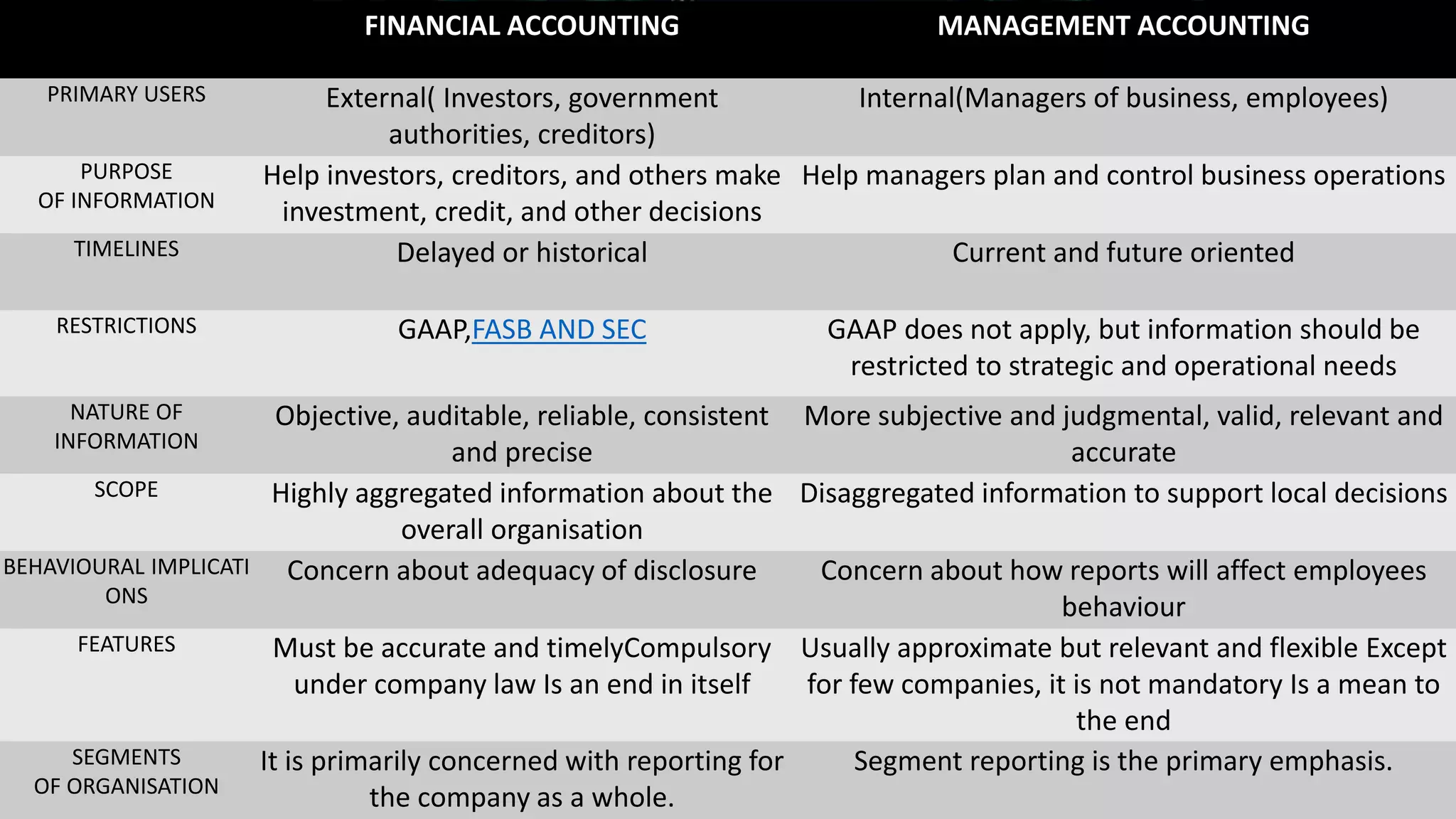
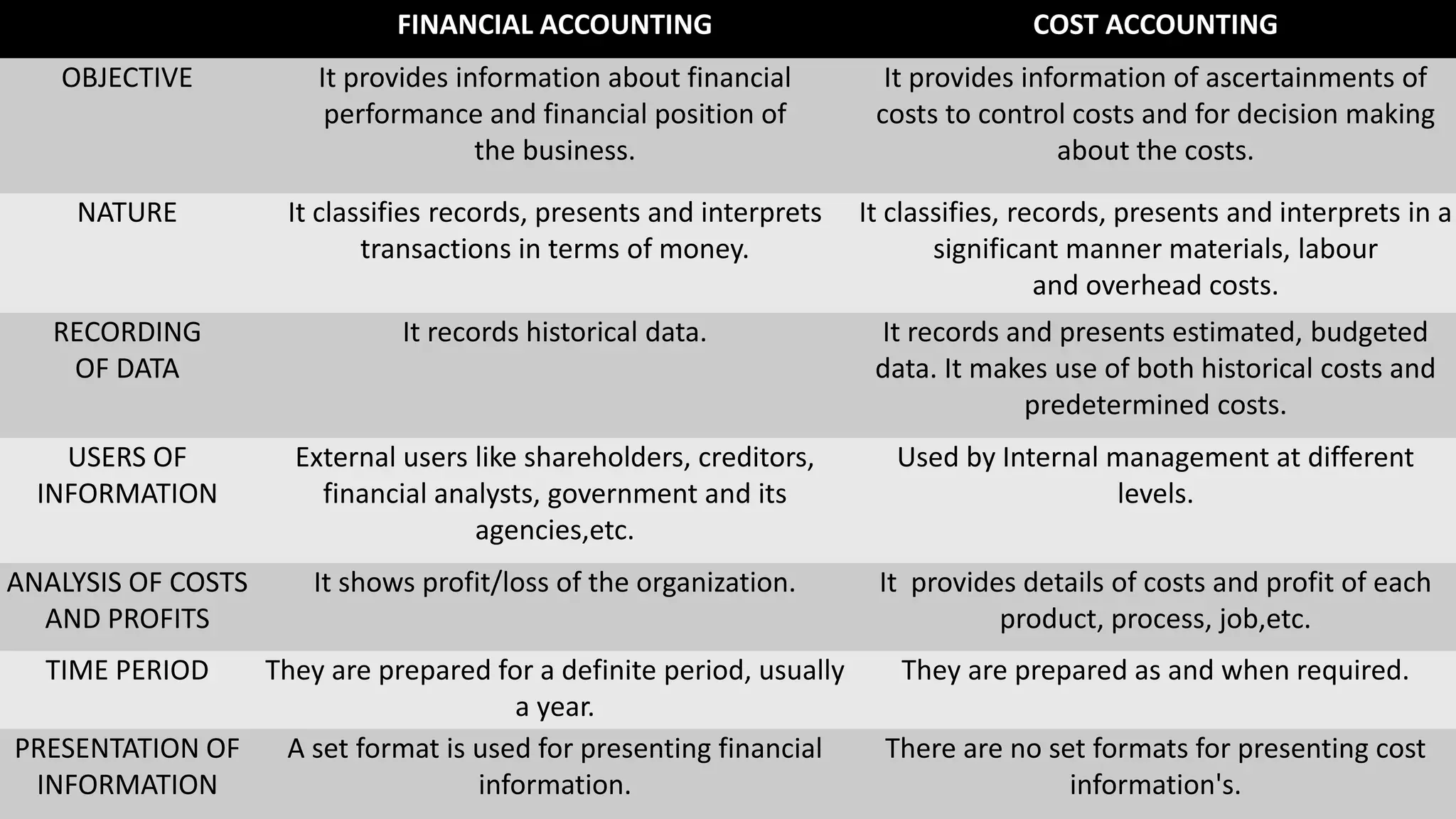
Financial accounting, cost accounting, and management accounting differ in their purpose, users, and nature of information. Financial accounting keeps records of financial transactions for external users like investors and creditors. Cost accounting analyzes expenditures to determine product costs and prices for management decision making. Management accounting assists management in policy decisions and evaluating the impact of decisions for internal users. Financial accounting provides objective, auditable information while management accounting provides more subjective information tailored to strategic needs.