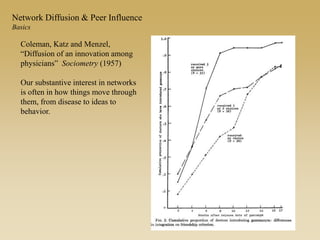
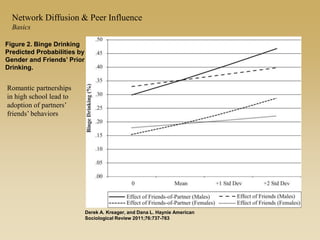
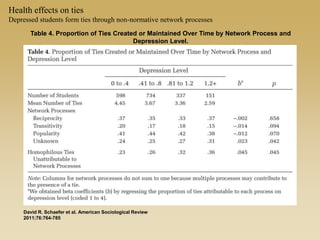
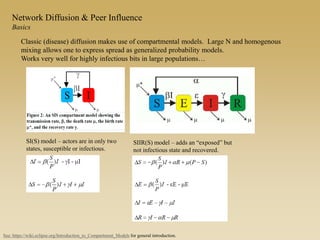
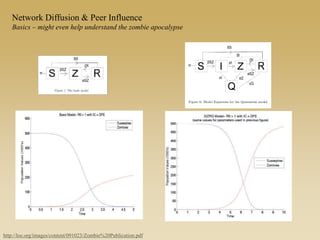
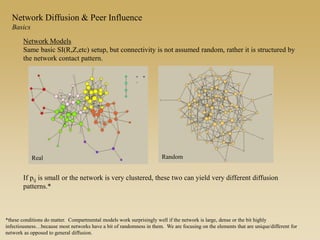
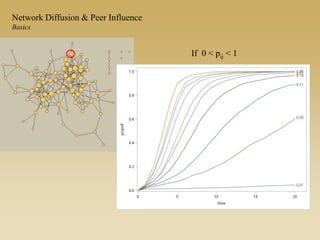
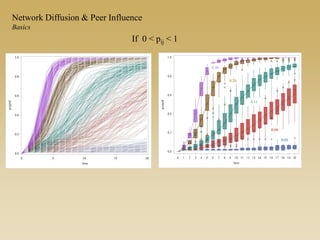
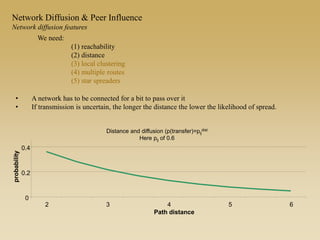
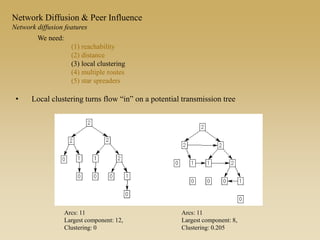
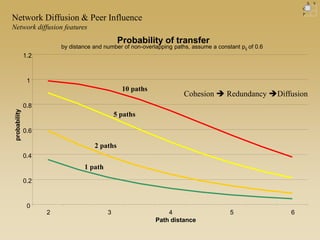
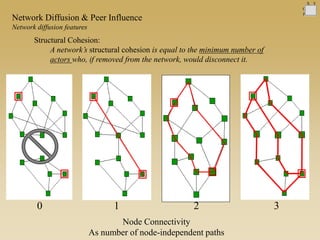
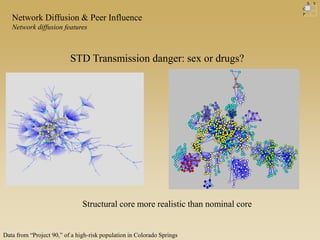
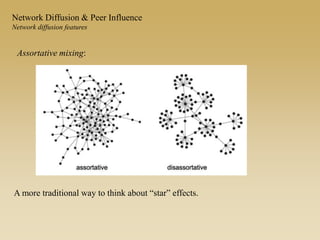
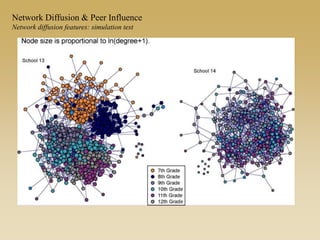
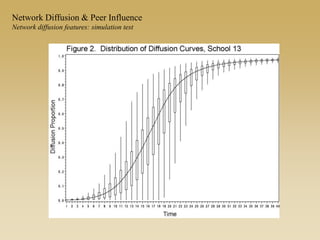
