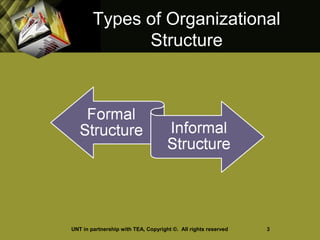
This document discusses business organization and management. It covers topics like organizational structures, guidelines for businesses, principles of effective organization, how departments are organized, levels of management, and the functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It also addresses managerial qualities and advantages/disadvantages of being a manager, as well as the importance of teamwork.