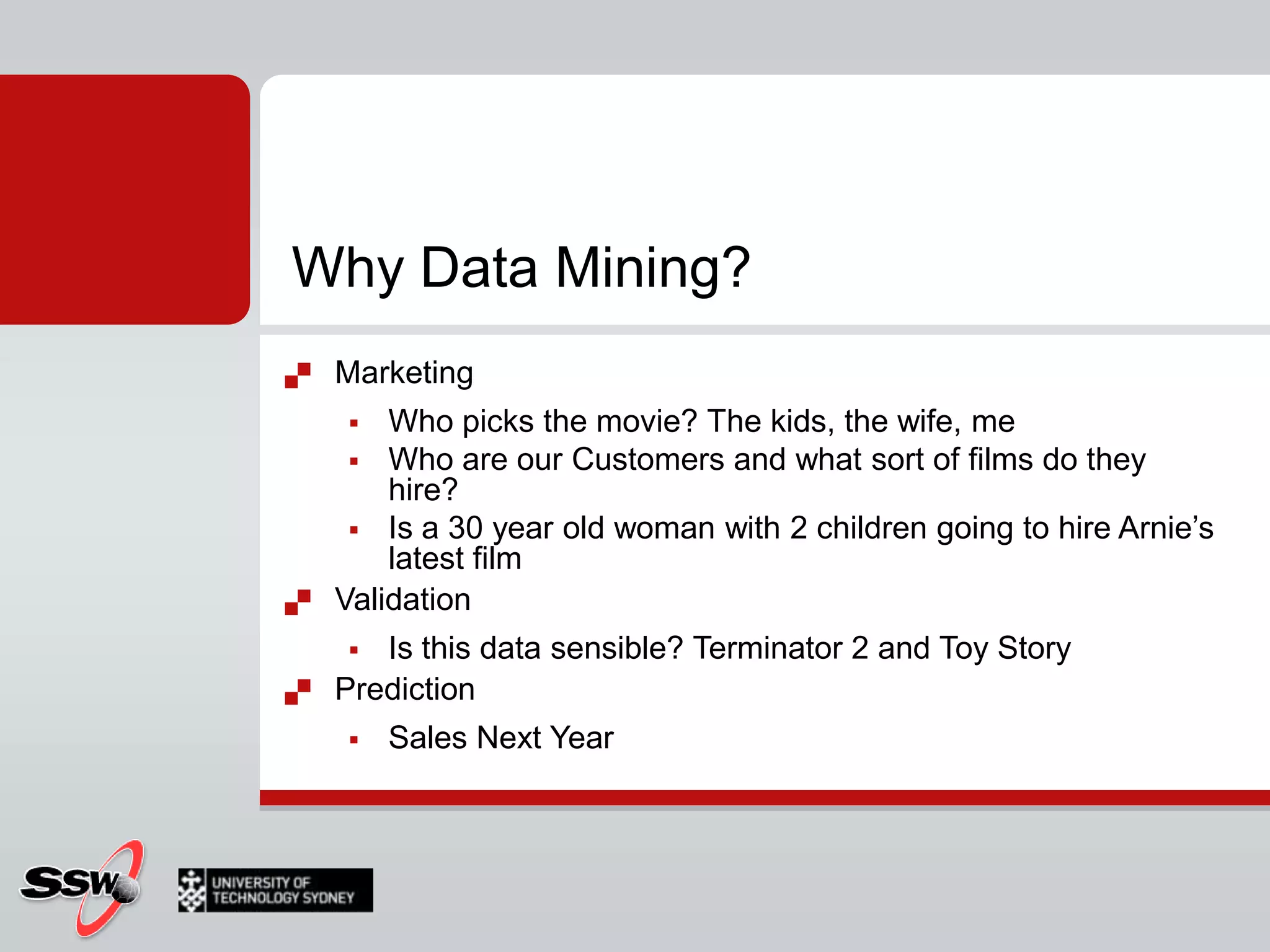
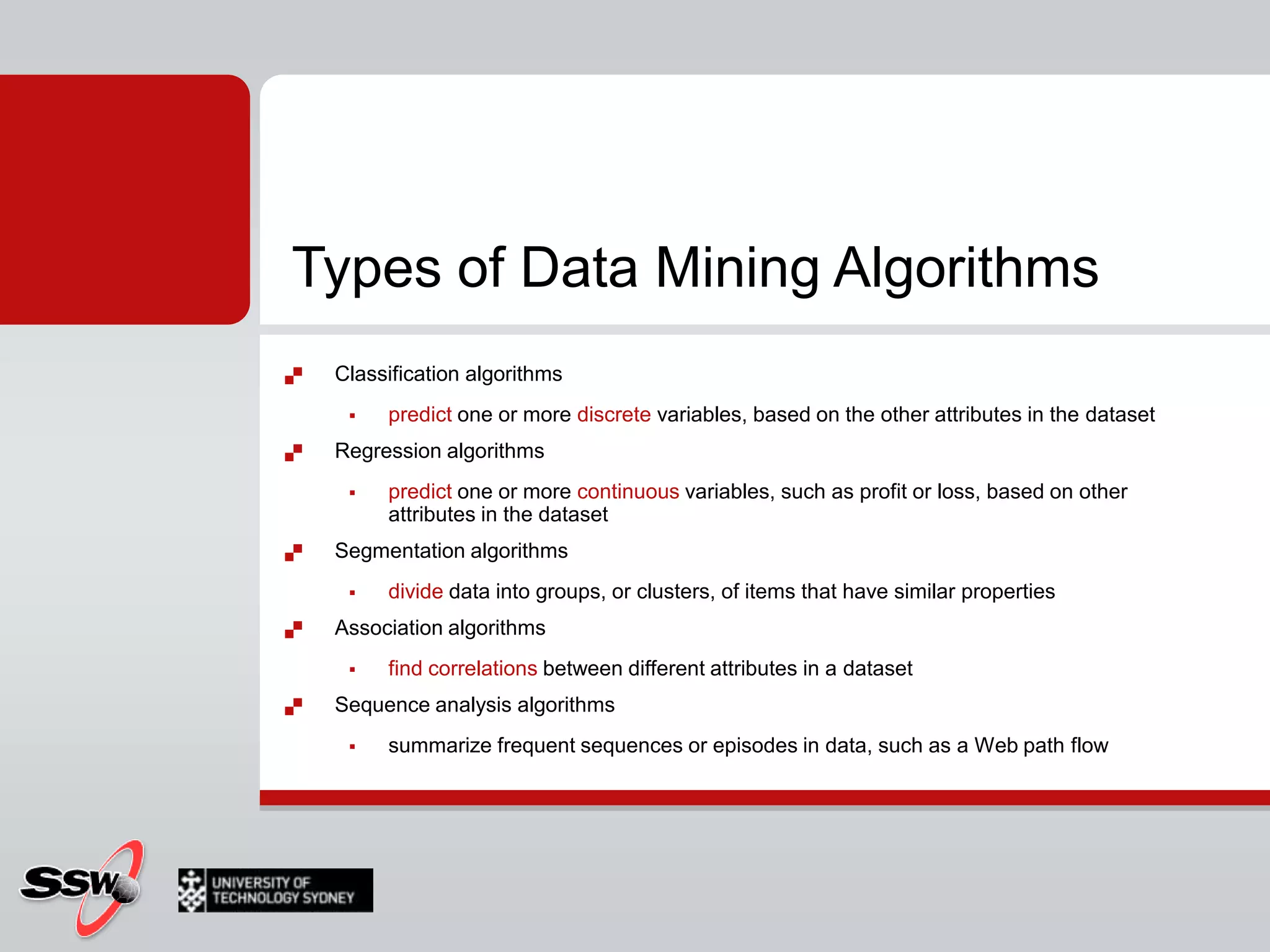
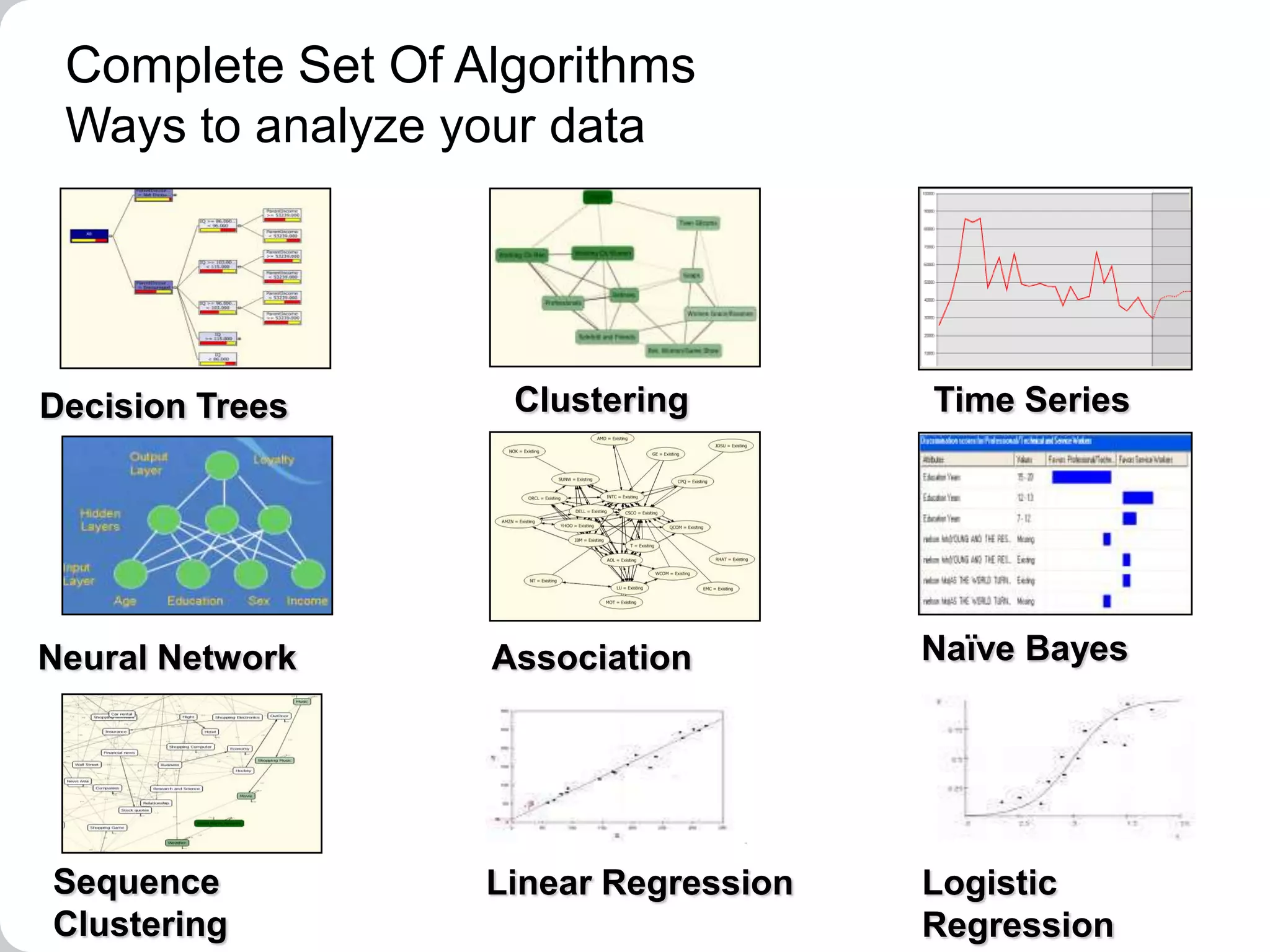
