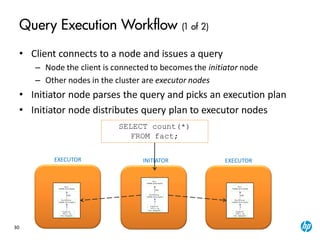
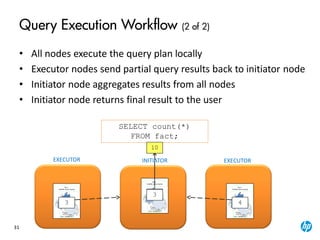
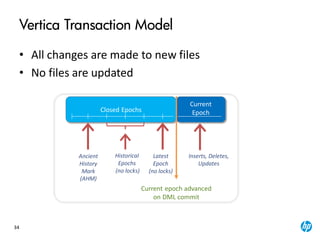
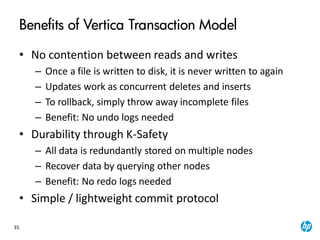
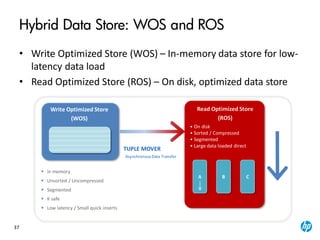
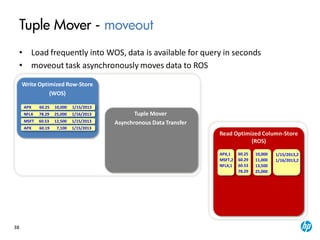
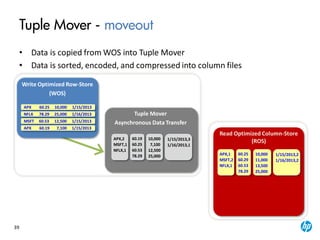
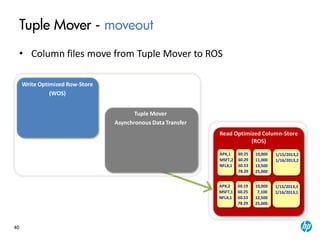
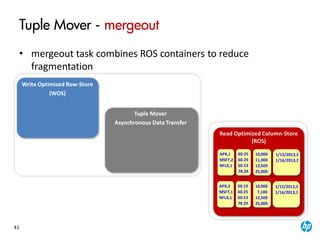
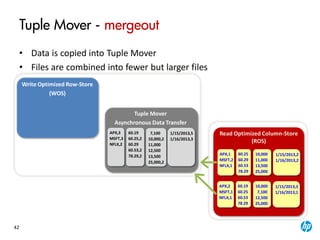
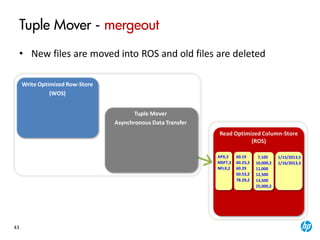
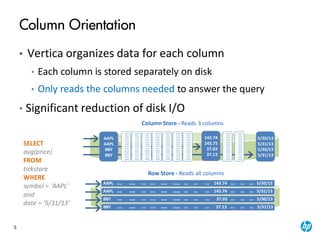
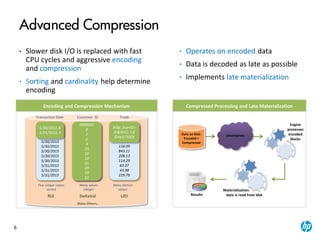
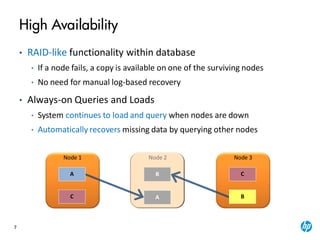
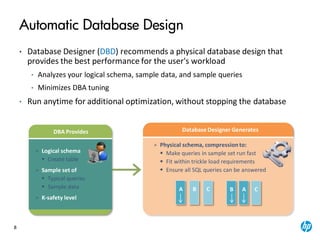
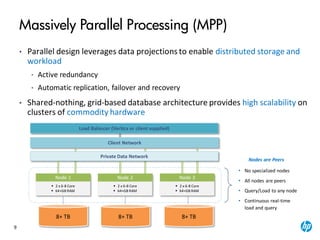
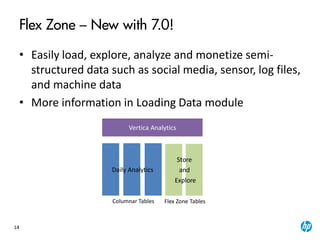
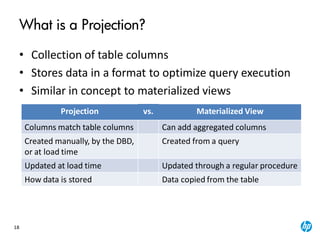
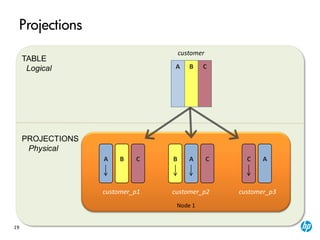
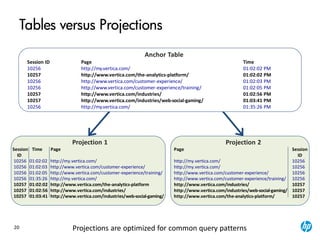
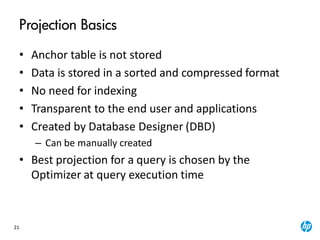
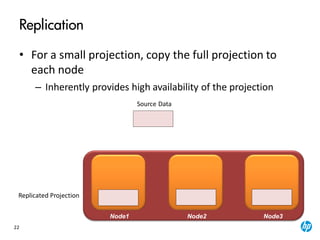
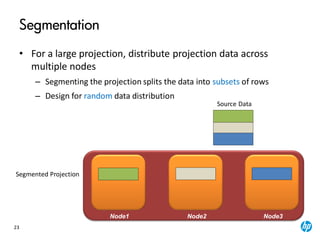
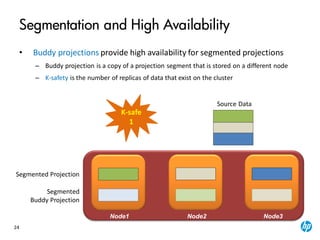
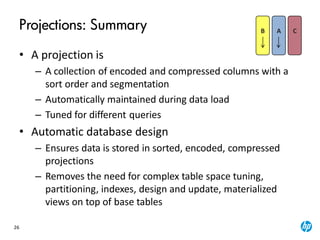
The document provides an overview of the Vertica analytics platform, detailing its architecture, features, and operational processes such as data storage and query execution. Key concepts include the column-oriented storage model, transaction handling, and high availability features that ensure continuous querying and data load. It also highlights the benefits of advanced compression, projections for optimized query execution, and integration with existing tools.















| Aggregates: customer_age), customer_age), count(*)
| Group By: customer_region, customer_name
| +---> STORAGE ACCESS for customer_dimension [Cost:407,Rows:6K](PATH ID:2)
| | Projection: public.customer_dimension_VMart_Design_node0001
| | Materialize: customer_region, customer_name, customer_age
| | Filter: (customer_gender = 'Male')
| | Filter: (customer_region = ANY (ARRAY['East', 'Midwest']))
EXPLAIN
SELECT customer_name,customer_region,avg(customer_age),count(*)
FROM customer_dimension
WHERE customer_gender='Male' and customer_region in('East','Midwest')
GROUP BY customer_region, customer_name;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1essentials7-160229065636/85/Vertica-7-0-Architecture-Overview-29-320.jpg)