The document discusses color vision theory and describes:
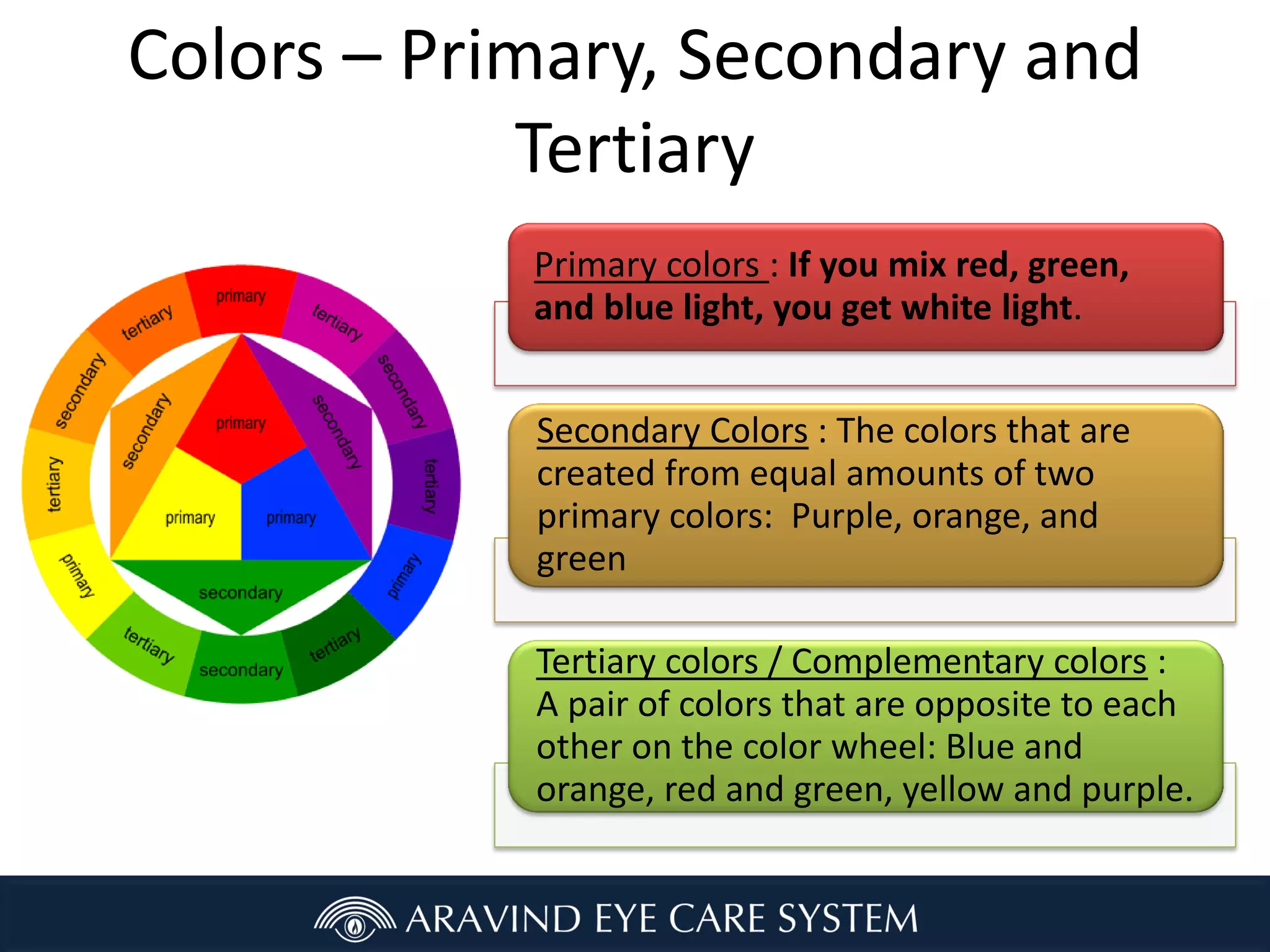
- The primary, secondary, and tertiary colors
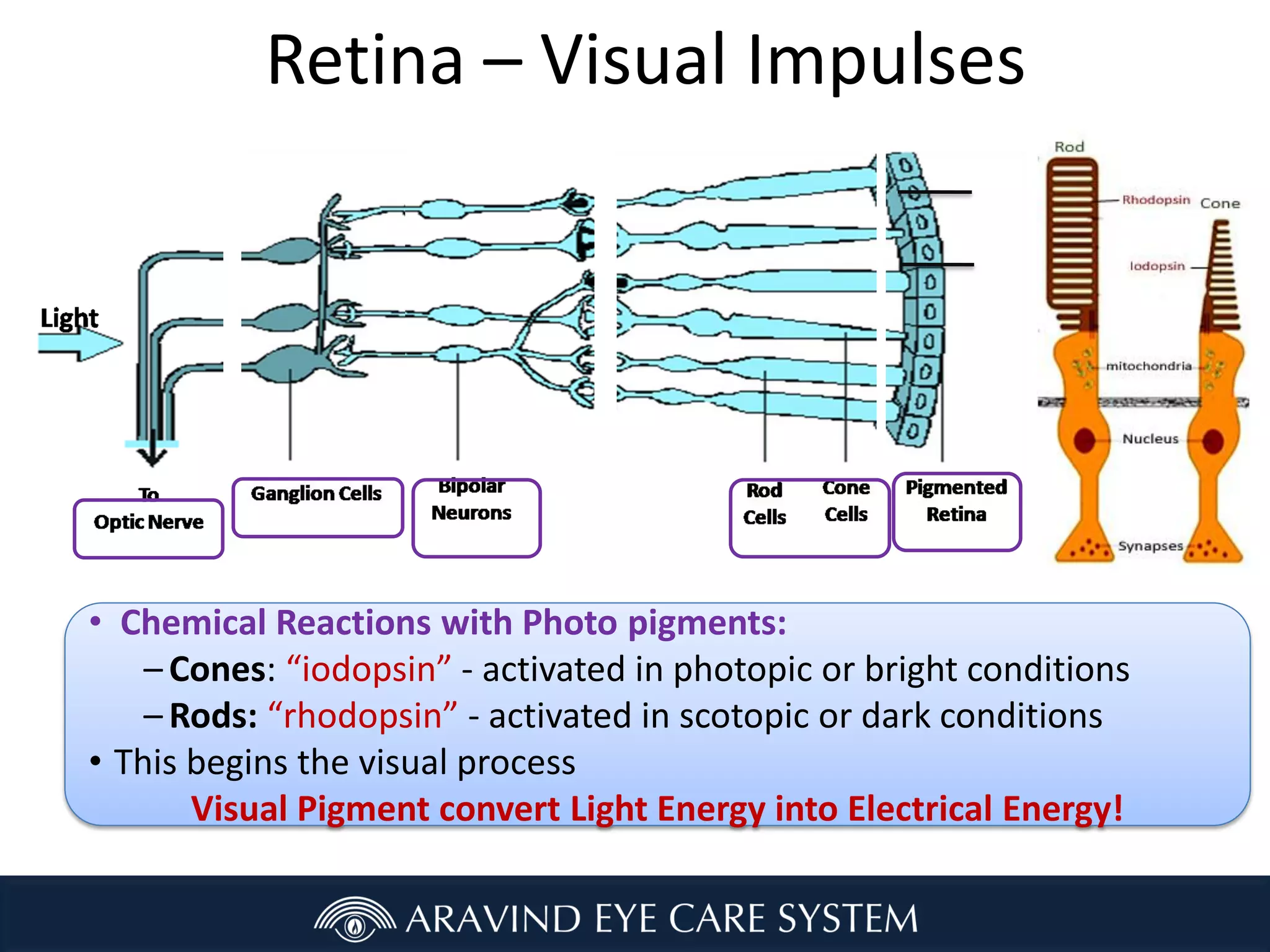
- How light is detected by the retina and processed by the visual system
