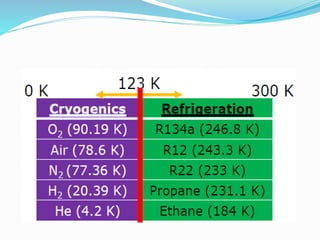
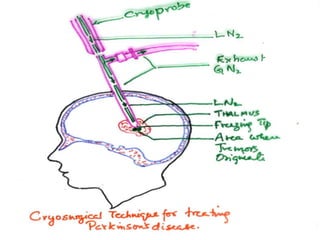
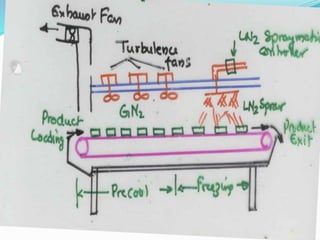
This document discusses cryogenics, which is the science of producing very cold temperatures below 123 K. Some key applications of cryogenics mentioned include space applications like rocket propulsion using liquid hydrogen and oxygen, medicine like cryosurgery and cell preservation, food processing like freezing foods, industrial gas production through cryogenic distillation of air, superconductivity in technologies like MRI machines, and high energy physics experiments like those at CERN.