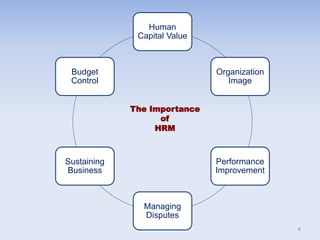
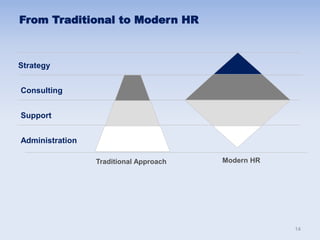
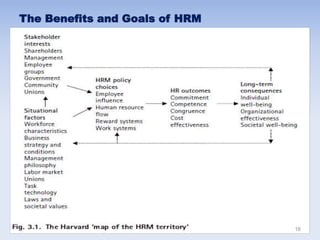
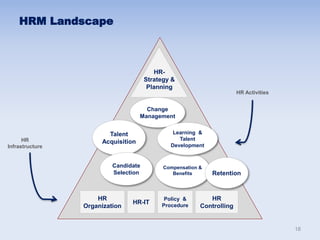
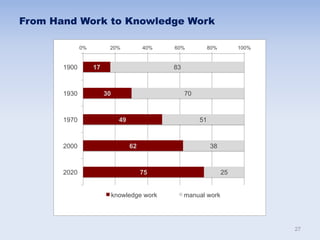
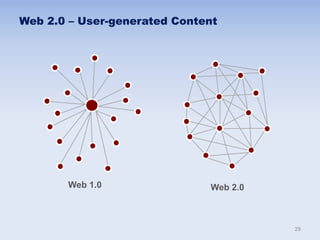
This document discusses human resources management (HRM). It begins by explaining the importance of HRM, including helping control budgets, improving organizational performance and image, and sustaining the business. Next, it describes how HRM has evolved from a traditional personnel administration function to a more modern, strategic role. The document then outlines the goals and benefits of HRM, the key activities within the HRM landscape, and some characteristics of effective HRM practices. Finally, it discusses challenges for HRM like managing innovation and the shift from manual to knowledge work in the modern economy.