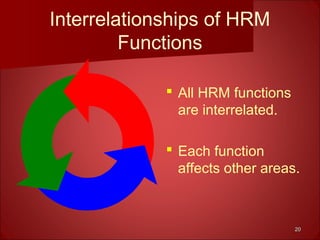
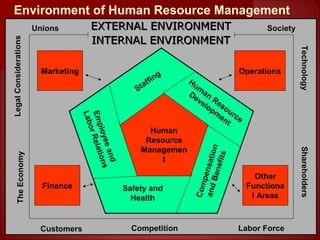
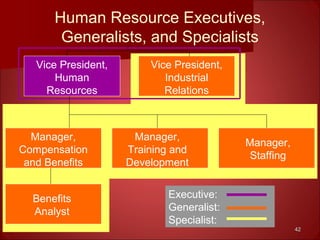
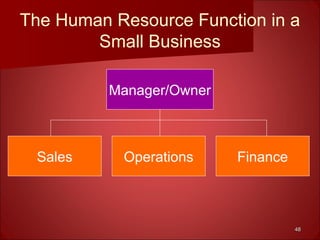
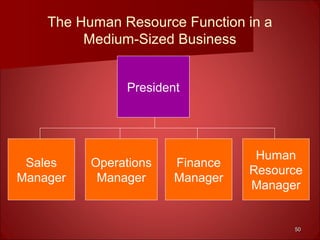
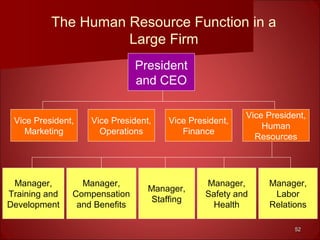
This document provides an overview of human resource management. It discusses the main functions of HRM including staffing, human resource development, compensation and benefits, safety and health, and employee and labor relations. It also examines the internal and external factors that influence HRM and how the roles and tasks of HRM are changing, with some functions now performed by HR managers, shared service centers, outsourcing firms or line managers. Finally, it differentiates between the roles of HR executives, generalists and specialists.