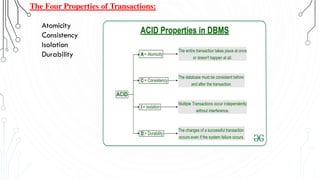
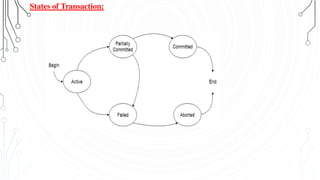
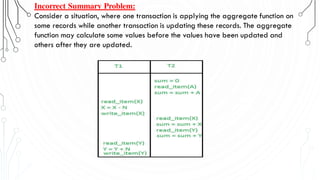
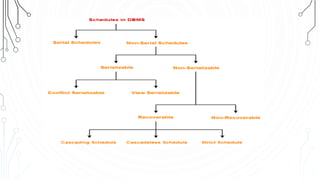
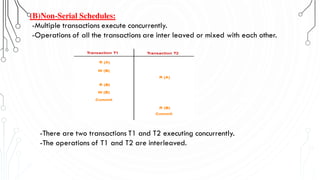
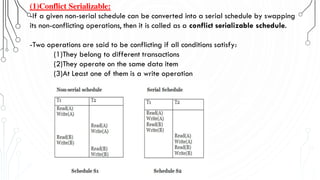
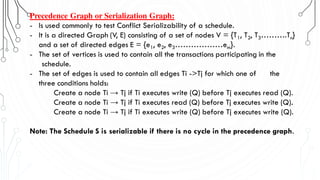
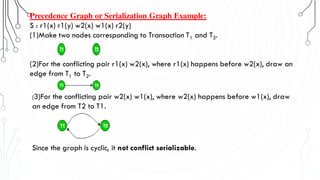
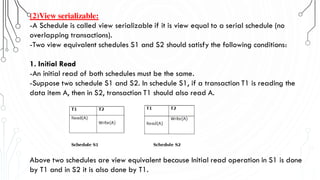
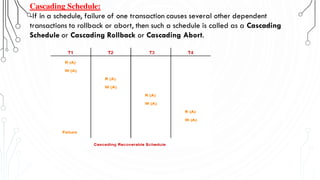
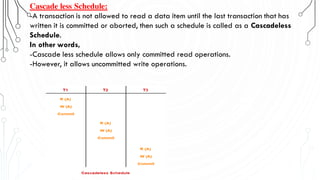
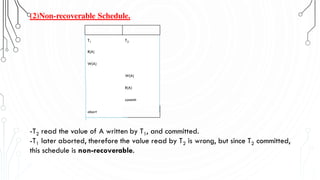
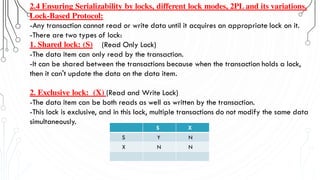
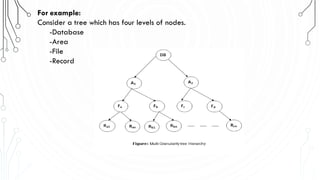
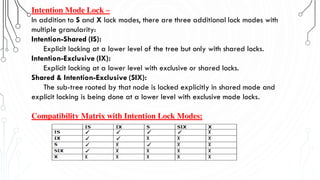
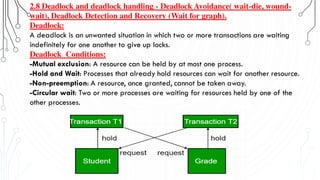
This document discusses transaction concepts and concurrency control. It defines a transaction as a collection of operations that performs a logical function in a database. The four properties of transactions are outlined as atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Transaction states such as active, committed, and aborted are defined. Concurrency control techniques including locking, timestamps, and deadlock handling are explained. Deadlock avoidance algorithms like wait-die and wound-wait are summarized.