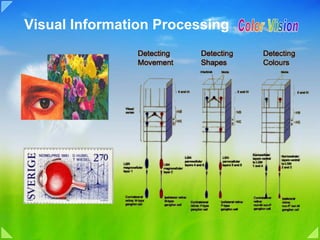
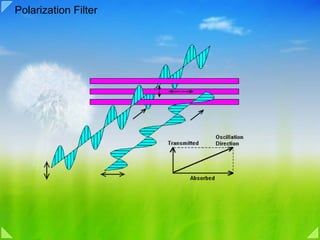
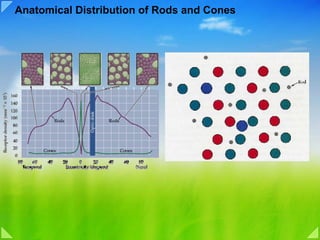
This document discusses various topics related to visual information processing and color vision, including:
- Polarized light and how polarization occurs through reflection and refraction
- Theories of color vision from Alberti, Cennini, Newton, Goethe, and Hering
- Evidence for opponent color theory from fish recordings and studies of the lateral geniculate nucleus
- The three types of cones and how color is processed in the visual cortex and beyond striate cortex
- Tests for color blindness like the Ishihara chart