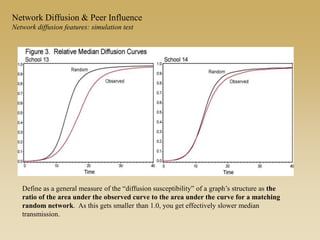
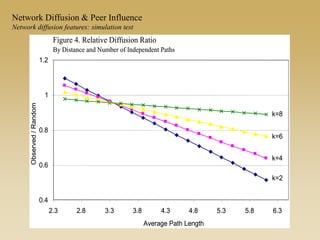
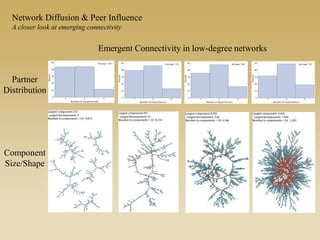
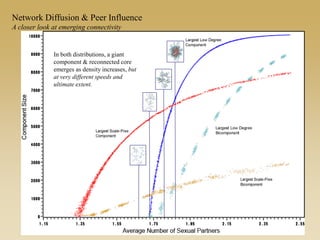
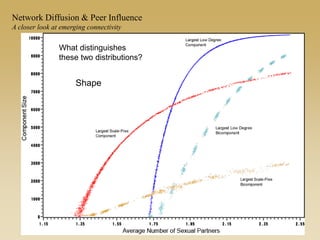
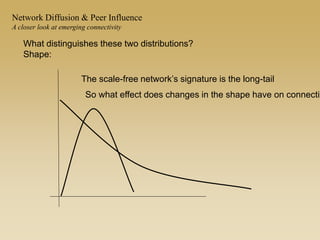
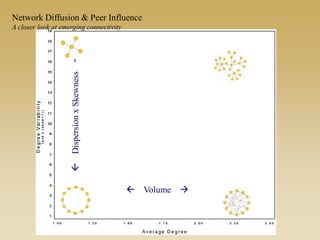
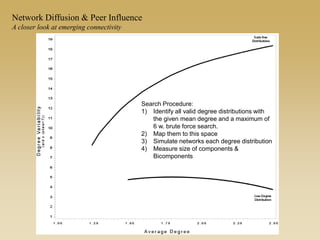
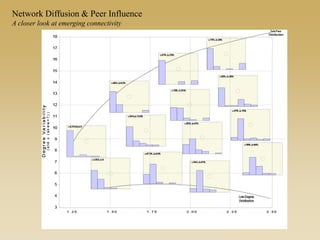
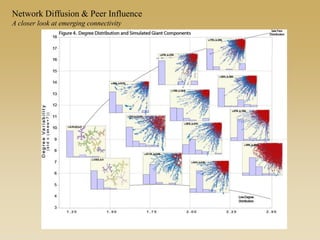
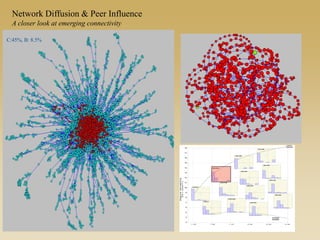
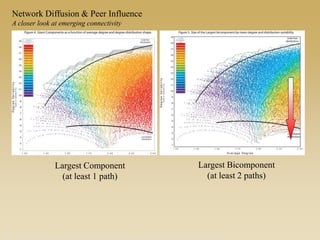
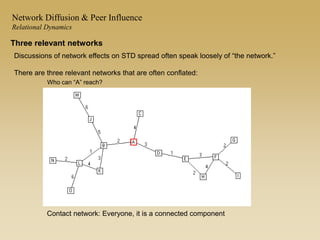
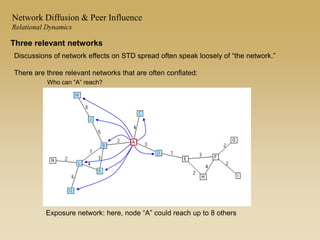
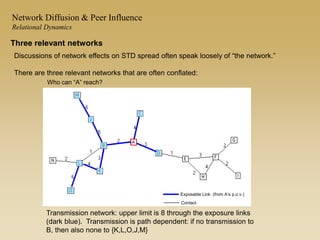
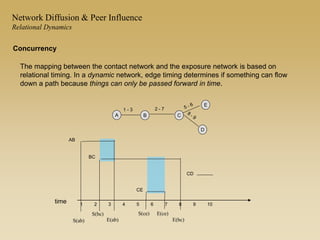