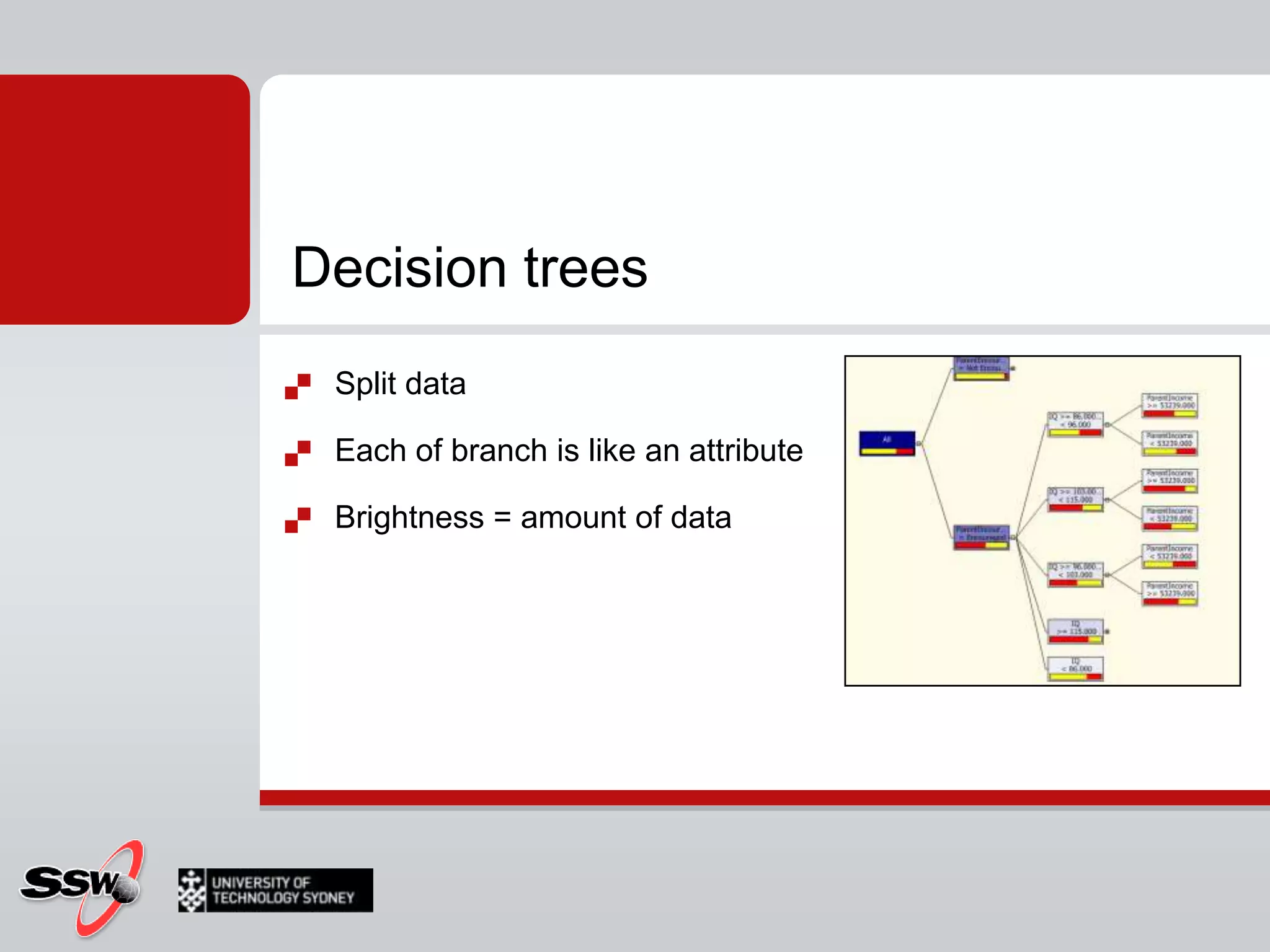
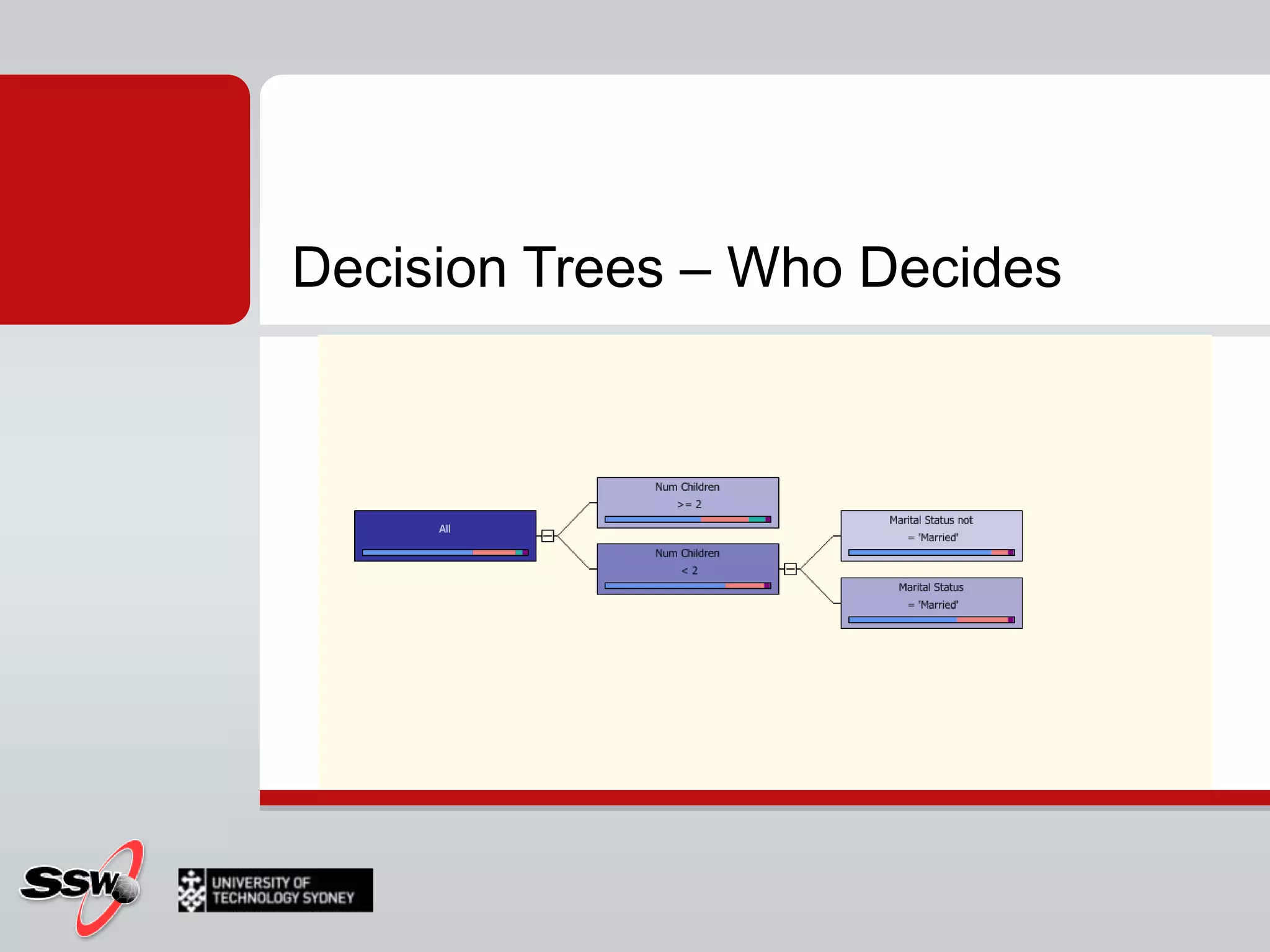
