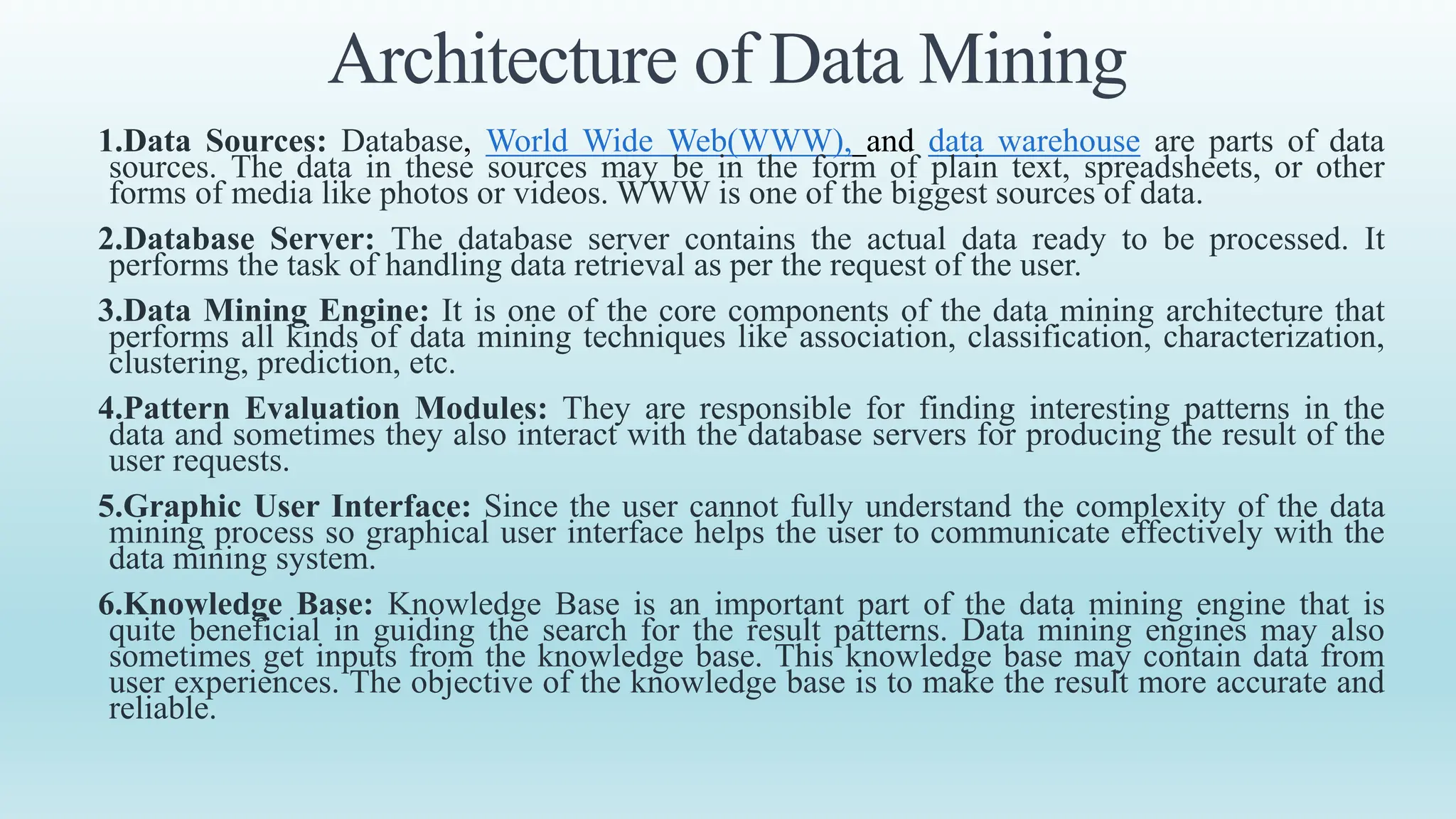
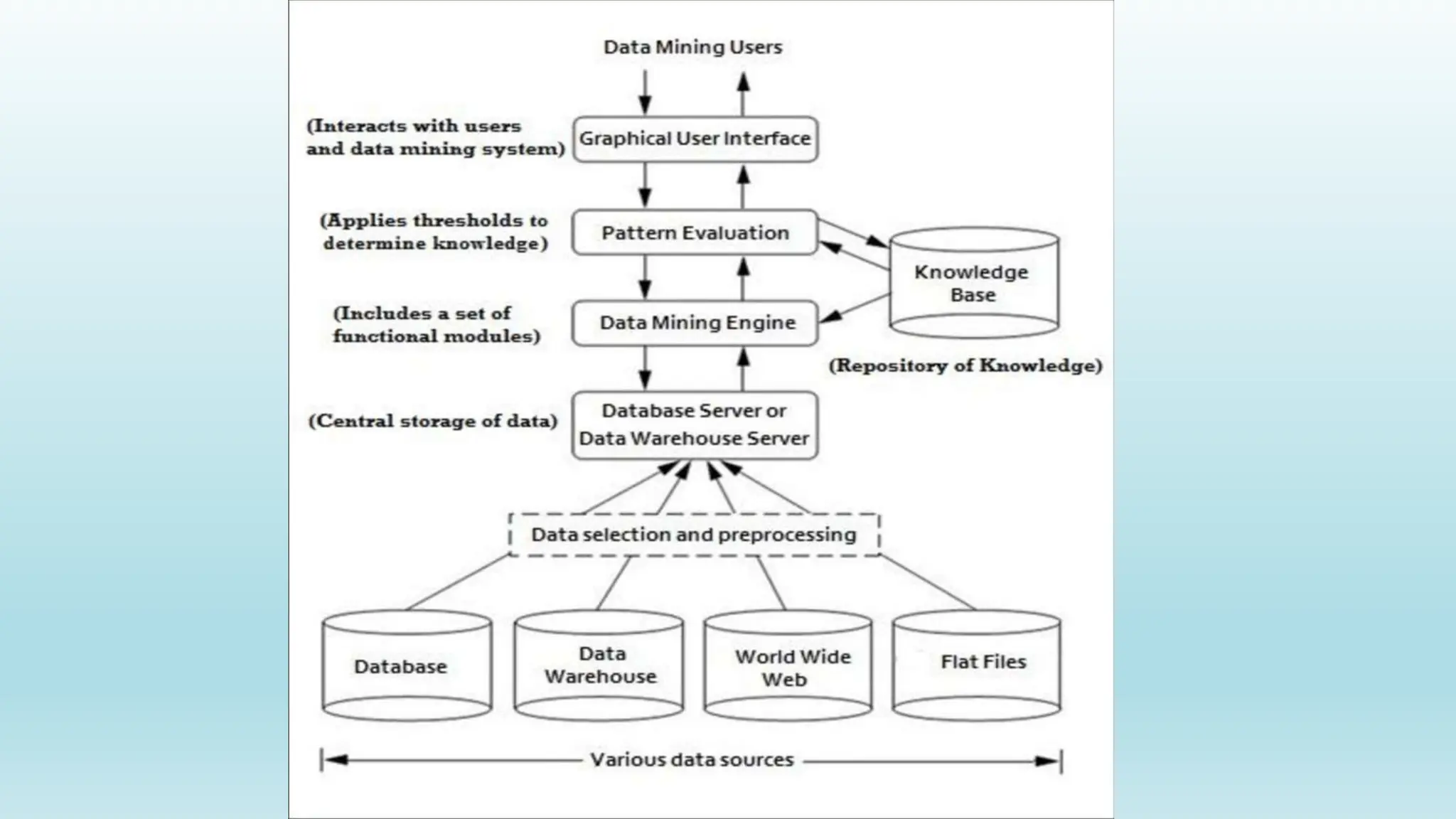
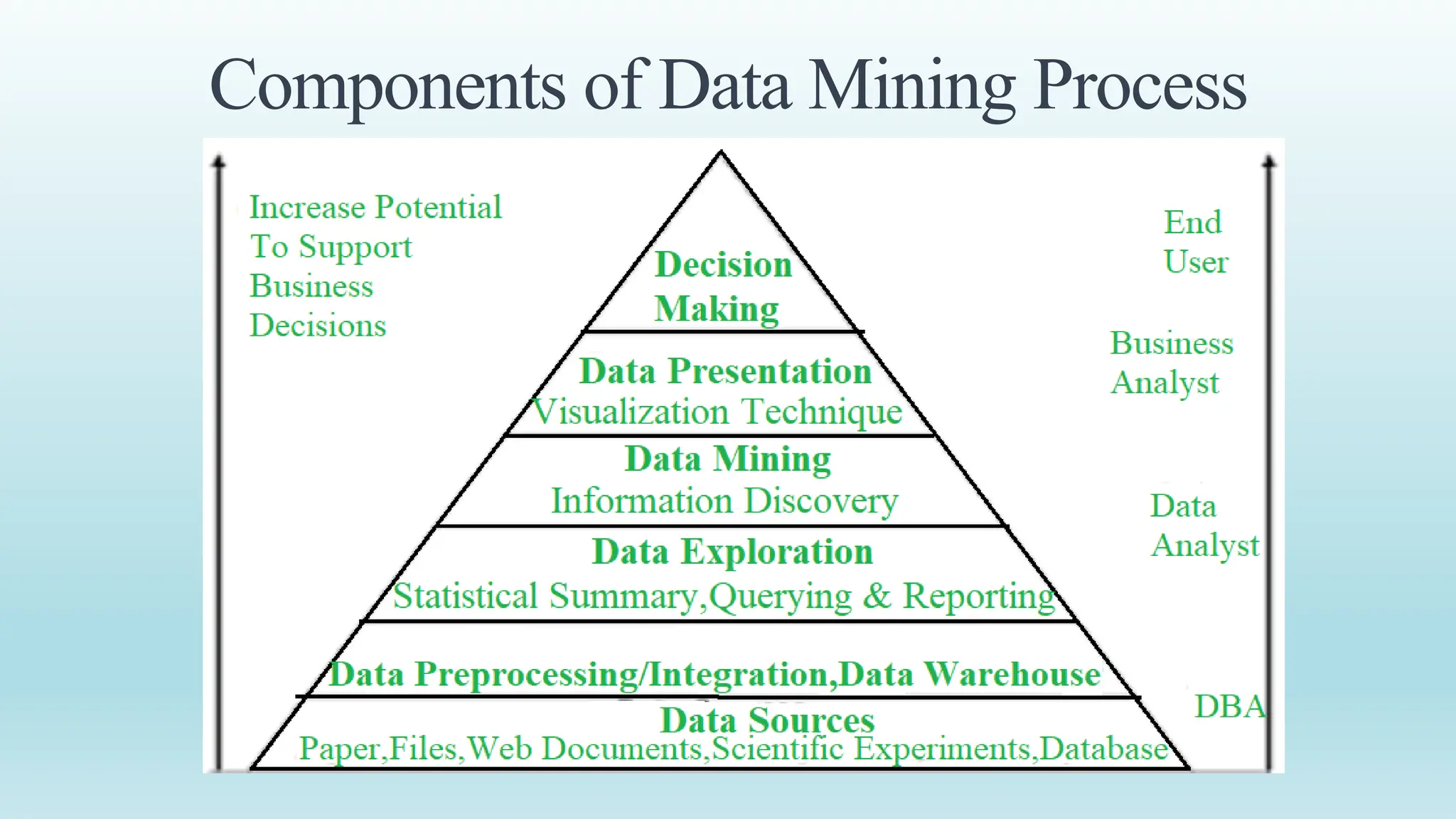
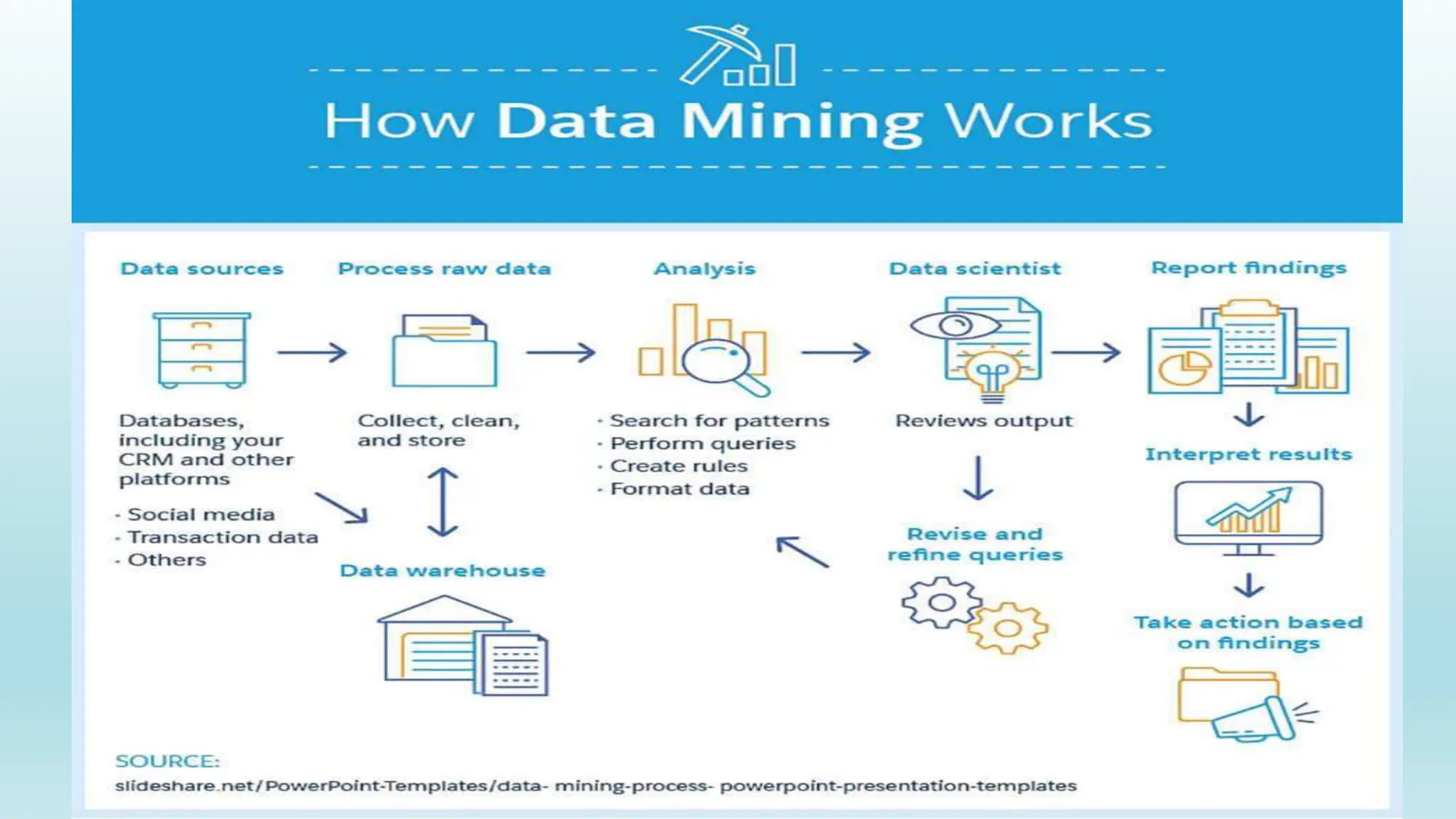
This document provides an overview of data mining, including its definition, process, applications, and challenges. Data mining involves analyzing large datasets to extract useful patterns and trends. It has several key steps: data is collected and loaded into warehouses, analysts determine how to organize it, software sorts and organizes the data, and it is presented to end users. Data mining is used by organizations in retail, finance, marketing and other industries to determine customer preferences and behaviors to help with decisions. While powerful, data mining also faces challenges to do with performance, data issues, and selecting the right techniques.