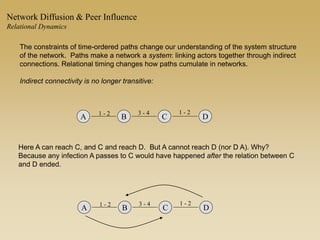
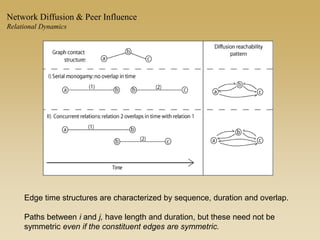
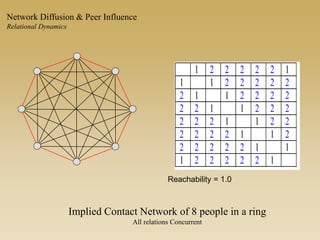
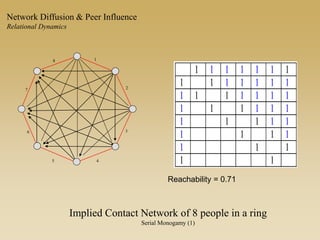
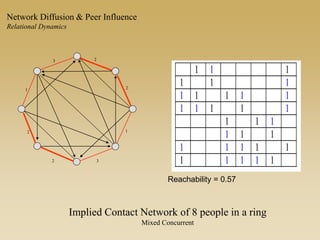
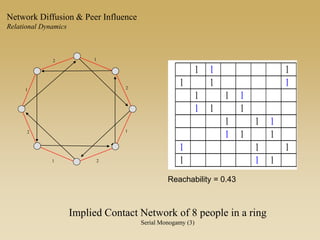
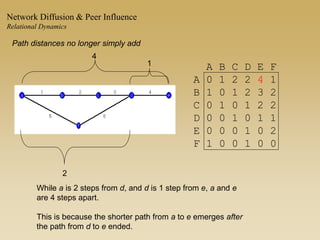
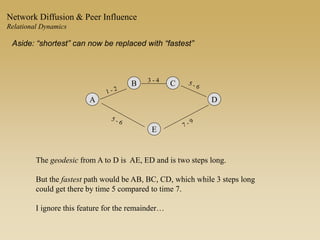
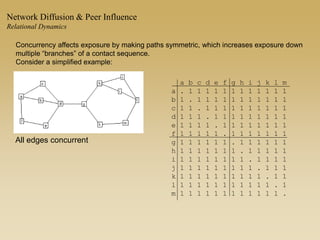
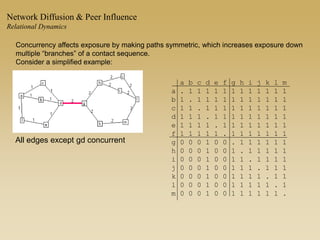
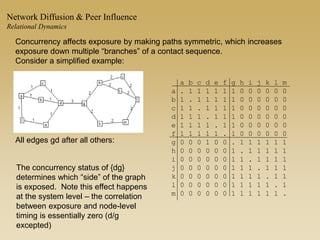
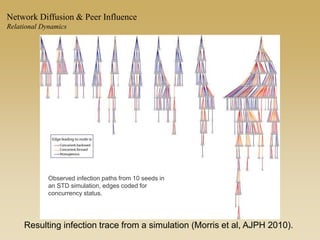
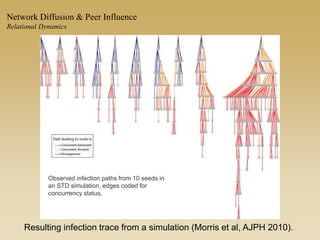
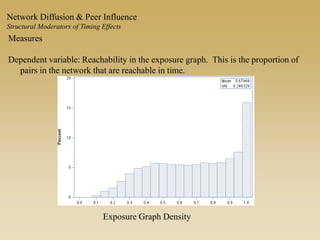
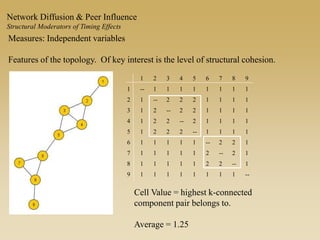
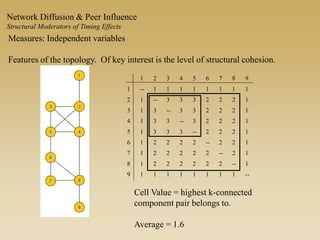
