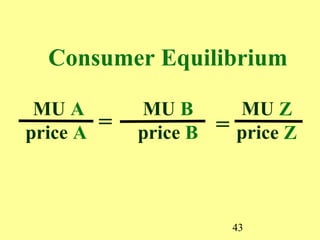
The document summarizes key concepts from consumer choice theory in economics. It discusses the concepts of utility, total utility, marginal utility, diminishing marginal utility, and consumer equilibrium. It explains that consumer equilibrium occurs when the marginal utility per dollar is equal for all goods purchased. This can be used to derive the downward-sloping demand curve, as when price falls, consumption increases to restore equilibrium. The income and substitution effects are also summarized as complementary explanations for the law of demand. When price decreases, these effects work together to increase the quantity demanded.