Embed presentation
Downloaded 45 times






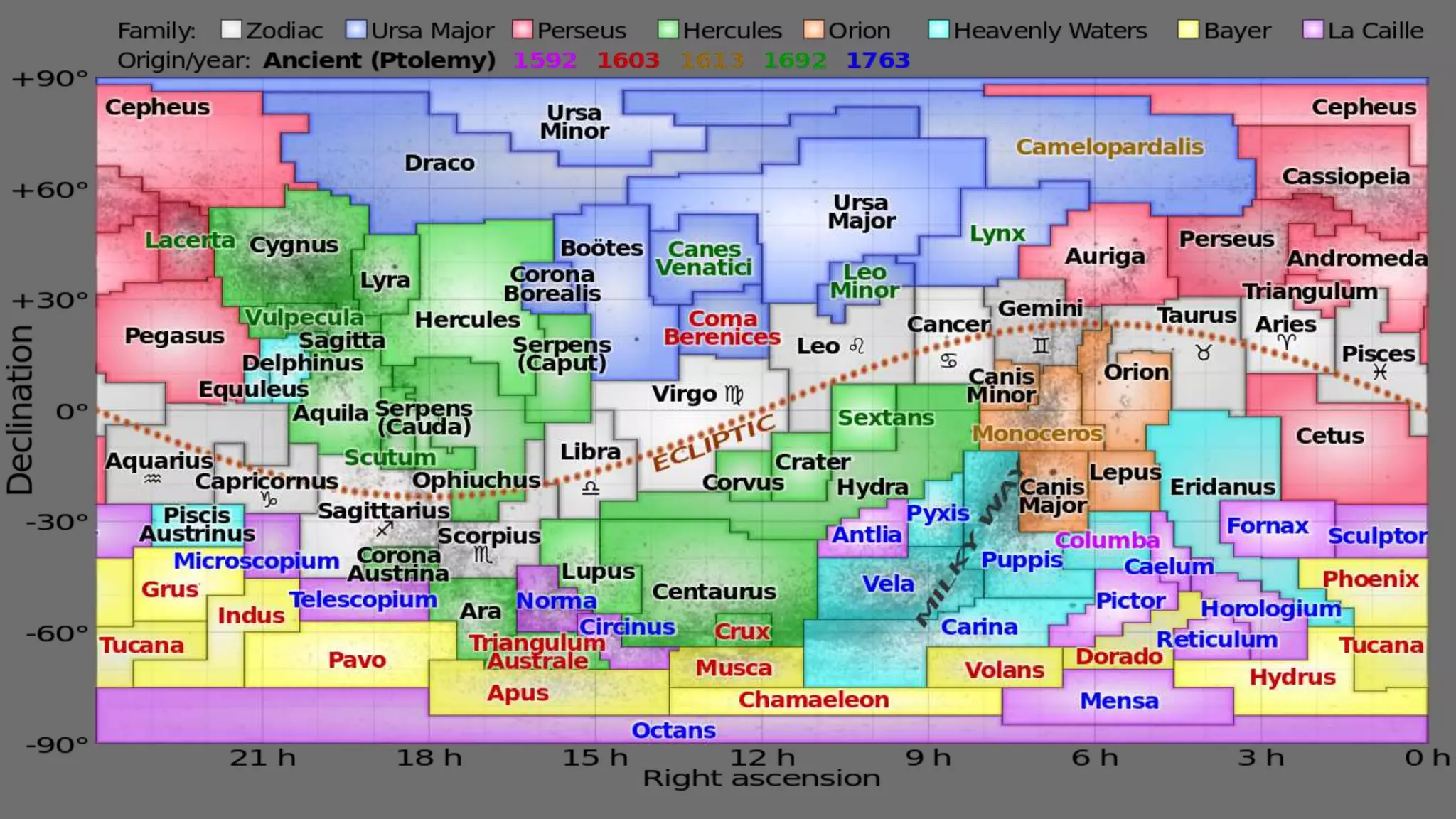

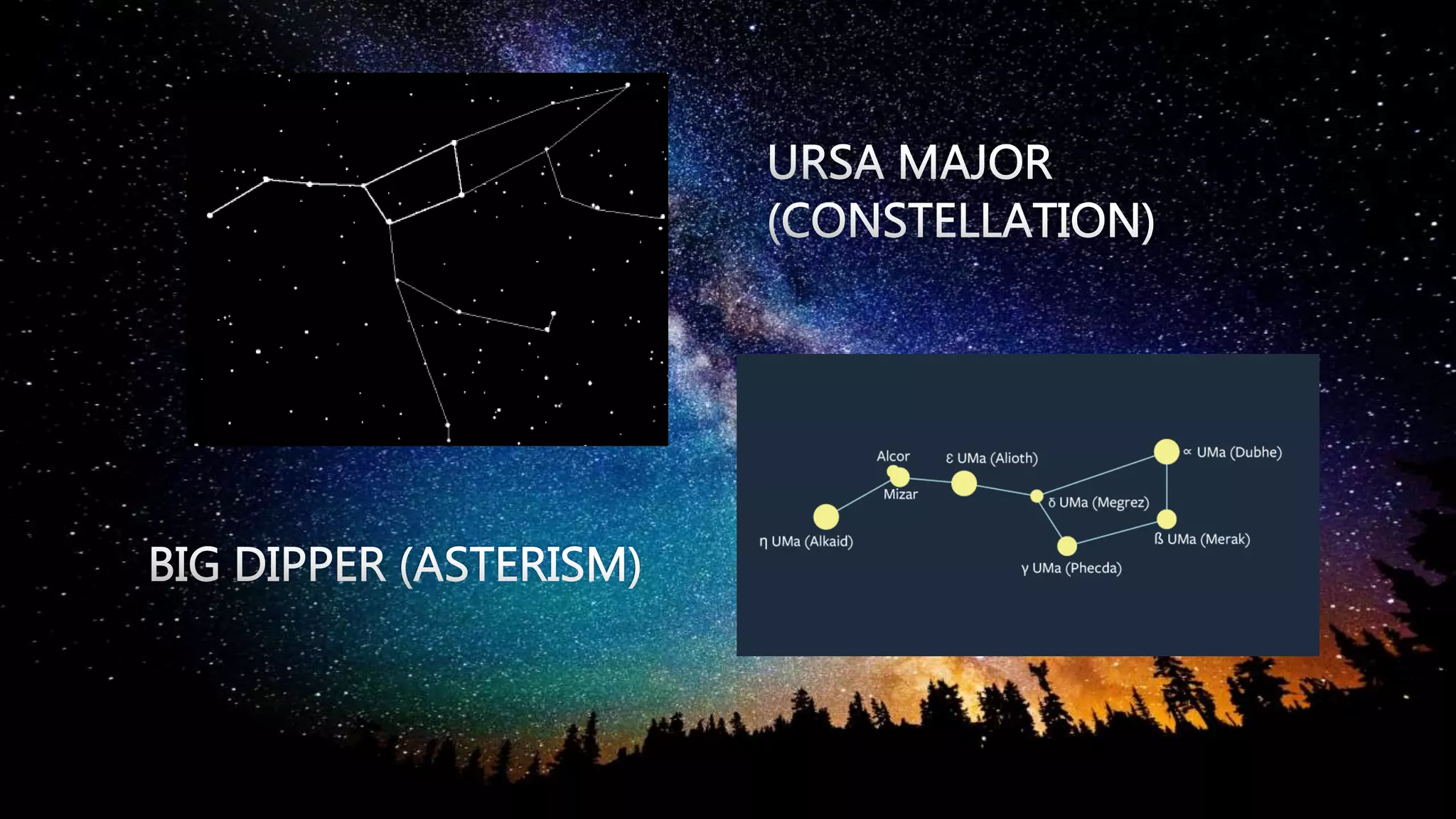

