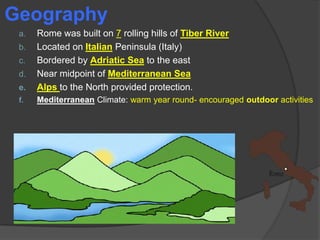
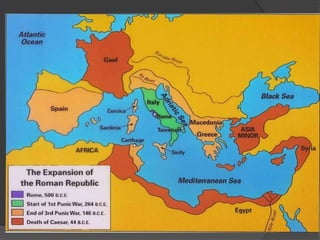
The ancient Romans originated from three groups - the Latins, Greeks, and Etruscans - who settled the Italian peninsula between 1000-500 BC. The Latins built the original settlement of Rome. In 509 BC, the Romans overthrew their Etruscan kings and established a republic where elected officials governed. Over time, the Romans conquered the Italian peninsula through their organized military. This led to conflicts with the powerful city of Carthage in North Africa in the Punic Wars from 264-146 BC, ultimately resulting in Rome establishing itself as the dominant power in the Mediterranean world.