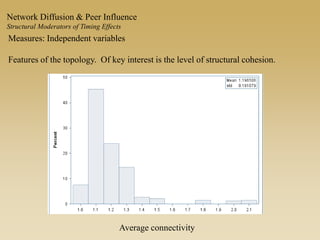
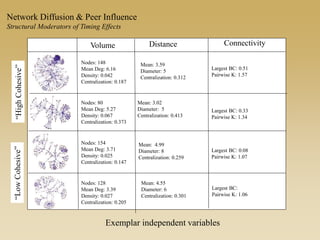
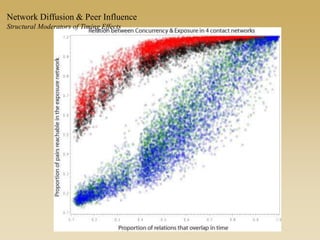
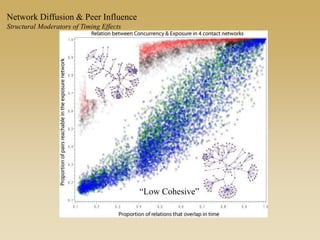
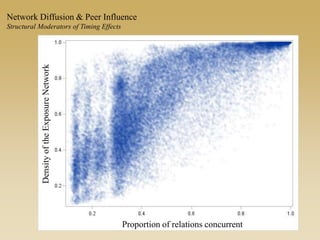
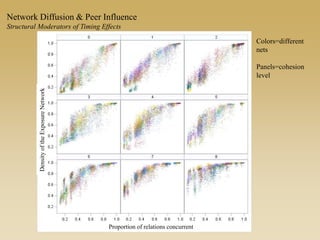
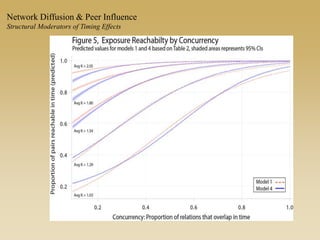
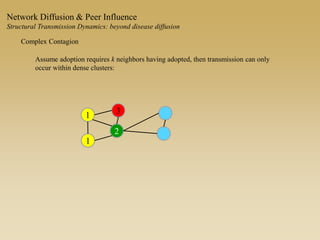
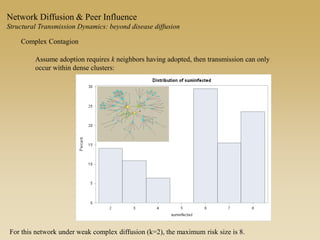
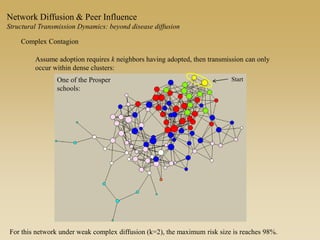
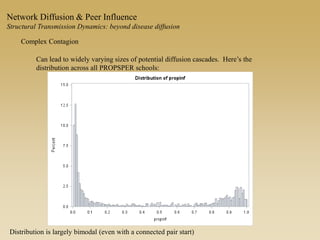
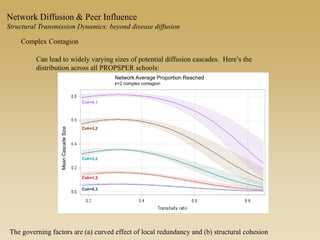
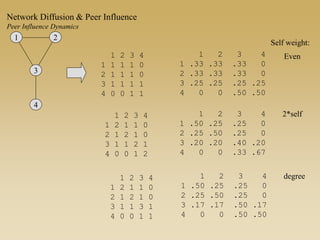
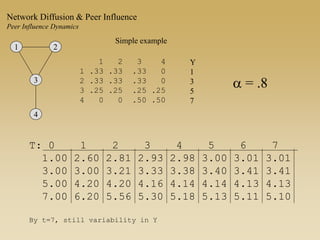
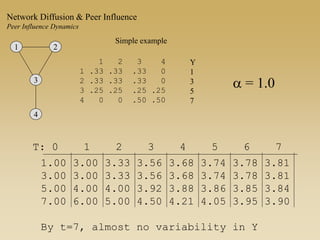