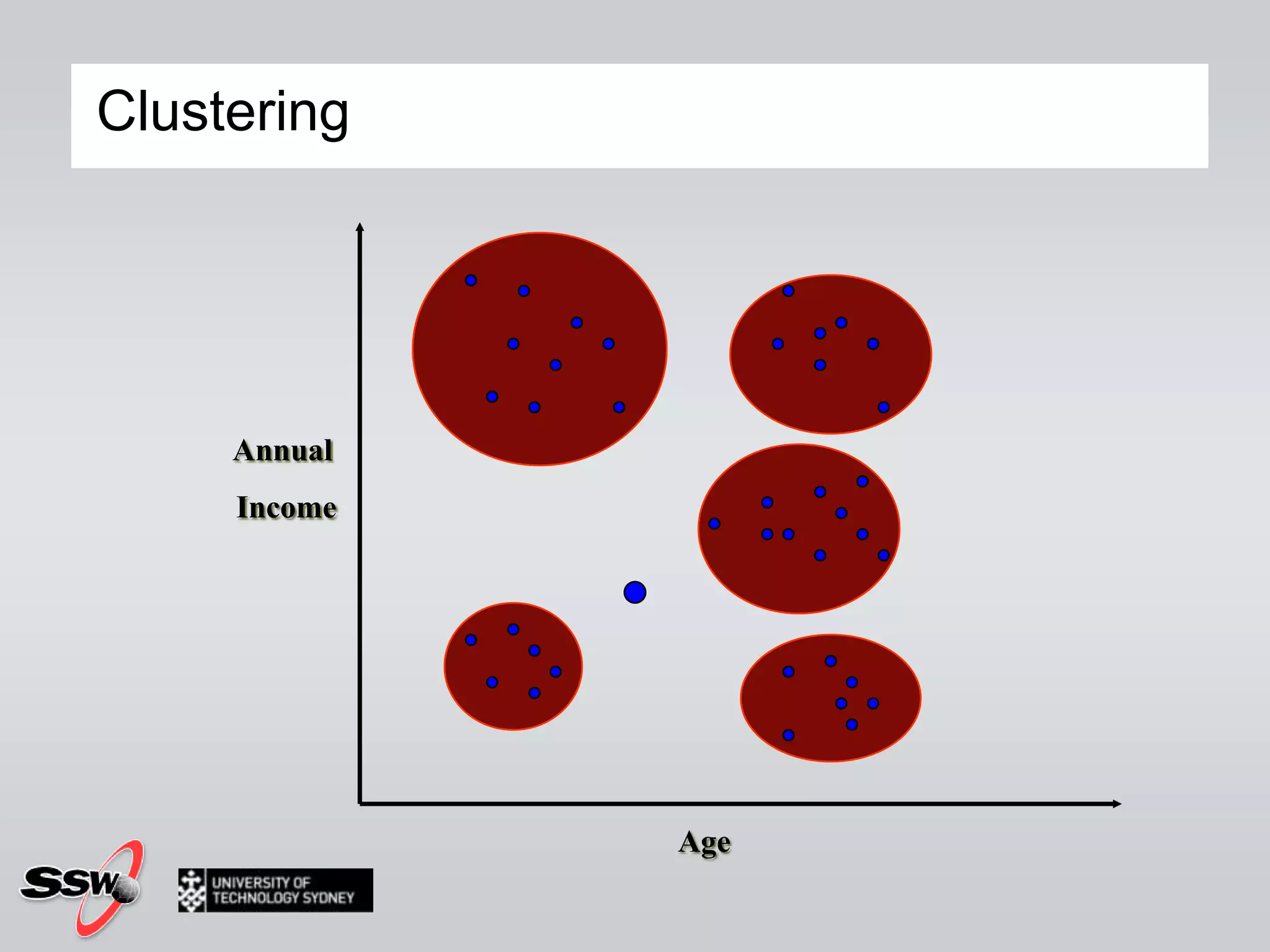
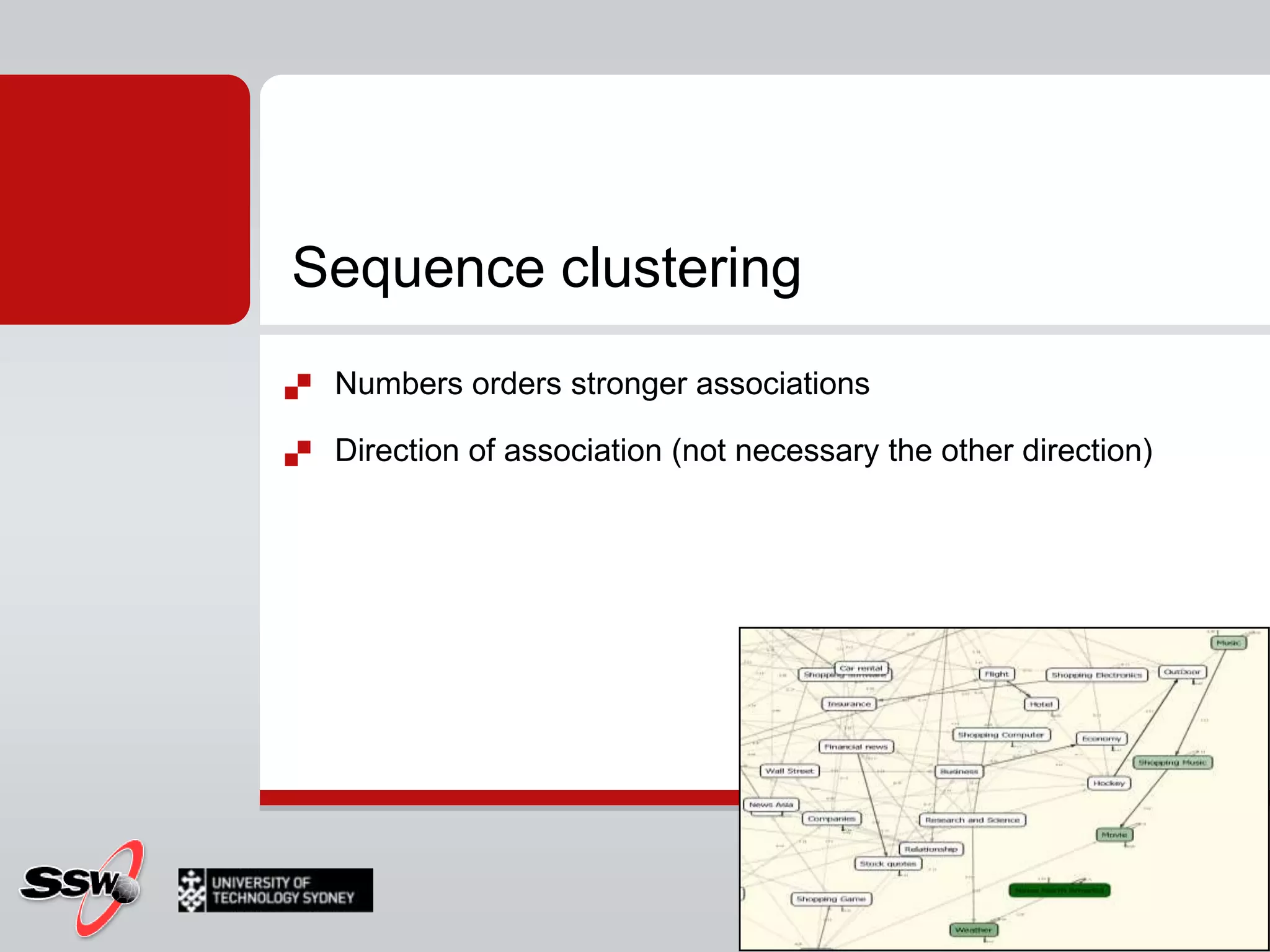
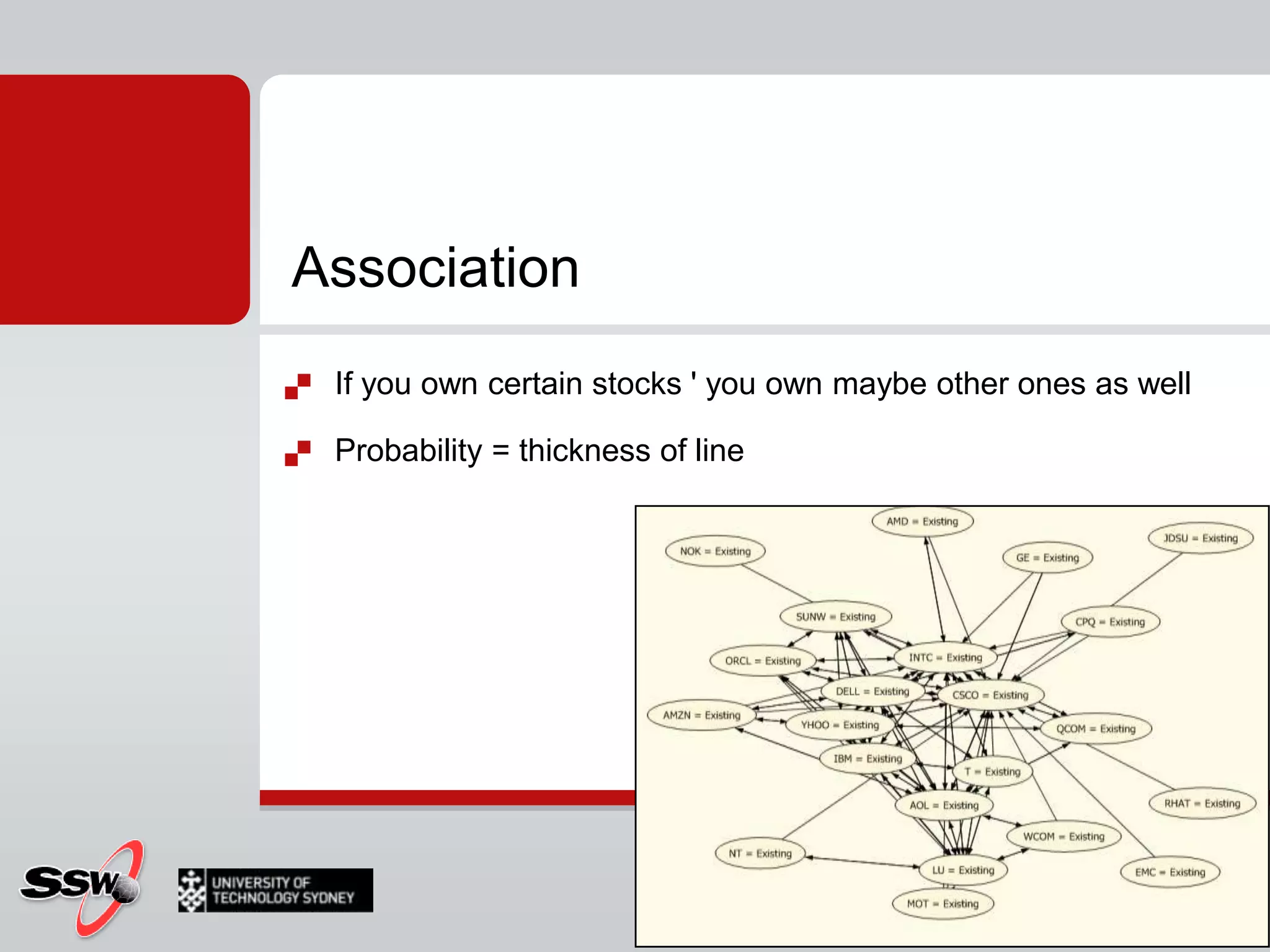
