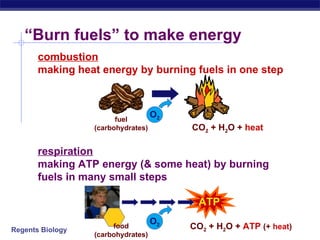
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms harvest chemical energy from food to produce ATP in mitochondria using oxygen. Glucose and oxygen are broken down to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of ATP. Mitochondria contain enzymes and oxygen that allow them to act as the "furnace" to make ATP from fuels like carbohydrates and fats. If oxygen is missing, fermentation can partially generate ATP from glucose through processes like alcohol or lactic acid fermentation.