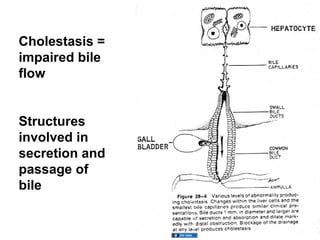
This document provides an overview of cholestatic liver diseases. It defines cholestasis as impaired bile flow and classifies cholestatic diseases as involving the hepatocyte, small intrahepatic bile ducts, or large/extrahepatic bile ducts. Specific examples of intrahepatic cholestasis discussed include those caused by decreased bile formation from sepsis or estrogens, and diseases like primary biliary cirrhosis that destroy bile ducts. Extrahepatic obstruction can result from gallstones, strictures, or tumors compressing the bile ducts. The document outlines approaches to diagnosing the cause of cholestasis through imaging and biopsy and discusses consequences like secondary liver damage if cholestasis is