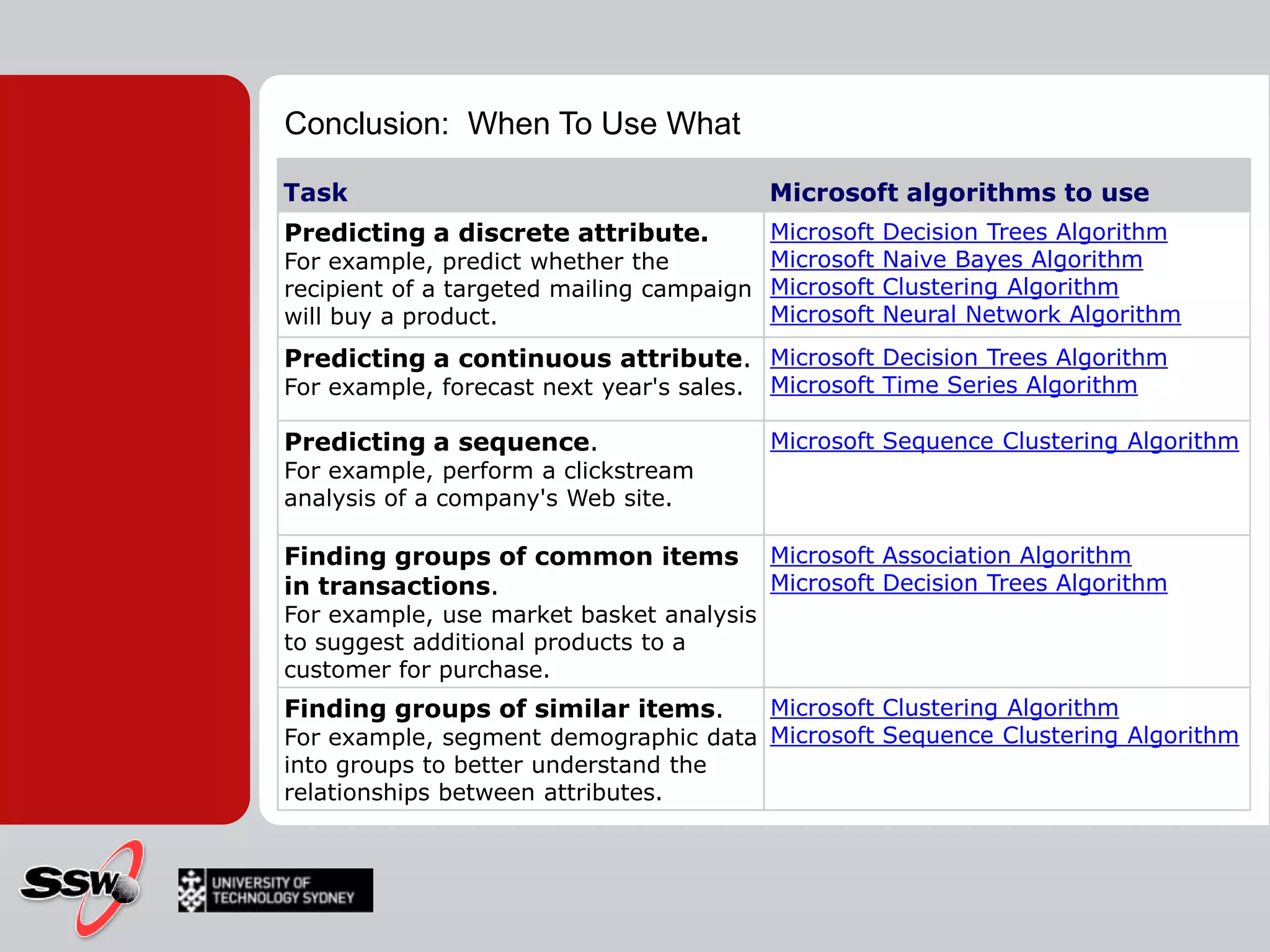
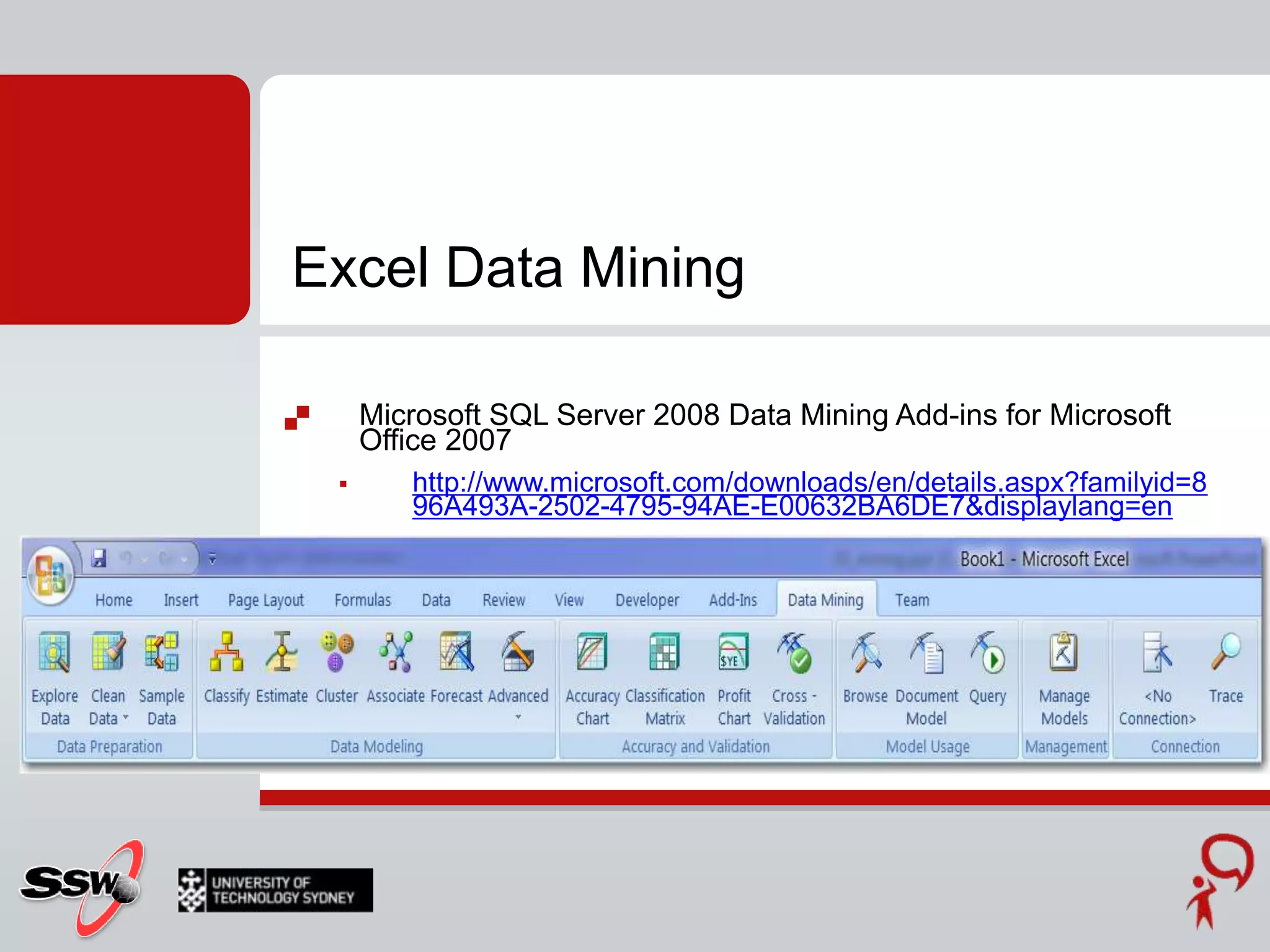
This document provides an overview of a SQL Server 2008 for Business Intelligence short course. It discusses the course instructor's background and specialties. The course will cover creating a data warehouse, OLAP cubes, and reports. It will also discuss data mining concepts like why it's used, common algorithms, and include a hands-on lab. Data mining algorithms that will be covered include classification, clustering, decision trees, and neural networks.