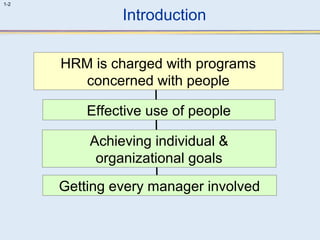
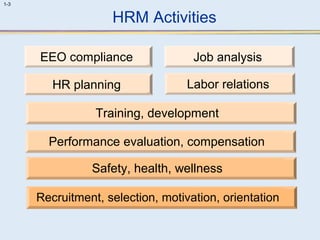
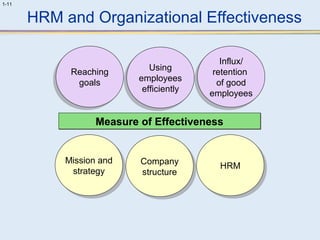
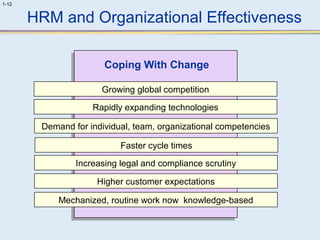
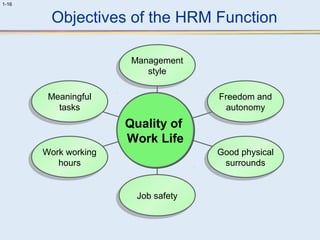
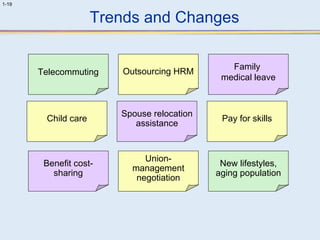
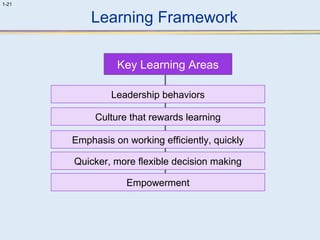
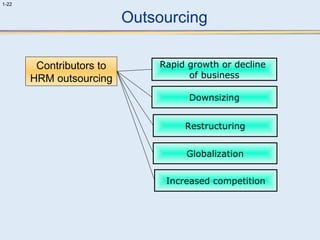
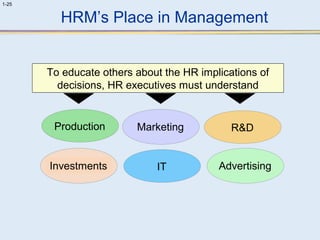
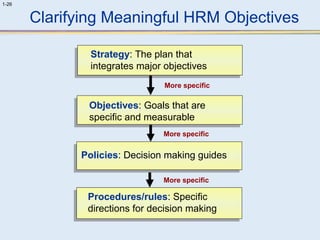
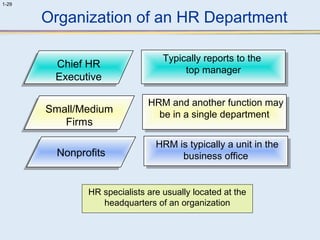
This document provides an overview of human resource management (HRM). It discusses the strategic importance of HRM and how HRM contributes to organizational effectiveness. Key topics covered include the history and activities of HRM, strategic HRM approaches, objectives of the HRM function like providing trained workers and increasing job satisfaction, and trends impacting HRM like outsourcing and a global environment. The document also examines how HRM policies and procedures provide guidance for decision-making.