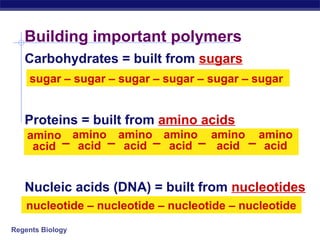
The document discusses the key chemical elements - carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen - that make up 96% of living organisms. These elements are combined to form important molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids that the body needs. We eat food to take in these molecules for building new cells, tissues, and energy in the form of ATP. The body breaks down large molecules into smaller units through digestion and reassembles them into larger structures through synthesis.