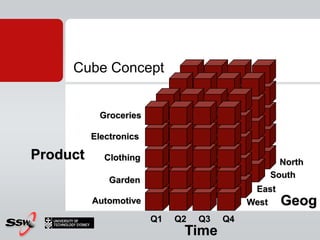
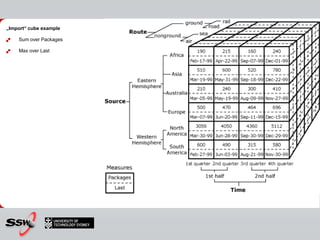
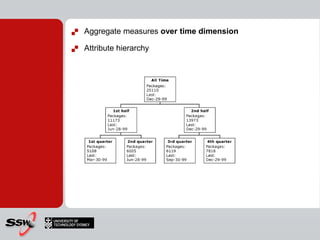
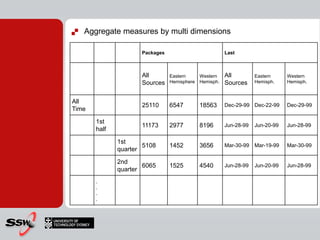
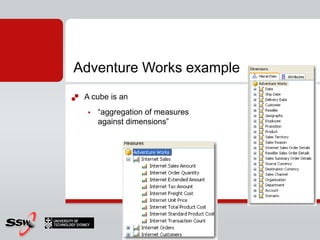
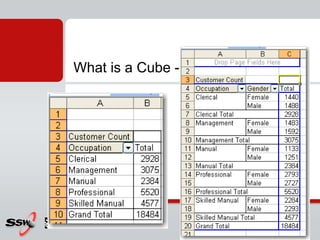
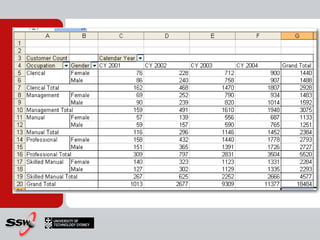
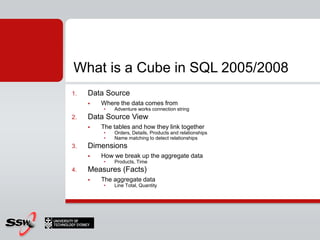
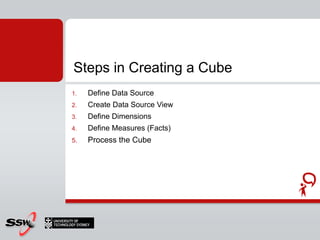
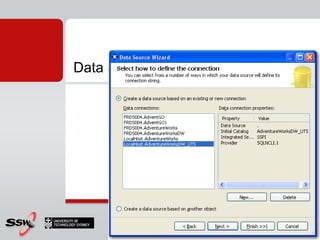
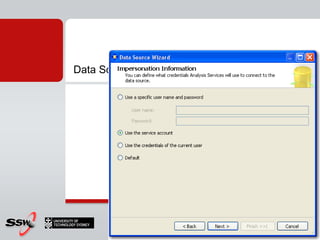
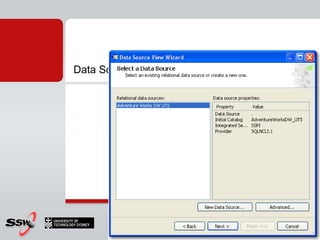
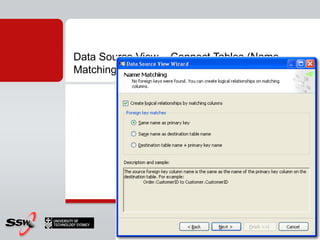
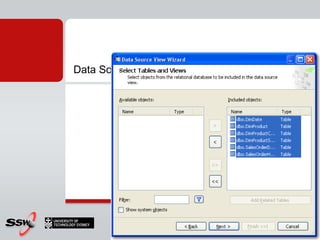
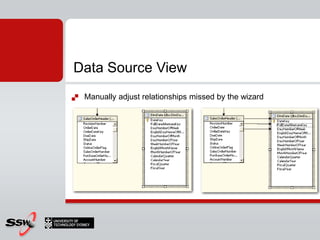
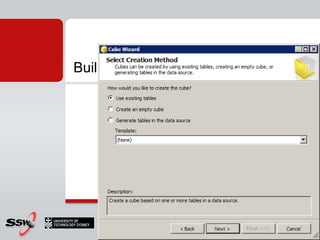
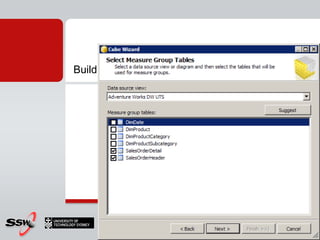
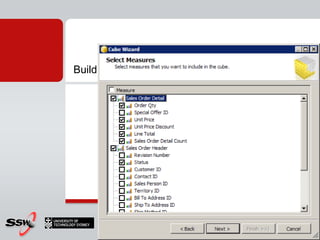
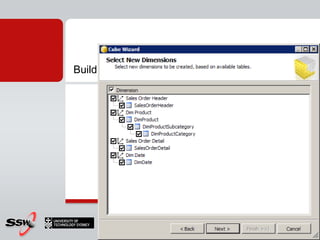
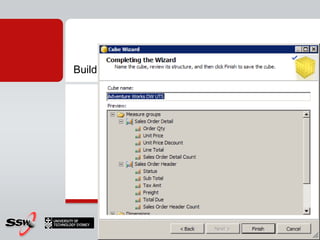
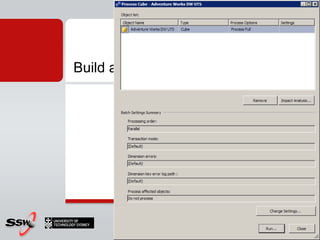
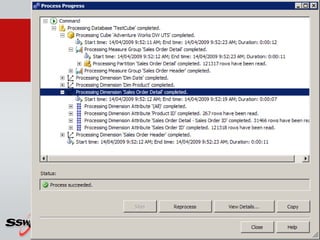
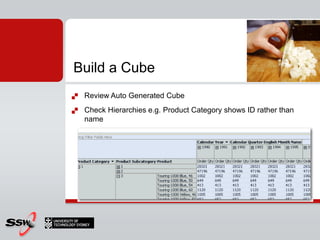
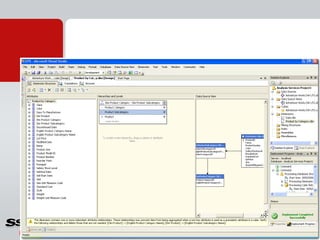
This document provides information about a SQL Server 2008 for Business Intelligence short course. The course aims to help developers step to the next level by learning modern engineering practices using Visual Studio 2010, Team Foundation Server, and the Scrum framework. Certifications are available upon completion of assessments. Contact and resource details are provided for the course instructor Peter Gfader, including his areas of specialization and online profiles. An overview of the course schedule and topics is also given.