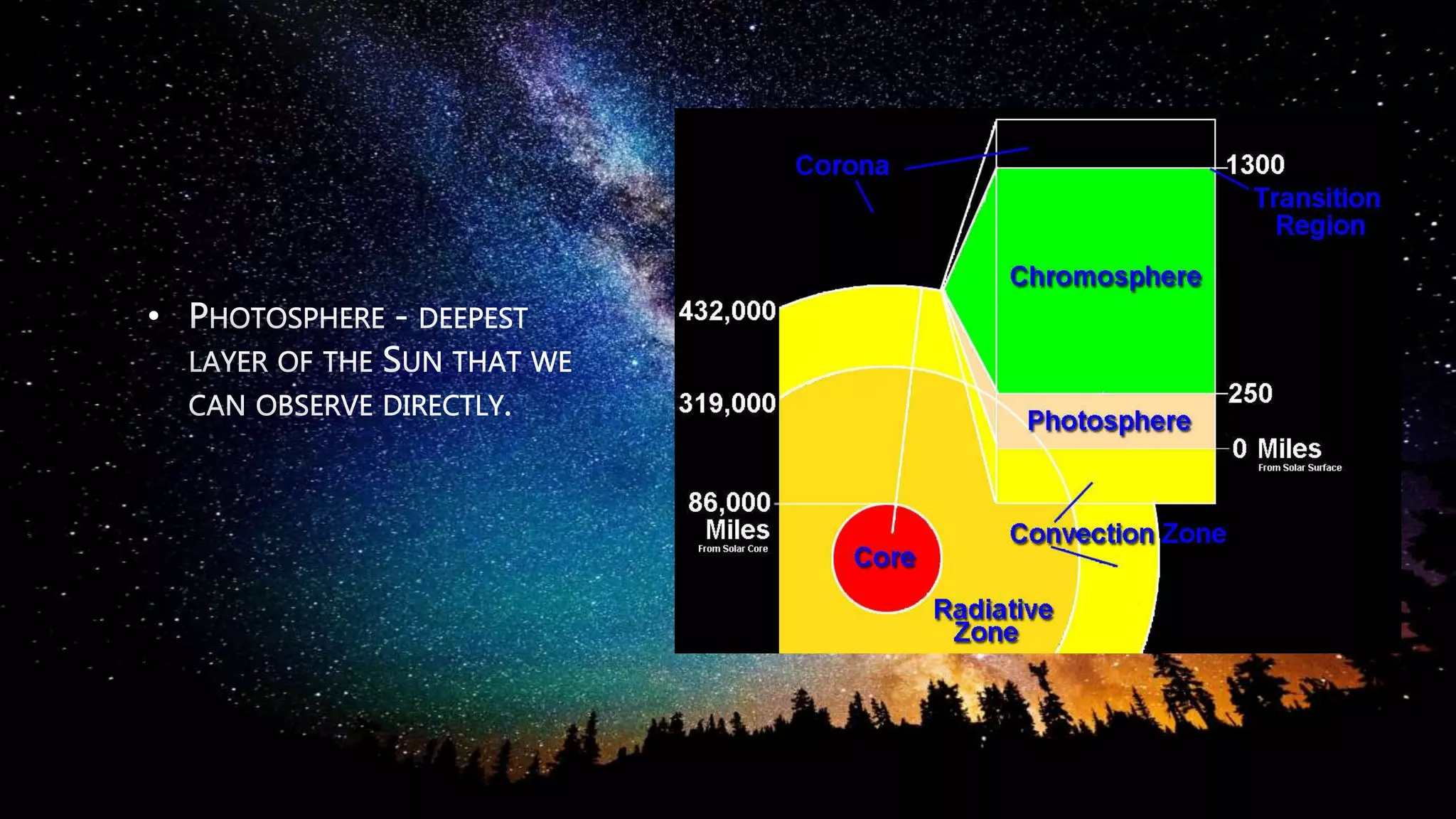
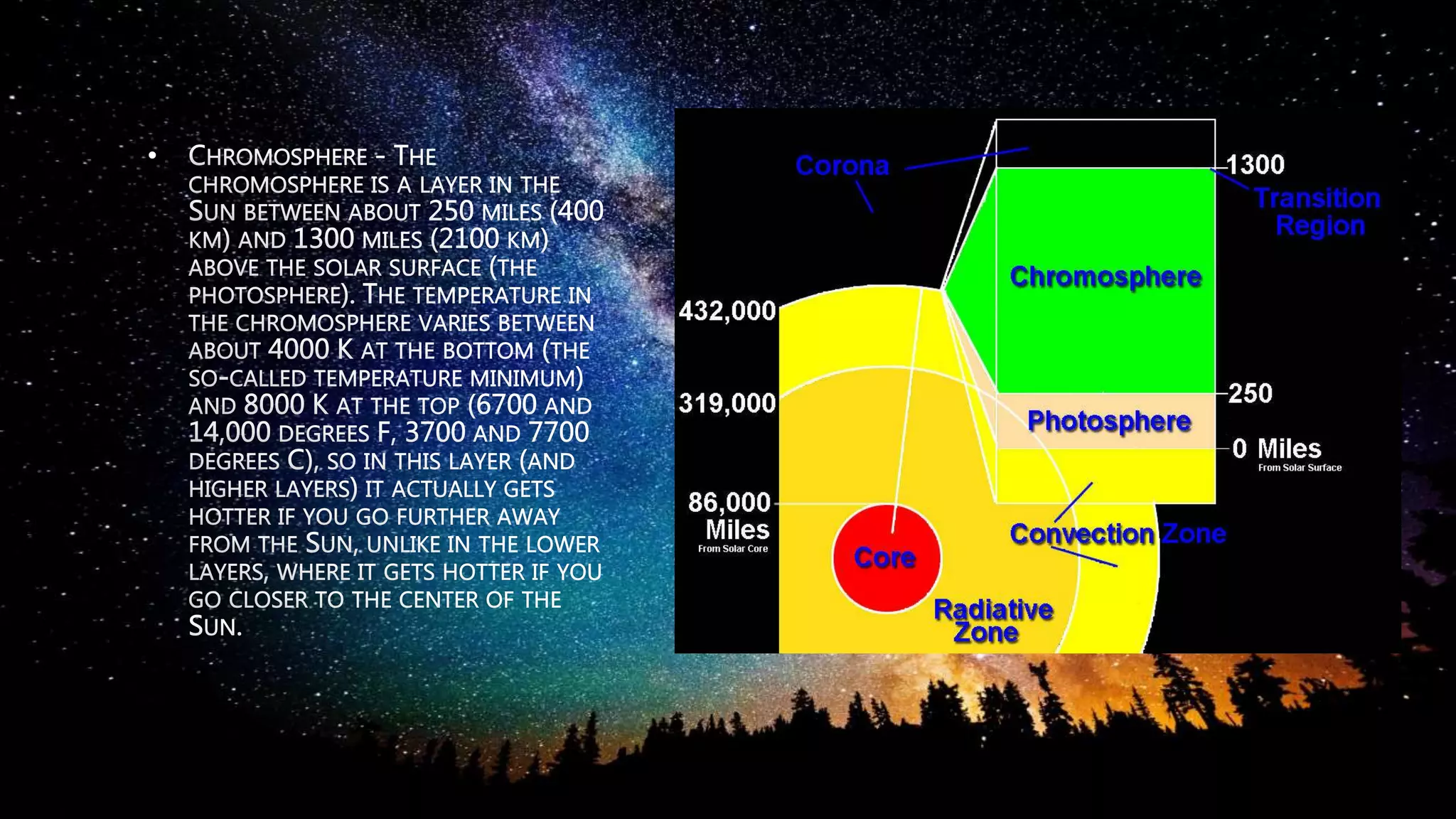
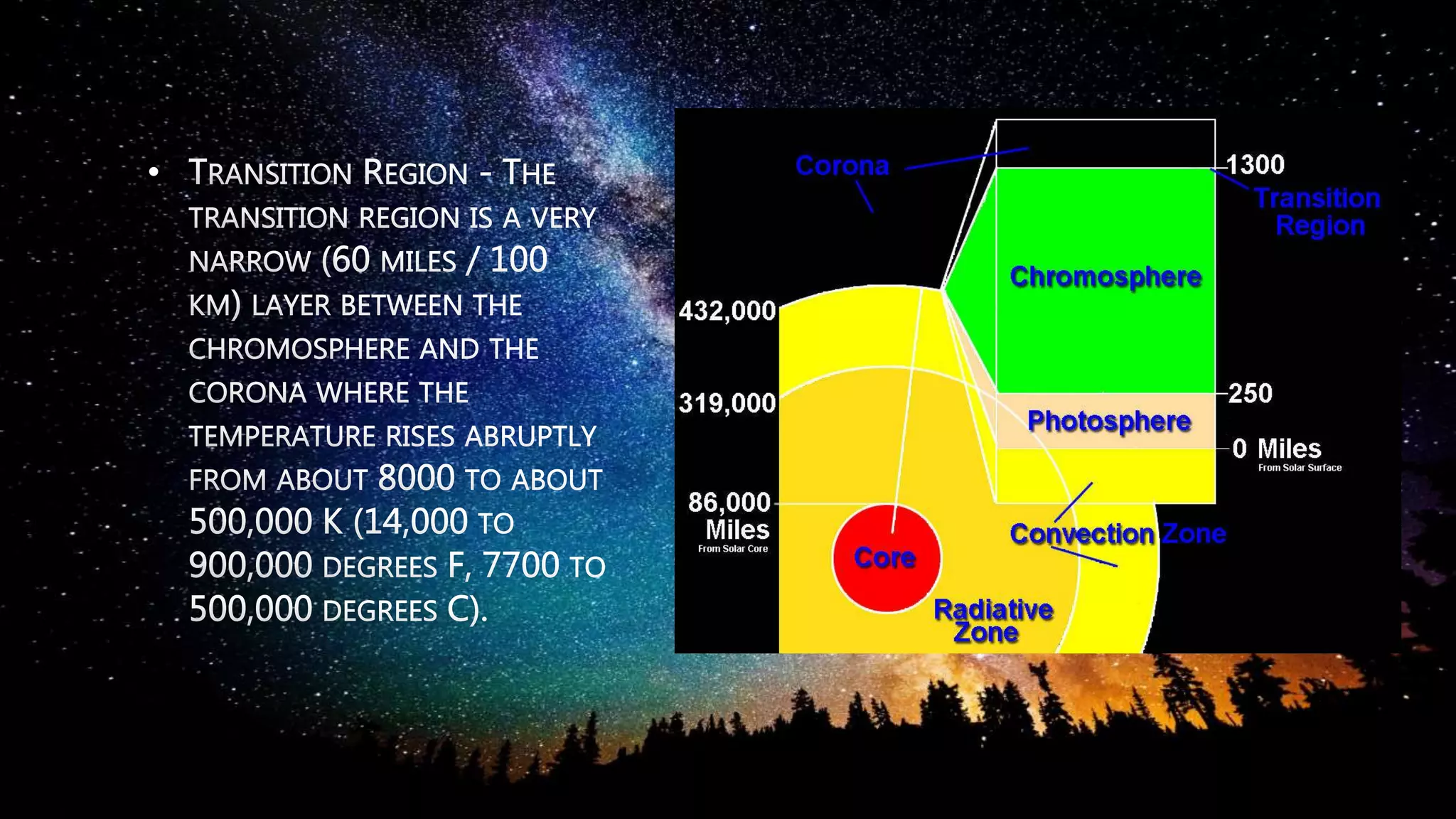
