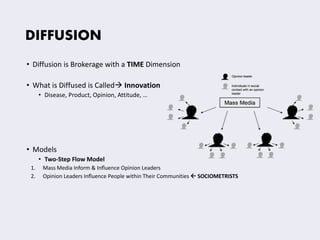
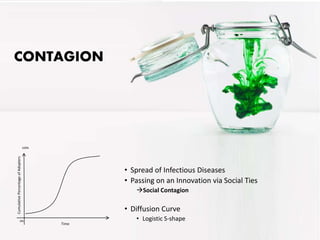
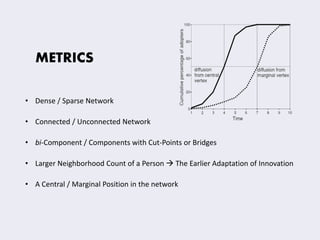
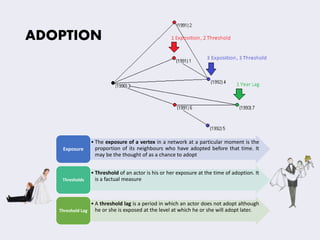
This document discusses concepts related to the diffusion and spread of innovations through social networks. It covers key topics such as diffusion models like the two-step flow model, metrics for analyzing social network structures, factors that influence adoption rates like centrality and density, and concepts like critical mass and thresholds. Models of contagion are also referenced, drawing parallels to the spread of diseases.