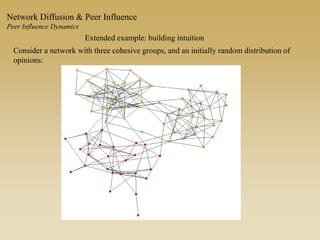
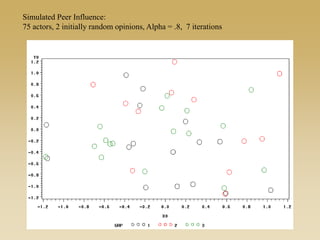
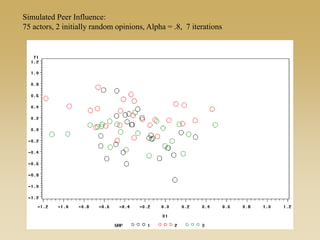
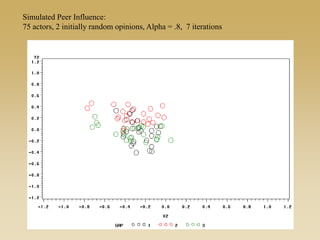
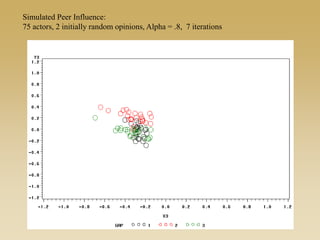
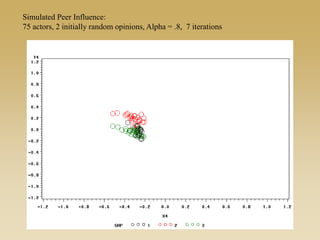
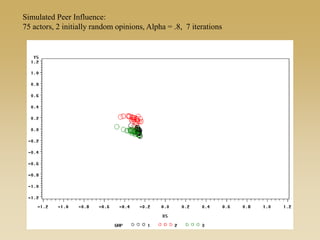
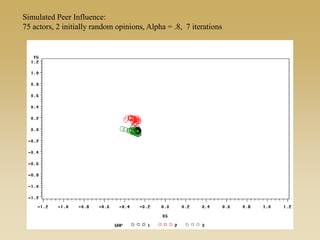
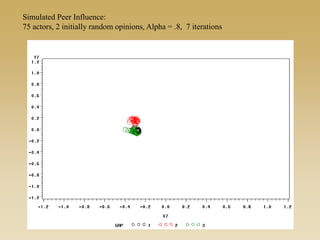
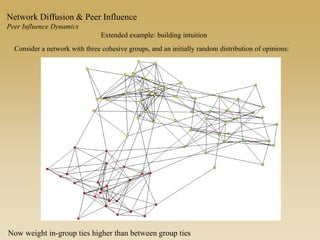
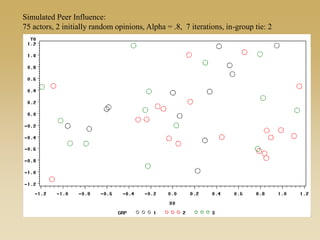
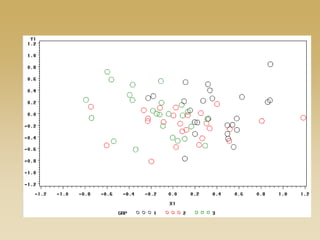
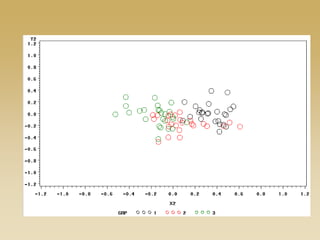
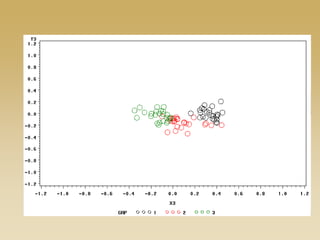
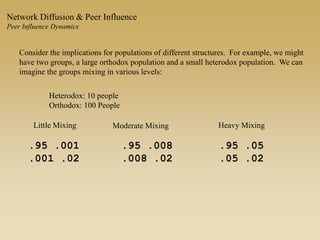
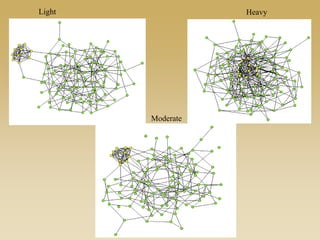