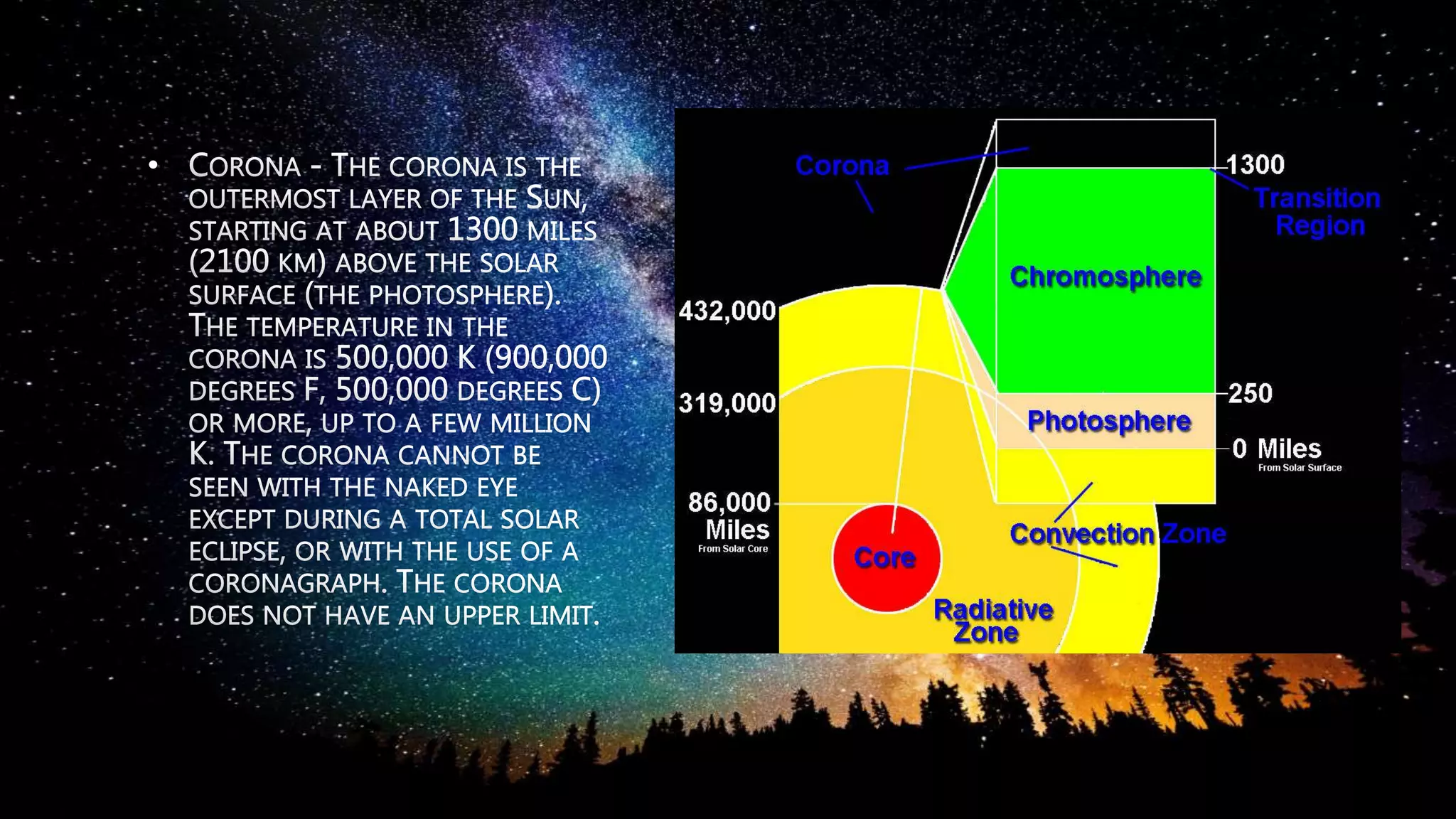



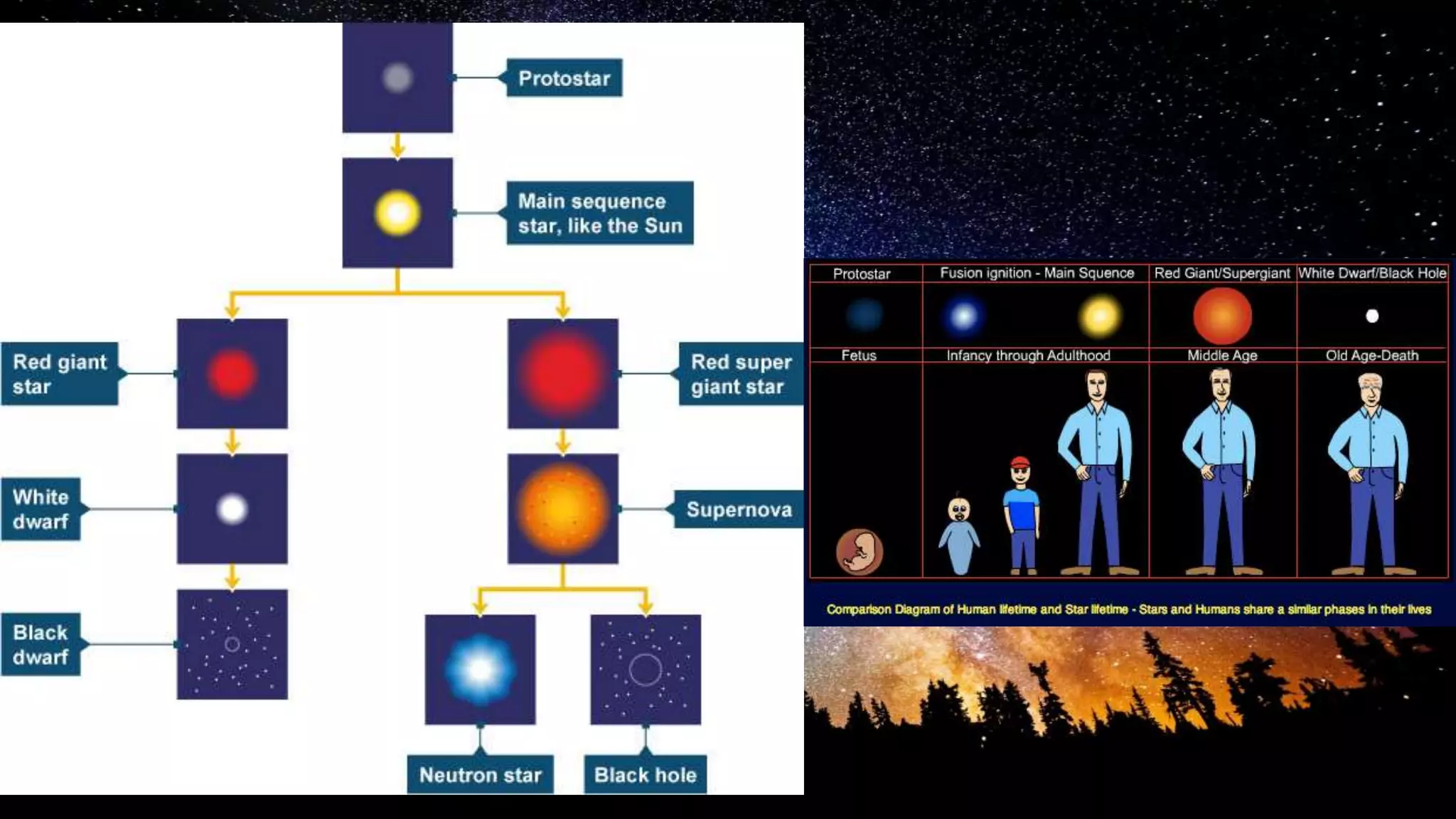


























Stars are luminous spheres of plasma held together by gravity that produce heat, light, and radiation. They are composed largely of gas and plasma and are responsible for distributing heavy elements throughout the universe. The nearest star to Earth is our Sun. Constellations are specific areas of the celestial sphere defined by groups of prominent stars that make identifiable patterns, with some famous examples being Orion and Cassiopeia.










































