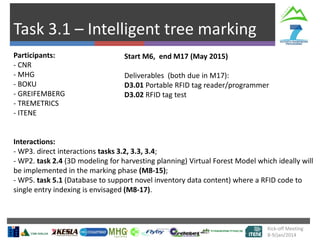
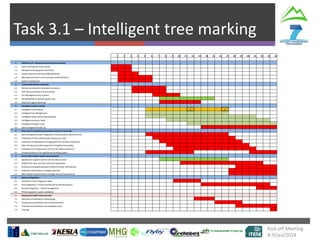
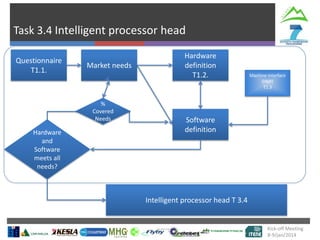
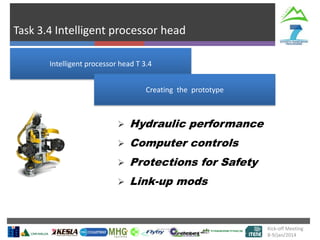
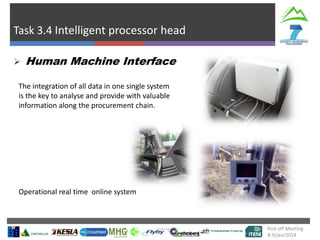
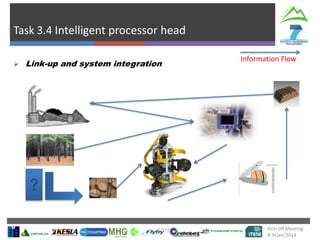
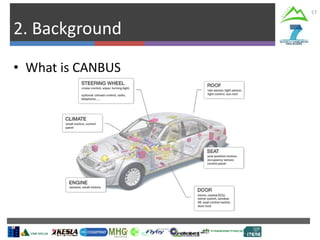
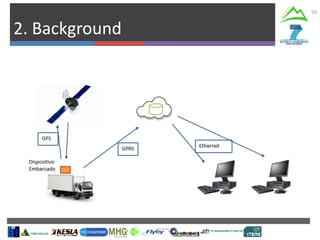
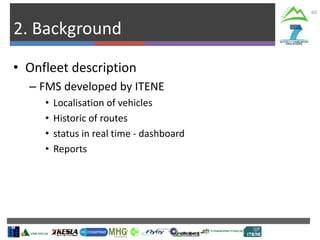
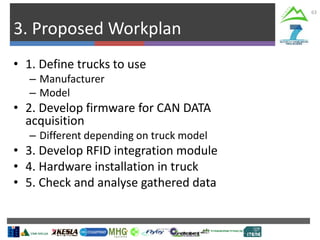
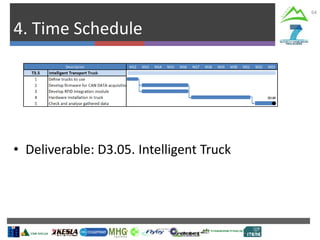
The document describes Project SLOPE which aims to develop intelligent systems for tree marking, felling, hauling, and processing in mountain forests. It outlines the tasks, participants, goals, challenges, and timeline for Task 3.1 which focuses on developing an intelligent system for tree marking using RFID tags, GPS, and a rugged tablet computer to store and access forest inventory data and mark trees efficiently in mountainous terrain. The key challenges are ensuring the systems are ergonomic for mountain forest conditions and have high tag survival and reading rates to enable full traceability.