- Thomas Young and Hermann von Helmholtz's trichromatic theory that the eye contains three types of cone cells sensitive to different wavelengths corresponding to red, green, and blue light
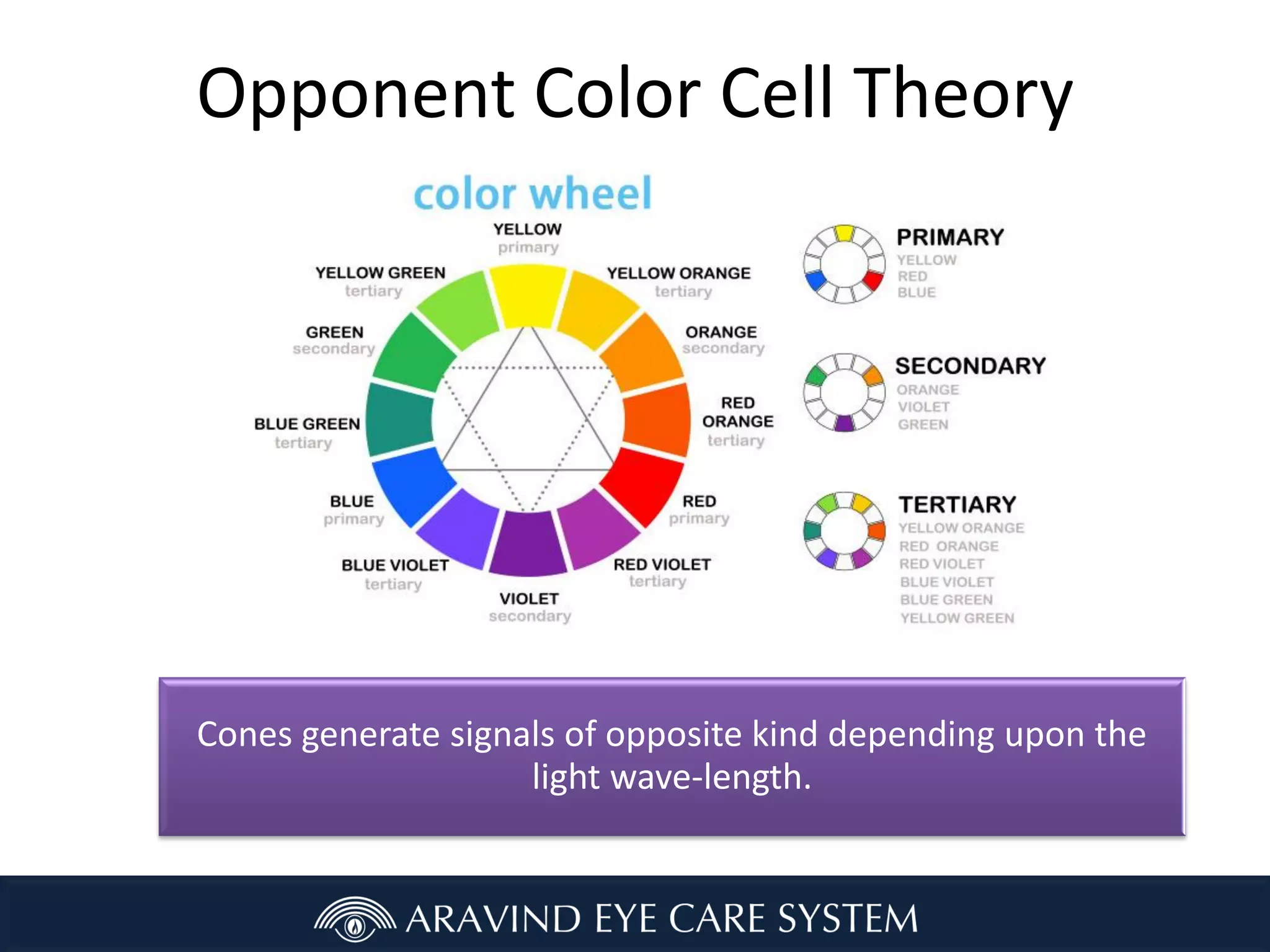
- Karl Hering's opponent process theory that the retina contains cells that respond in opposition to colors like red/green and yellow/blue
- Different theories on color vision from Aristotle and the role of elements to the modern understanding of cone cell function in the retina.