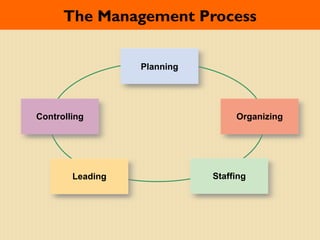
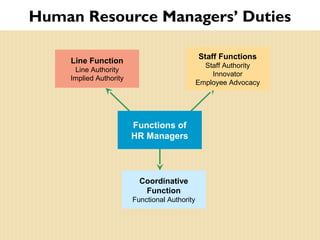
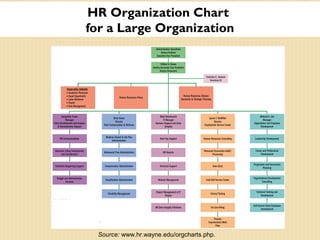
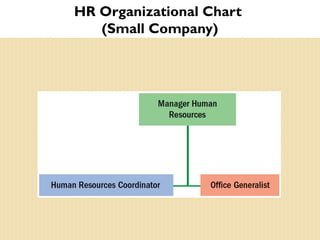
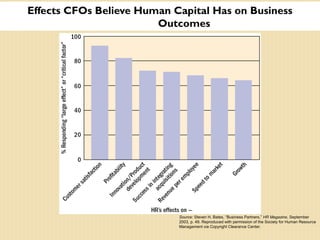
The document discusses important trends in strategic human resource management. It outlines how HR is shifting from an administrative function to a strategic partner focused on measuring its impact on business outcomes. It also discusses the need for HR to use evidence-based practices and metrics to demonstrate how it contributes to organizational strategy through high-performance work systems, training, and other initiatives. Managing a global, diverse workforce and complying with employment laws are also key responsibilities for modern HR.