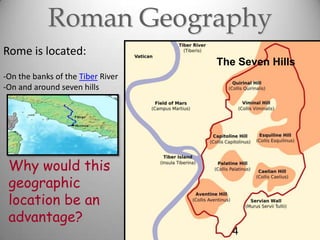
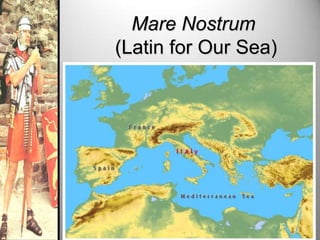
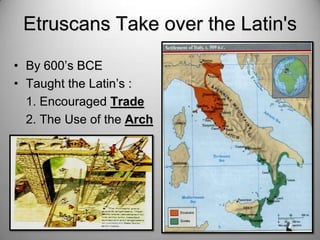
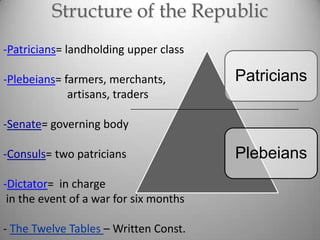
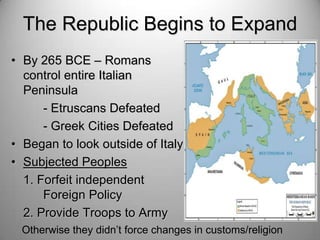
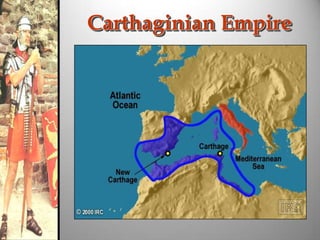
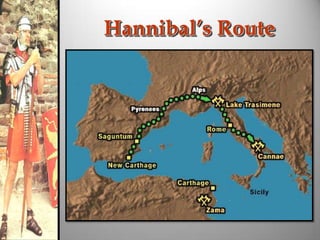
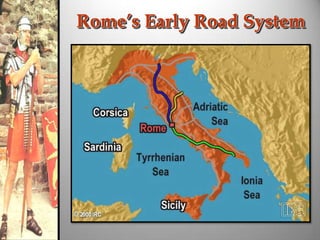
Rome's location on the Tiber River and seven hills provided strategic advantages for the city's growth as an empire. The geography isolated Rome but also enabled access to the sea and rich agricultural lands. These natural defenses and resources allowed Rome to expand throughout Italy and eventually dominate the Mediterranean world through a series of Punic Wars against Carthage between 264-146 BCE. Rome's victory in these wars established its dominance and control of lands around the Mediterranean.