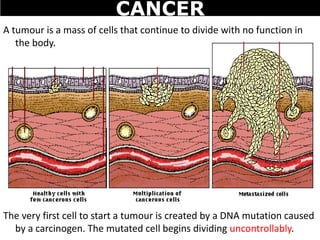
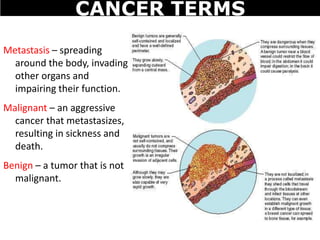
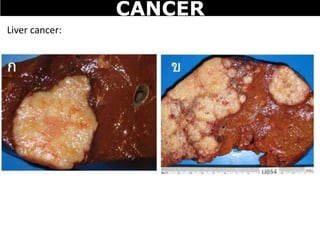
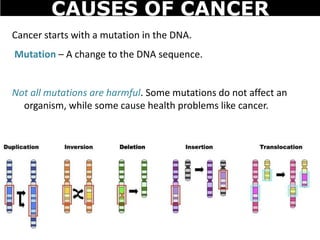
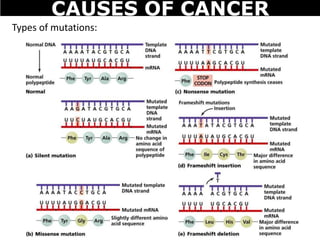
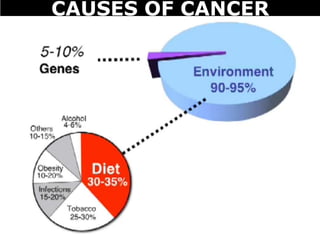
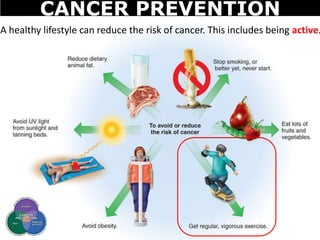
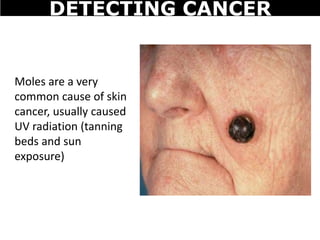
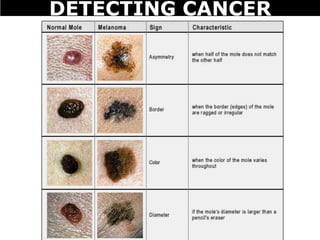
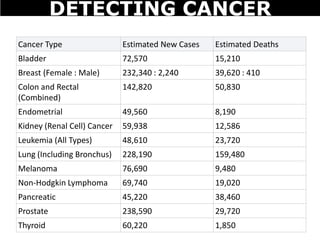
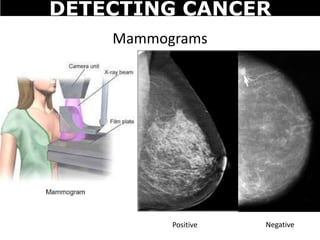
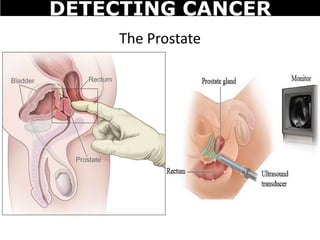
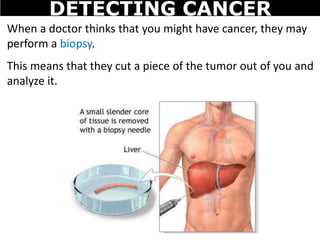
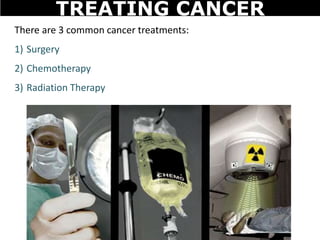
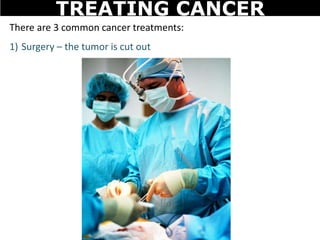
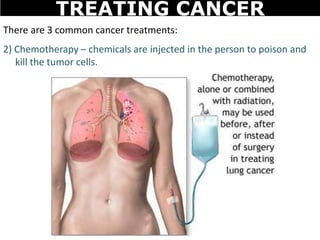
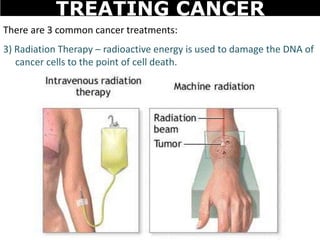
Cancer is a deadly disease where cells divide uncontrollably and can spread throughout the body. There are several types of cancer that originate from different cell types. Cancer is caused by mutations in DNA and can be influenced by factors like tobacco, radiation, viruses, and diet. Doctors use tests like biopsies, mammograms, and prostate exams to detect cancer early. The main treatment options are surgery to remove tumors, chemotherapy to poison cancer cells, and radiation therapy to damage cancer cell DNA.