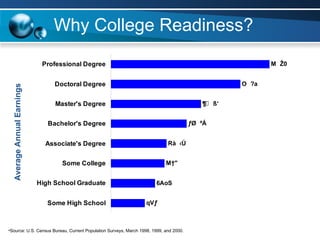
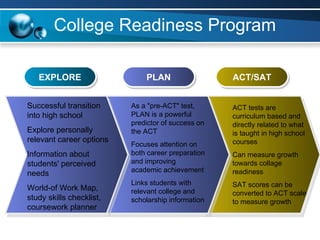
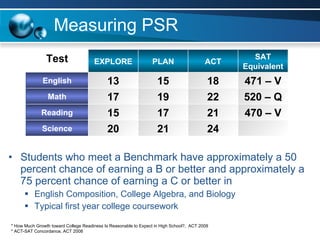
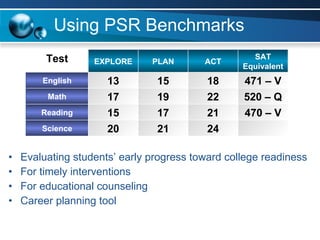
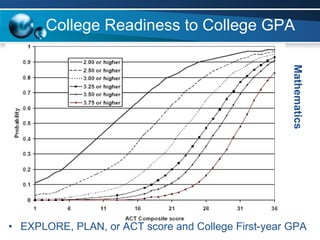
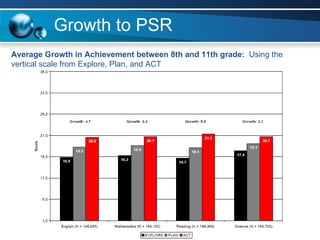
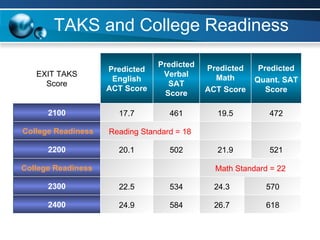
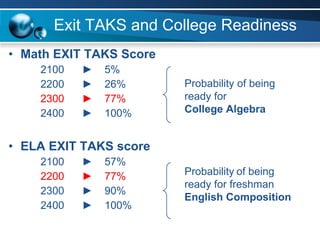
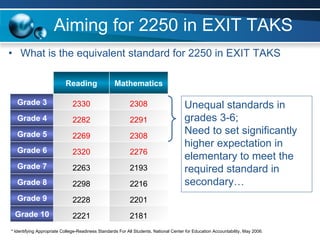
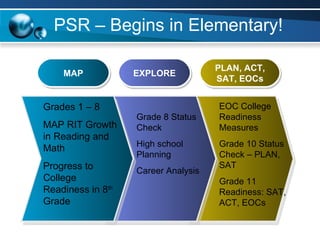
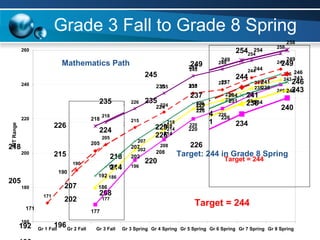
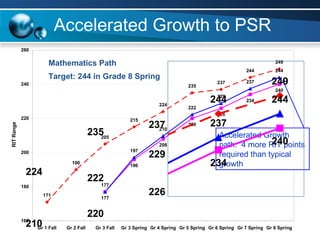
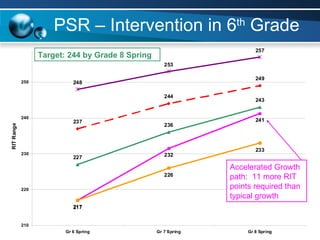
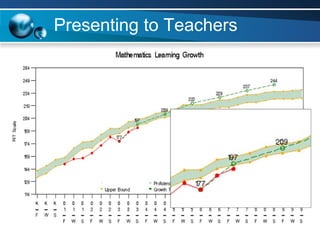
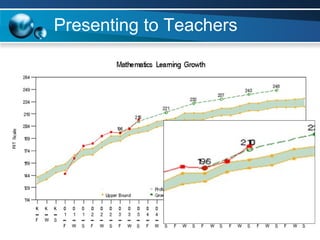
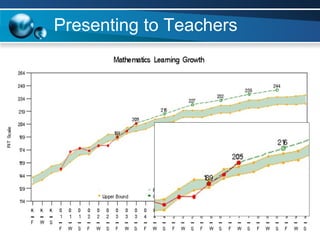
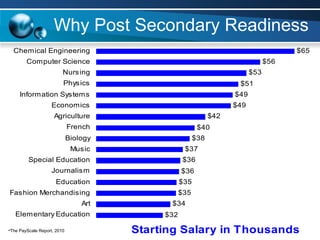
The document discusses paths to post secondary readiness (PSR) and measuring student progress towards college readiness. It outlines a college preparation program that helps students stay in high school, earn higher test scores, enroll and persist in college, and earn a degree. The document also discusses using standardized test scores from middle school through high school to measure PSR growth and set benchmarks to indicate readiness for first-year college coursework. School districts can chart student growth trajectories starting in elementary school to monitor their progress towards meeting PSR targets.





![Paths to Post Secondary Readiness Dr. Dash Weerasinghe Assessment and Accountability Plano ISD [email_address] 4 th Annual Texas MAP User Conference - July 28, 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20100729post-secondary-readinessmapuserconf-100727234721-phpapp01/85/20100729-post-secondary-readiness-mapuserconf-23-320.jpg)