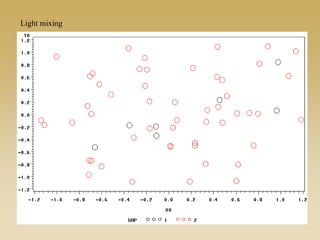
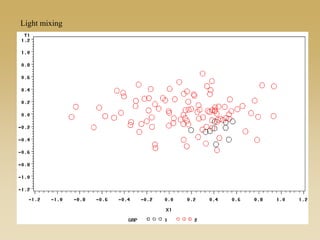
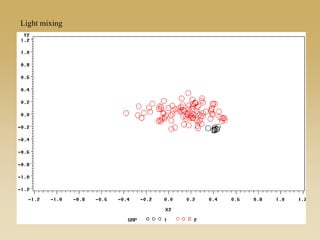
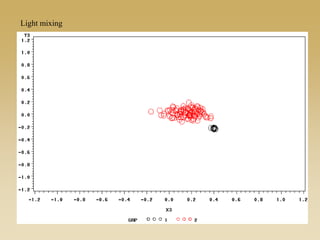
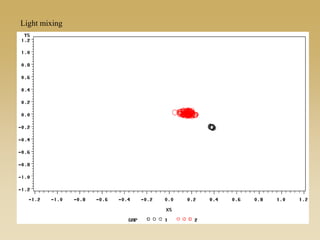
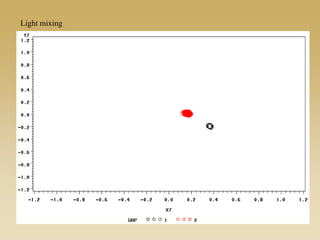
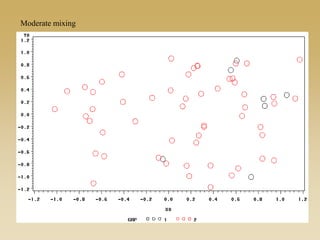
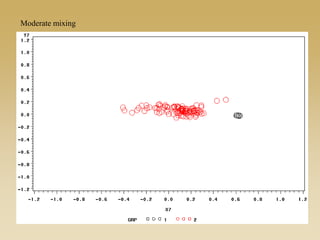
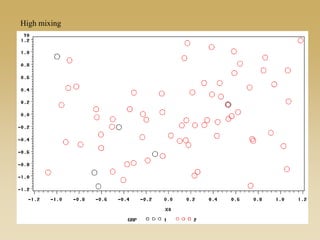
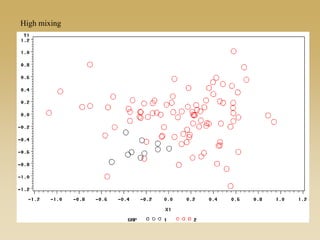
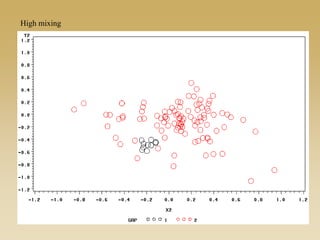
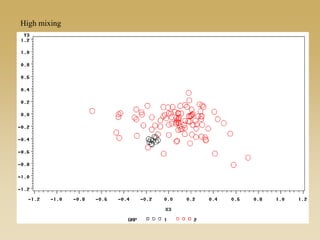
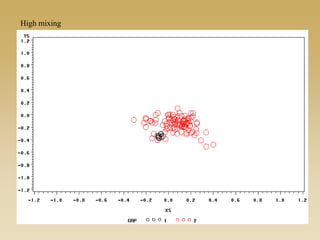
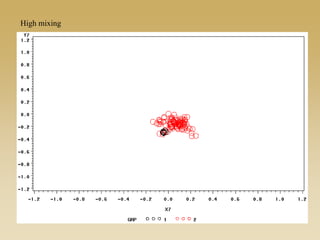
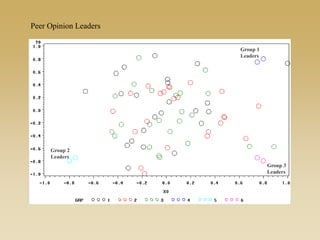
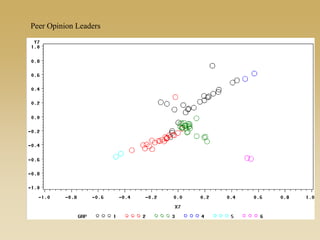
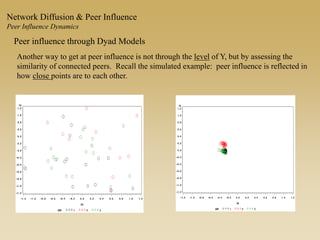
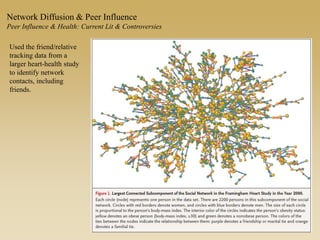
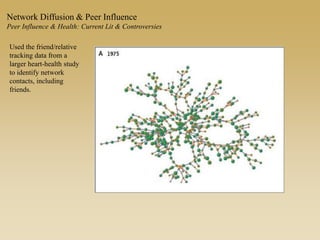
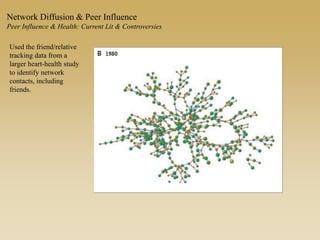
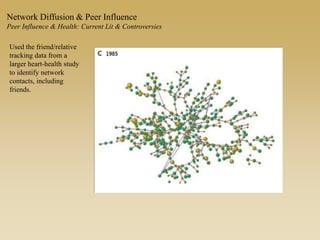
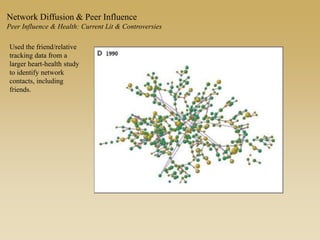
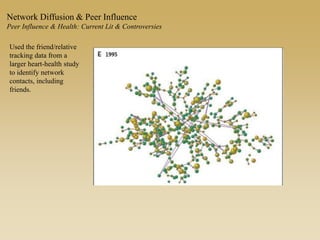
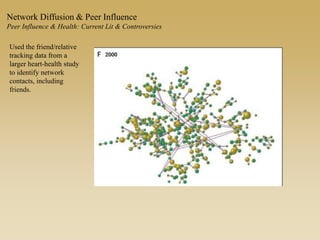
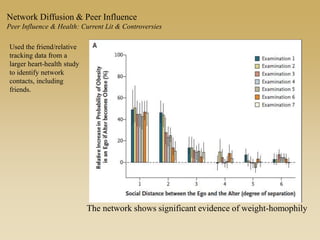
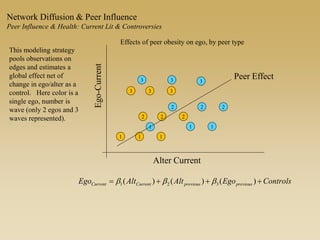
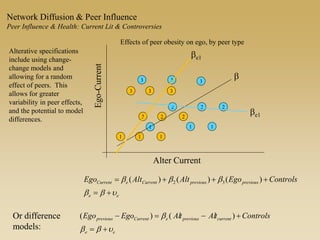
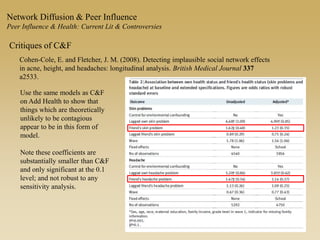
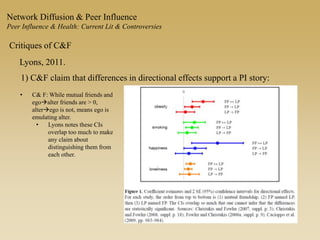
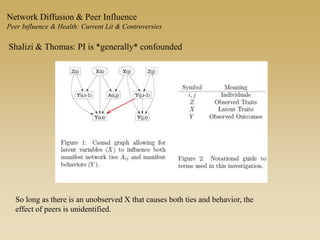
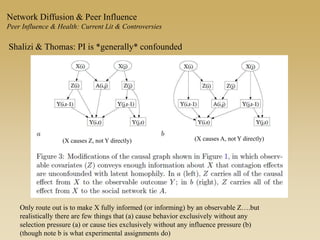
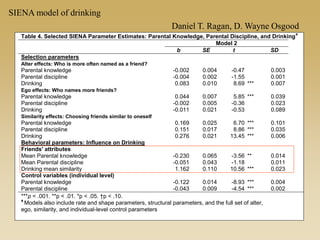
This document discusses diffusion and peer influence through networks. It begins by defining diffusion and compartment models used to model disease spread. It then discusses how network structure, including topology, timing of connections, and clustering, can impact diffusion compared to random mixing. Key network features that influence diffusion speed and reach include distance between actors, number of alternate paths, presence of highly connected "star" nodes, and assortative mixing. The document concludes by exploring how different degree distributions in emergent low-density networks can impact the formation of large connected components.